S8P2 Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of
... from one form into another. • Transformations of energy usually release some energy typically in the form of heat. • Temperature changes as heat is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one. • Heat transfer occurs by conduction, convection, or ...
... from one form into another. • Transformations of energy usually release some energy typically in the form of heat. • Temperature changes as heat is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one. • Heat transfer occurs by conduction, convection, or ...
Atomic Structure
... Neutrons – neutrally charged (no charge); in nucleus Electrons – negatively charged; in energy levels around nucleus These particles are themselves made up of different combinations of the quark, an even smaller particle. Four Forces The nucleus (the positively-charged center of the atom) is held to ...
... Neutrons – neutrally charged (no charge); in nucleus Electrons – negatively charged; in energy levels around nucleus These particles are themselves made up of different combinations of the quark, an even smaller particle. Four Forces The nucleus (the positively-charged center of the atom) is held to ...
Physical Science STEM Academy Syllabus
... participants should be on task at all times, and all side conversations and use of technology (i.e. cell phones/tablets) should be at a minimum, or not occur at all. Participants are responsible for watching all podcast videos prior to each session. The content in these videos will be referenced dur ...
... participants should be on task at all times, and all side conversations and use of technology (i.e. cell phones/tablets) should be at a minimum, or not occur at all. Participants are responsible for watching all podcast videos prior to each session. The content in these videos will be referenced dur ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... 3. A biochemist is performing an experiment to determine the effects of Chemical X on the growth of bacteria. Which tube is the experimental control? a. Test tube 1 b. Test tube 2 c. Test tube 3 d. Test tube 4 Objective 2.01: Analyze the historical development of the current atomic theory. 4. Which ...
... 3. A biochemist is performing an experiment to determine the effects of Chemical X on the growth of bacteria. Which tube is the experimental control? a. Test tube 1 b. Test tube 2 c. Test tube 3 d. Test tube 4 Objective 2.01: Analyze the historical development of the current atomic theory. 4. Which ...
7 - MIT
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
Waves Review
... and surface waves. A transverse wave is a wave in which particles of the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction which the wave moves. Suppose that a slinky is stretched out in a horizontal direction across the classroom and that a pulse is introduced into the slinky on the left en ...
... and surface waves. A transverse wave is a wave in which particles of the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction which the wave moves. Suppose that a slinky is stretched out in a horizontal direction across the classroom and that a pulse is introduced into the slinky on the left en ...
pkt 6 oscillations and waves
... how fast the medium vibrates. To change wave speed, you must change the medium or its properties. ...
... how fast the medium vibrates. To change wave speed, you must change the medium or its properties. ...
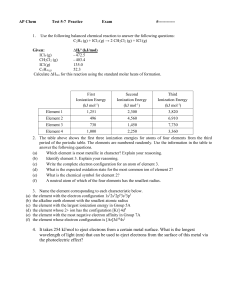
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
CHEM 121 Chp 2 Spaulding
... The chemical properties of an element are determined by the number of electrons in an atom ◦ Electrons do not move freely in space – restricted to a region with a particular energy ◦ Electrons occupy discrete energy levels that are restricted to specific values – the energy is ...
... The chemical properties of an element are determined by the number of electrons in an atom ◦ Electrons do not move freely in space – restricted to a region with a particular energy ◦ Electrons occupy discrete energy levels that are restricted to specific values – the energy is ...
Refraction - Mr Linseman`s wiki
... Remember, light is electromagnetic radiation, which is transmitted in waves. The particles in a medium, like the students in a hall, slow down the passage of waves. Glass is more dense than air, so light travels slower in glass than in air. ...
... Remember, light is electromagnetic radiation, which is transmitted in waves. The particles in a medium, like the students in a hall, slow down the passage of waves. Glass is more dense than air, so light travels slower in glass than in air. ...
Study Guide Chapter 11 – Introduction to Atoms
... Rutherford – discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a dense, positive nucleus A. Rutherford model – dense nucleus with electrons surrounding at a distance Nucleus – an atom’s central region, which is made up of protons and neutrons Bohr’s model – electrons move around the nucleus in certa ...
... Rutherford – discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a dense, positive nucleus A. Rutherford model – dense nucleus with electrons surrounding at a distance Nucleus – an atom’s central region, which is made up of protons and neutrons Bohr’s model – electrons move around the nucleus in certa ...