General Licensing Class
... D. A computer model which can simulate performance of a radio to aid in the design process. ...
... D. A computer model which can simulate performance of a radio to aid in the design process. ...
Neural Impulse Control Design
... provide an integrator, used as a low-pass filter developing the reference for IC-1. This results in a baseline-correction that produces a low-frequency cutoff at 1.6 Hz. It also allows the output of IC-1 to operate near its center, providing good linearity. The second stage provides a gain of 390 an ...
... provide an integrator, used as a low-pass filter developing the reference for IC-1. This results in a baseline-correction that produces a low-frequency cutoff at 1.6 Hz. It also allows the output of IC-1 to operate near its center, providing good linearity. The second stage provides a gain of 390 an ...
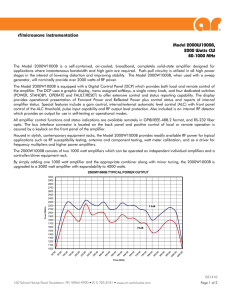
Model 2000W1000B, 2000 Watts CW 80
... The Model 2000W1000B is a self-contained, air-cooled, broadband, completely solid-state amplifier designed for applications where instantaneous bandwidth and high gain are required. Push-pull circuitry is utilized in all high power stages in the interest of lowering distortion and improving stabilit ...
... The Model 2000W1000B is a self-contained, air-cooled, broadband, completely solid-state amplifier designed for applications where instantaneous bandwidth and high gain are required. Push-pull circuitry is utilized in all high power stages in the interest of lowering distortion and improving stabilit ...
Dual Differential Amplifier/ADC Driver Delivers 10GHz Gain
... 100MHz than other similar class dual amplifiers. Also its wide DC common mode voltage ranges, 0V to 3.5V at the input, and 0.5V to 3.5V at the output, make the part particularly useful in DC coupled applications interfacing between two dissimilar DC levels, such as from the outputs of an I/Q demodul ...
... 100MHz than other similar class dual amplifiers. Also its wide DC common mode voltage ranges, 0V to 3.5V at the input, and 0.5V to 3.5V at the output, make the part particularly useful in DC coupled applications interfacing between two dissimilar DC levels, such as from the outputs of an I/Q demodul ...
DN50 - High Frequency Amplifier Evaluation Board
... to the end of the input lines — not at the connector. While stripline techniques aren’t absolutely necessary for the demo board, they are important on larger layouts where line lengths are longer. The short lines on the demo board can be terminated in 50Ω, 75Ω, or 93Ω without adversely affecting per ...
... to the end of the input lines — not at the connector. While stripline techniques aren’t absolutely necessary for the demo board, they are important on larger layouts where line lengths are longer. The short lines on the demo board can be terminated in 50Ω, 75Ω, or 93Ω without adversely affecting per ...
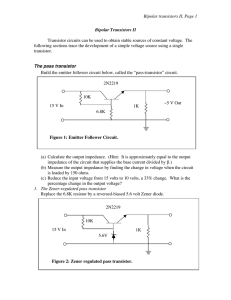
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
IC Technology and Device Models
... output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. In general terms we see that a class A amplifier, with dc bias at one-half the supply voltage level, uses a good amount of power to maintain bias, even with no input signal applied. This results in very poor efficiency, esp ...
... output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. In general terms we see that a class A amplifier, with dc bias at one-half the supply voltage level, uses a good amount of power to maintain bias, even with no input signal applied. This results in very poor efficiency, esp ...
Manual Bridging
... “Bridged mode” refers to the combining or “bridging” of two amplifier channels into a single amplifier channel. The primary reason for doing this is to achieve a single amplifier channel with much greater output power. When two 3B channels or two 4B channels are bridged, the combined single channel ...
... “Bridged mode” refers to the combining or “bridging” of two amplifier channels into a single amplifier channel. The primary reason for doing this is to achieve a single amplifier channel with much greater output power. When two 3B channels or two 4B channels are bridged, the combined single channel ...
DC characteristics Input offset voltage
... Open loop gain infinite Input impedance infinite Output impedance low Bandwidth infinite Zero offset, ie, Vo=0 when V1=V2=0 ...
... Open loop gain infinite Input impedance infinite Output impedance low Bandwidth infinite Zero offset, ie, Vo=0 when V1=V2=0 ...
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Department of Electrical
... 1. Note that a real operational amplifier has finite output impedance, rout and finite open loop gain, Avo . Derive formulae that give the output impedance for the two amplifiers you have designed and tested above. A symbolic solution with Mathematica is acceptable as well as hand calculations. For ...
... 1. Note that a real operational amplifier has finite output impedance, rout and finite open loop gain, Avo . Derive formulae that give the output impedance for the two amplifiers you have designed and tested above. A symbolic solution with Mathematica is acceptable as well as hand calculations. For ...
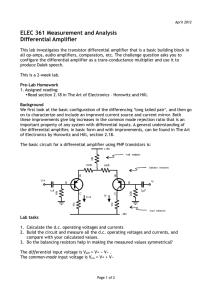
ELEC 361 Measurement and Analysis Differential Amplifier
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... replacement of DC voltage sources with short circuits (because voltage can’t change across a DC voltage source) and DC current sources with open circuits (because current through DC current source can’t change) why DC voltage sources are typically bypassed at AC (i.e., at signal frequency) using cap ...
