Design of an Audio Amplifier
... frequencies. LM386 audio power amplifier chip is used in this project. LM386: The LM386 is an audio power amplifier that is designed for use in low voltage applications. The gain for this amplifier is usually 20 but can go up to 200 by introducing components like resistor and capacitors at appropria ...
... frequencies. LM386 audio power amplifier chip is used in this project. LM386: The LM386 is an audio power amplifier that is designed for use in low voltage applications. The gain for this amplifier is usually 20 but can go up to 200 by introducing components like resistor and capacitors at appropria ...
LED dimmer
... pressure regulator, which changes the output of the controller, until they get the satisfactory LED output brightness so far. When the 【Analog IN 】port impending, controller all light output; When the 【 Analog IN 】 port two terminals short circuit, the output shut down. ...
... pressure regulator, which changes the output of the controller, until they get the satisfactory LED output brightness so far. When the 【Analog IN 】port impending, controller all light output; When the 【 Analog IN 】 port two terminals short circuit, the output shut down. ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... • Power MOSFETs have become the device of choice in many power switching circuits. • The gate is voltage activated, and requires essentially no power. • MOSFETs switch quickly. Power is consumed during the time it takes to switch, so the faster the better. • For low to moderate currents, the VDS dro ...
... • Power MOSFETs have become the device of choice in many power switching circuits. • The gate is voltage activated, and requires essentially no power. • MOSFETs switch quickly. Power is consumed during the time it takes to switch, so the faster the better. • For low to moderate currents, the VDS dro ...
E831 Miniature Piezo Driver Piezo Control
... OEM Module, Power Supply for up to 3 Axes steadystate operation and the power consumption depends on the operating frequency, high-powered amplifiers are not required for many applications. With a peak output current of 100 mA (sink/source) the E-831 is well-suited for switching applications and fas ...
... OEM Module, Power Supply for up to 3 Axes steadystate operation and the power consumption depends on the operating frequency, high-powered amplifiers are not required for many applications. With a peak output current of 100 mA (sink/source) the E-831 is well-suited for switching applications and fas ...
Experiment 1 - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or sourcing current to the load from a positive power supply. Vacuum tubes (valves) are not available in complementary types (as are pnp/npn transistors), so the tube push–pull amplifier has a pair of identical output tubes or groups ...
... load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or sourcing current to the load from a positive power supply. Vacuum tubes (valves) are not available in complementary types (as are pnp/npn transistors), so the tube push–pull amplifier has a pair of identical output tubes or groups ...
7796 SPECIFICATION SHEET
... reduced power. • Rugged chassis for stand-alone or rack mounted operation. No additional power supplies are required. • Protection circuitry protects the AE Techron 7796 from input overloads, improper output connection (including shorted and improper loads), over-temperature, over-current, and suppl ...
... reduced power. • Rugged chassis for stand-alone or rack mounted operation. No additional power supplies are required. • Protection circuitry protects the AE Techron 7796 from input overloads, improper output connection (including shorted and improper loads), over-temperature, over-current, and suppl ...
Low Power Op Amp Fun: Low Power Filter
... Measured supply current consumption is about 230µA, although data sheet supply maximum values suggest that the consumption across production and temperature may be slightly higher. The values of resistors chosen minimize consumption at the expense of in-band noise. If VREF is derived from a high imp ...
... Measured supply current consumption is about 230µA, although data sheet supply maximum values suggest that the consumption across production and temperature may be slightly higher. The values of resistors chosen minimize consumption at the expense of in-band noise. If VREF is derived from a high imp ...
Document
... After noise is added, the original amplitudes of a digital signal can be determined. This is not true for an analog signal. ...
... After noise is added, the original amplitudes of a digital signal can be determined. This is not true for an analog signal. ...
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #13 solution
... 4.86. Figure P4.86 shows a scheme for coupling and amplifying a high-frequency pulse signal. The circuit utilizes two MOSFETs whose bias details are not shown and a 50-Ω coaxial cable. Transistor Q1 operates as a CS amplifier and Q2 as a CG amplifier. For proper operation, transistor Q2 is required ...
... 4.86. Figure P4.86 shows a scheme for coupling and amplifying a high-frequency pulse signal. The circuit utilizes two MOSFETs whose bias details are not shown and a 50-Ω coaxial cable. Transistor Q1 operates as a CS amplifier and Q2 as a CG amplifier. For proper operation, transistor Q2 is required ...
by Kenneth A - Kenneth A. Kuhn
... For many amplifier applications it is desirable for the input impedance to be very high. Thus, it is common for the first amplifier stage to be either a common-collector (a.k.a. emitter follower) bipolar junction transistor stage or a common-drain (a.k.a. source follower) or even common-source field ...
... For many amplifier applications it is desirable for the input impedance to be very high. Thus, it is common for the first amplifier stage to be either a common-collector (a.k.a. emitter follower) bipolar junction transistor stage or a common-drain (a.k.a. source follower) or even common-source field ...
Multichannel Waveform Generator
... current into pFET gate when on • IN is either high or low voltage resulting in passing current or open ...
... current into pFET gate when on • IN is either high or low voltage resulting in passing current or open ...
