* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download F.S.S. Rosa
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Antiproton Decelerator wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
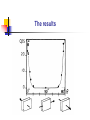
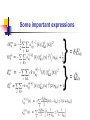
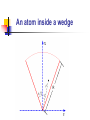
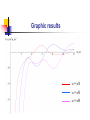
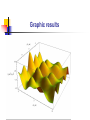
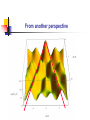
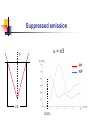
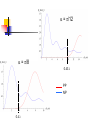
Spontaneous emission of an atom near a wedge F. S. S. Rosa Los Alamos National Laboratory Work in collaboration with T.N.C. Mendes, C. Farina and A. Tenorio Plan of the talk Introduction The method An atom inside a wedge The spontaneous emission rate Final remarks Introduction “A splendid light has dawned on me about the absorption and emission of radiation.” A. Einstein QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QED (1927) : Spontaneous emission and boundary conditions - Theory Parallel polarization Normal polarization G. Barton (1970), P. Stehle (1970), P.W. Milonni and P.L. Knight (1973), M.R. Philpott (1973). Experiments • Feher et al. (1958) - microwave range • Drexhage et al. (1968) - visible range An experiment on suppression - Jhe et al. (1987) Beam of atoms Oven Conducting plates Detector The results The method • We use a master equation approach developed by Dalibard, Dupont-Roc and Cohen-Tannoudji to describe a particle (in our case, an atom) interacting with a reservoir (the radiation field). • This approach provides general expressions for the atomic energy shifts and the exchange rates. Using some reasonable approximations for the master equation, we get transition rate energy shift Some important expressions } } = = An atom inside a wedge R Some Motivations • The wedge has been used for some important measurements of the van der Waals force. • It is the most soft departing from the plane geometry, and its relative simplicity allows some analytical calculations. • To use an alternative method that gives expressions valid in both retarded and nonretarded regimes. The excited potential Graphic results = /3 = /5 = /8 The spontaneous emission rate Graphic results From another perspective Suppressed emission = /3 y PP NP /2 0.24 = /12 = /8 0.43 PP NP 0.4 Final remarks • Everything seems to be working fine for the wedge setup. • Refine our investigation: introduce temperature and finite conductivity effects. • Investigate the possibility of trapping particles using the vacuum field.