... replacement of DC voltage sources with short circuits (because voltage can’t change across a DC voltage source) and DC current sources with open circuits (because current through DC current source can’t change) why DC voltage sources are typically bypassed at AC (i.e., at signal frequency) using cap ...
svokke_epi_valve_jr_..
... and this proved to be a good solution. I did not like the idea though because the resulting voltage in my amplifier was only 5.8V DC. So I cut some traces, removed jumper 1 and put the heater wiring above the PCB. I also referenced the heaters to the cathode of the EL84 with the 100ohm resistors R10 ...
... and this proved to be a good solution. I did not like the idea though because the resulting voltage in my amplifier was only 5.8V DC. So I cut some traces, removed jumper 1 and put the heater wiring above the PCB. I also referenced the heaters to the cathode of the EL84 with the 100ohm resistors R10 ...
Lab02-GL Rev. 2 - geek @ EE @ NMT
... Using a LM 741 op-amp, build an inverting voltage amplifier with a gain of approximately 1000, using a feedback resistor of 100 kΩ. Measure the relationship between the output and the input for several positive and negative input voltages. You may use a voltage divider to create small voltages or a ...
... Using a LM 741 op-amp, build an inverting voltage amplifier with a gain of approximately 1000, using a feedback resistor of 100 kΩ. Measure the relationship between the output and the input for several positive and negative input voltages. You may use a voltage divider to create small voltages or a ...
Basic non-inverting operational amplifier circuit with
... AC Coupling The Non-inverting Op-amp Circuit • In most cases it is possible to DC couple the circuit. However in this case it is necessary to ensure that the non-inverting has a DC path to earth for the very small input current that is needed. • This can be achieved by inserting a high value resist ...
... AC Coupling The Non-inverting Op-amp Circuit • In most cases it is possible to DC couple the circuit. However in this case it is necessary to ensure that the non-inverting has a DC path to earth for the very small input current that is needed. • This can be achieved by inserting a high value resist ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... for the pinch-off voltage with the rather liberal limits given on the data page for “GateSource Cutoff Voltage”. Common-source transfer characteristics The program measures the current by measuring the voltage drop across the 1k drain resistor. Make a copy of the computer plot of drain current vs. ...
... for the pinch-off voltage with the rather liberal limits given on the data page for “GateSource Cutoff Voltage”. Common-source transfer characteristics The program measures the current by measuring the voltage drop across the 1k drain resistor. Make a copy of the computer plot of drain current vs. ...
TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIER - IDC
... Rc is the collector resistor and Re is the emitter resistor. Values of Rc and Re are so selected that 50% of Vcc gets dropped across the collector & emitter of the transistor.This is done to ensure that the operating point is positioned at the center of the load line. 40% of Vcc is dropped across R ...
... Rc is the collector resistor and Re is the emitter resistor. Values of Rc and Re are so selected that 50% of Vcc gets dropped across the collector & emitter of the transistor.This is done to ensure that the operating point is positioned at the center of the load line. 40% of Vcc is dropped across R ...
original publication
... All rights reserved. Reproduction of this preprint, or any portion thereof, is not permitted without directpermission from the Journalof the Audio EngineeringSociety. ...
... All rights reserved. Reproduction of this preprint, or any portion thereof, is not permitted without directpermission from the Journalof the Audio EngineeringSociety. ...
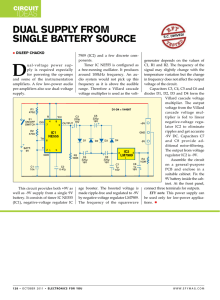
Dual Supply From Single Battery SourCe
... voltage of the circuit. Capacitors C3, C4, C5 and C6 and diodes D1, D2, D3 and D4 form the Villard cascade voltage multiplier. The output voltage from the Villard cascade voltage multiplier is fed to linear negative-voltage regulator IC2 to eliminate ripples and get accurate -9V DC. Capacitors C7 an ...
... voltage of the circuit. Capacitors C3, C4, C5 and C6 and diodes D1, D2, D3 and D4 form the Villard cascade voltage multiplier. The output voltage from the Villard cascade voltage multiplier is fed to linear negative-voltage regulator IC2 to eliminate ripples and get accurate -9V DC. Capacitors C7 an ...
PT 2.1 - HARMAN Professional Solutions
... status of the low voltage power supply. Signal/IOC: Each channel has a two color indicator that flashes green to show signal presence and yellow if the amplifier causes distortion of 0.05% or more. ...
... status of the low voltage power supply. Signal/IOC: Each channel has a two color indicator that flashes green to show signal presence and yellow if the amplifier causes distortion of 0.05% or more. ...
PT 1.1 - HARMAN Professional Solutions
... status of the low voltage power supply. Signal/IOC: Each channel has a two color indicator that flashes green to show signal presence and yellow if the amplifier causes distortion of 0.05% or more. ...
... status of the low voltage power supply. Signal/IOC: Each channel has a two color indicator that flashes green to show signal presence and yellow if the amplifier causes distortion of 0.05% or more. ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.