Energy Test Review Sheet Document
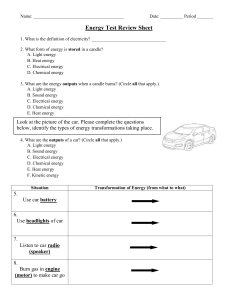
... 4. What are the outputs of a car? (Circle all that apply.) A. Light energy B. Sound energy C. Electrical energy D. Chemical energy E. Heat energy F. Kinetic energy Situation ...
... 4. What are the outputs of a car? (Circle all that apply.) A. Light energy B. Sound energy C. Electrical energy D. Chemical energy E. Heat energy F. Kinetic energy Situation ...
Topic IX - Magnetism - Science - Miami
... 3. Permanent and electromagnetism similarities D. Electric Motors and Generators 1. Mechanical to electrical energy a. Electromagnetic induction b. Generator-electricity 2. Electrical to mechanical energy a. Electric motors 3. Direct and alternating currents ...
... 3. Permanent and electromagnetism similarities D. Electric Motors and Generators 1. Mechanical to electrical energy a. Electromagnetic induction b. Generator-electricity 2. Electrical to mechanical energy a. Electric motors 3. Direct and alternating currents ...
Final Revision
... 3- Occurrence of mirage phenomenon in desert regions at noon. 4- Anthers of some flowers are hanging. 5-Aluminium foil is an opaque. 6- We see lightning before hearing thunder. 7- Metallic pots are not used in microwave ovens. 8-The ears of fennec fox are big and concave. 9- Fallopian tube is lined ...
... 3- Occurrence of mirage phenomenon in desert regions at noon. 4- Anthers of some flowers are hanging. 5-Aluminium foil is an opaque. 6- We see lightning before hearing thunder. 7- Metallic pots are not used in microwave ovens. 8-The ears of fennec fox are big and concave. 9- Fallopian tube is lined ...
Jeopardy - Physics B
... To produce more electrons per unit time but with less kinetic energy per electron, the experimenter should do which of the following? (A) Increase the intensity and decrease the wavelength of the light. (B) Increase the intensity and the wavelength of the light. (C) Decrease the intensity and the wa ...
... To produce more electrons per unit time but with less kinetic energy per electron, the experimenter should do which of the following? (A) Increase the intensity and decrease the wavelength of the light. (B) Increase the intensity and the wavelength of the light. (C) Decrease the intensity and the wa ...
experimentfest 2016 - University of Newcastle
... waves goes upstream and downstream, the other goes across stream and back. Finally, they come together into the telescope and the eye. If the one that took longer is half a wavelength behind, its troughs will be on top of the crests of the first wave, they will cancel, and nothing will be seen. If t ...
... waves goes upstream and downstream, the other goes across stream and back. Finally, they come together into the telescope and the eye. If the one that took longer is half a wavelength behind, its troughs will be on top of the crests of the first wave, they will cancel, and nothing will be seen. If t ...
Lecture 2. Atom. Periodic Table
... • Each step down a group is adding an energy level • Ions therefore get bigger as you go down, because of the additional energy level. ...
... • Each step down a group is adding an energy level • Ions therefore get bigger as you go down, because of the additional energy level. ...
Bohr suggested that electrons in hydrogen could have
... collapsing into the nucleus. This atom model is disastrous, because it predicts that all atoms are unstable. Also, as the electron spirals inward, the emission would gradually increase in frequency as the orbit got smaller and faster. This would produce a continuous smear, in frequency, of electroma ...
... collapsing into the nucleus. This atom model is disastrous, because it predicts that all atoms are unstable. Also, as the electron spirals inward, the emission would gradually increase in frequency as the orbit got smaller and faster. This would produce a continuous smear, in frequency, of electroma ...
Energy Transformations
... •Thermal: movement of microscopic particles (such as atoms, molecules) EX: heat, movement of helium gas atoms –Kinetic thermal energy can be transferred from one particle to another via conduction and convection (there is a 3rd, but we are skipping it for now) see the next slide ...
... •Thermal: movement of microscopic particles (such as atoms, molecules) EX: heat, movement of helium gas atoms –Kinetic thermal energy can be transferred from one particle to another via conduction and convection (there is a 3rd, but we are skipping it for now) see the next slide ...