Home Audio Equipment Measurements
... The Odyssey Audio Khartago is a medium-power solid-state design with typically wide bandwidth and low output impedance. Chart 1 shows the frequency response of the amp with varying loads. As can be seen, the output impedance, as judged by the closeness of spacing between the curves of open circuit, ...
... The Odyssey Audio Khartago is a medium-power solid-state design with typically wide bandwidth and low output impedance. Chart 1 shows the frequency response of the amp with varying loads. As can be seen, the output impedance, as judged by the closeness of spacing between the curves of open circuit, ...
DN190 - Op Amp, Comparator and Reference IC Provides Micropower Monitoring Capability
... The LTC®1541 combines a micropower amplifier, comparator and 1.2V reference in an 8-pin package. The part operates from a single 2.5V to 12.6V supply with typical supply current of 5µA. Both op amp and comparator feature a common mode input voltage range that extends from the negative supply to with ...
... The LTC®1541 combines a micropower amplifier, comparator and 1.2V reference in an 8-pin package. The part operates from a single 2.5V to 12.6V supply with typical supply current of 5µA. Both op amp and comparator feature a common mode input voltage range that extends from the negative supply to with ...
4.6 Basic Input Circuits
... * Photoconductive Transducers (Cells) are fabricated from semiconductor materials (e.g., CdS, PbSe, PbS, InSb,…) which exhibit a strong photoconductive response. * Can be used to measure EM radiation at all wavelengths. ...
... * Photoconductive Transducers (Cells) are fabricated from semiconductor materials (e.g., CdS, PbSe, PbS, InSb,…) which exhibit a strong photoconductive response. * Can be used to measure EM radiation at all wavelengths. ...
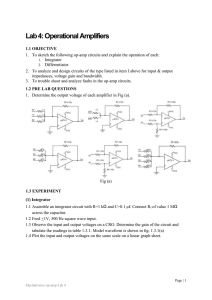
Sheet 4
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
Chapter 8 FET Amplifiers
... have certain advantages over BJT amplifiers such as high input impedance. However, the BJT normally has a higher voltage gain. There are also similarities in the three amplifier configurations of FETs and BJTs. Common-source (emitter), common-drain (collector), and common-gate (base) are the three F ...
... have certain advantages over BJT amplifiers such as high input impedance. However, the BJT normally has a higher voltage gain. There are also similarities in the three amplifier configurations of FETs and BJTs. Common-source (emitter), common-drain (collector), and common-gate (base) are the three F ...
LK 85/LK 140
... power amplifiers are engineered to bring purity of sound and ease of use to a wide range of applications where high quality sound is important. The LK85 and LK140 are compatible with all other Linn amplifiers and can enhance a dedicated Hi-fi, AV, or KNEKT multi-room sound system. The LK85 is a high ...
... power amplifiers are engineered to bring purity of sound and ease of use to a wide range of applications where high quality sound is important. The LK85 and LK140 are compatible with all other Linn amplifiers and can enhance a dedicated Hi-fi, AV, or KNEKT multi-room sound system. The LK85 is a high ...
DN230 - Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers Operate on 2.7V with 20µV Offset
... mode is nulled, then the differential mode input voltage is converted to a differential input current and appears unattenuated across R7. The common mode input voltage can theoretically be as high as about 250V (limited by the output of U1B going to ground and the ÷100 ratio maintaining common mode ...
... mode is nulled, then the differential mode input voltage is converted to a differential input current and appears unattenuated across R7. The common mode input voltage can theoretically be as high as about 250V (limited by the output of U1B going to ground and the ÷100 ratio maintaining common mode ...
Epiphone_Valve_Junio..
... Install a jumper across R6 (1M). There is an extra set of holes marked for a capacitor that may come in handy for jumpering across R6. If you want to be adventurous, you can even install a single pole switch here to allow you to switch to higher or lower gain. What this does As designed, the amp thr ...
... Install a jumper across R6 (1M). There is an extra set of holes marked for a capacitor that may come in handy for jumpering across R6. If you want to be adventurous, you can even install a single pole switch here to allow you to switch to higher or lower gain. What this does As designed, the amp thr ...
Lecture 7 Overview - Home - University of Delaware Dept
... is usually small (typically 100Hz) to ensure that the gain is <1 at a phase shift of 180º • Closed-loop gain (gain of amplifier with feedback) begins dropping when open loop gain approaches RF/RS (in the case of the inverting amp) • Cut off frequency will be higher for lower closed-loop gain circuit ...
... is usually small (typically 100Hz) to ensure that the gain is <1 at a phase shift of 180º • Closed-loop gain (gain of amplifier with feedback) begins dropping when open loop gain approaches RF/RS (in the case of the inverting amp) • Cut off frequency will be higher for lower closed-loop gain circuit ...
ETEE3211 Fall 2007
... to the base of an npn transistor as shown in the figure to the right. The internal resistance of the ac source is shown as Rsource. a. Determine ICQ, VCEQ, and Vout when the ac input is zero, assuming β=100, VBE=0.7V and RB=0. b. What value of resistor needs to be added in the base circuit to make t ...
... to the base of an npn transistor as shown in the figure to the right. The internal resistance of the ac source is shown as Rsource. a. Determine ICQ, VCEQ, and Vout when the ac input is zero, assuming β=100, VBE=0.7V and RB=0. b. What value of resistor needs to be added in the base circuit to make t ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.