AN3 - Applications for a Switched-Capacitor Instrumentation Building Block
... sine wave source. A1’s positive feedback path is a Wein bridge, tuned for 1.5kHz. Q1, the LT1004 reference, and additional components in A1’s negative loop unity-gain stabilize the amplifier. A1’s output (Trace A, Figure 11), an amplitude stable sine wave, drives the LVDT. C1 detects zero crossings a ...
... sine wave source. A1’s positive feedback path is a Wein bridge, tuned for 1.5kHz. Q1, the LT1004 reference, and additional components in A1’s negative loop unity-gain stabilize the amplifier. A1’s output (Trace A, Figure 11), an amplitude stable sine wave, drives the LVDT. C1 detects zero crossings a ...
Linear IC Applications UNIT -1 DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
... The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier usable from 0 to over 1MH Z to which feedback is added to control its overall response characteristic i.e. gain and bandwidth. The op-amp exhibits the gain down to zero frequency. Such direct coupled (dc) amplifiers do not use blockin ...
... The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier usable from 0 to over 1MH Z to which feedback is added to control its overall response characteristic i.e. gain and bandwidth. The op-amp exhibits the gain down to zero frequency. Such direct coupled (dc) amplifiers do not use blockin ...
High-Speed ADC Sets Input Common-Mode Range
... receivers that include baseband-sampling, high-speed ADCs. A VCM is especially important for singlesupply, low-voltage circuits with DC-coupled inputs. For single-supply circuits, the input signal that feeds the drive amplifier and ADC should be biased at a DC level well within the VCM range. This a ...
... receivers that include baseband-sampling, high-speed ADCs. A VCM is especially important for singlesupply, low-voltage circuits with DC-coupled inputs. For single-supply circuits, the input signal that feeds the drive amplifier and ADC should be biased at a DC level well within the VCM range. This a ...
1.8-V, 7-MHz, 90-dB CMRR, SINGLE-SUPPLY, RAIL-TO-RAIL I/O OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER OPA2364-Q1 FEATURES
... The OPA2364 and OPA4364 are high-performance CMOS operational amplifiers optimized for low-voltage single-supply operation. These miniature low-cost amplifiers are designed to operate on single supplies from 1.8 V (±0.9 V) to 5.5 V (±2.75 V). Applications include sensor amplification and signal cond ...
... The OPA2364 and OPA4364 are high-performance CMOS operational amplifiers optimized for low-voltage single-supply operation. These miniature low-cost amplifiers are designed to operate on single supplies from 1.8 V (±0.9 V) to 5.5 V (±2.75 V). Applications include sensor amplification and signal cond ...
ca3160-a - CA3160, CA3160A - 4MHz, BiMOS Operational Amplifier
... lower curve in Figure 18) even though the output stage is strobed off. Figure 1A shows a dual-supply arrangement for the output stage that can also be strobed off, assuming RL = ∞, by pulling the potential of Terminal 8 down to that of Terminal 4. Let it now-be assumed that a load resistance of nomi ...
... lower curve in Figure 18) even though the output stage is strobed off. Figure 1A shows a dual-supply arrangement for the output stage that can also be strobed off, assuming RL = ∞, by pulling the potential of Terminal 8 down to that of Terminal 4. Let it now-be assumed that a load resistance of nomi ...
RF3934 120W GaN WIDEBAND POWER AMPLIFIER Features
... The GaN HEMT device is a depletion mode high electron mobility transistor (HEMT). At zero volts VGS the drain of the device is saturated and uncontrolled drain current will destroy the transistor. The gate voltage must be taken to a potential lower than the source voltage to pinch off the device pri ...
... The GaN HEMT device is a depletion mode high electron mobility transistor (HEMT). At zero volts VGS the drain of the device is saturated and uncontrolled drain current will destroy the transistor. The gate voltage must be taken to a potential lower than the source voltage to pinch off the device pri ...
How to Design a Boost Converter With the TPS61170 Application Report ......................................................................................
... Although the loop is stable with almost 90 degrees of phase margin and small signal control loop bandwidth, fBW, of 20 kHz, components R3 and C3 are not optimized to give the highest bandwidth, and therefore the smallest output capacitance to meet the load transient requirement. In fact, maximizing ...
... Although the loop is stable with almost 90 degrees of phase margin and small signal control loop bandwidth, fBW, of 20 kHz, components R3 and C3 are not optimized to give the highest bandwidth, and therefore the smallest output capacitance to meet the load transient requirement. In fact, maximizing ...
CA3160 - Experimentalists Anonymous
... lower curve in Figure 18) even though the output stage is strobed off. Figure 1A shows a dual-supply arrangement for the output stage that can also be strobed off, assuming RL = ∞, by pulling the potential of Terminal 8 down to that of Terminal 4. Let it now-be assumed that a load resistance of nomi ...
... lower curve in Figure 18) even though the output stage is strobed off. Figure 1A shows a dual-supply arrangement for the output stage that can also be strobed off, assuming RL = ∞, by pulling the potential of Terminal 8 down to that of Terminal 4. Let it now-be assumed that a load resistance of nomi ...
$doc.title
... error current. This improved inverting input impedance retains exceptional bandwidth to much higher gains and improves harmonic distortion over earlier solutions limited by inverting input linearity. Beyond simple high-gain applications, the OPA4684 CFBPLUS amplifier permits the gain setting element ...
... error current. This improved inverting input impedance retains exceptional bandwidth to much higher gains and improves harmonic distortion over earlier solutions limited by inverting input linearity. Beyond simple high-gain applications, the OPA4684 CFBPLUS amplifier permits the gain setting element ...
INA333 - Texas Instruments
... A single external resistor sets any gain from 1 to 1000. The INA333 is designed to use an industrystandard gain equation: G = 1 + (100 kΩ / RG). The INA333 device provides very low offset voltage (25 μV, G ≥ 100), excellent offset voltage drift (0.1 μV/°C, G ≥ 100), and high common-mode rejection (1 ...
... A single external resistor sets any gain from 1 to 1000. The INA333 is designed to use an industrystandard gain equation: G = 1 + (100 kΩ / RG). The INA333 device provides very low offset voltage (25 μV, G ≥ 100), excellent offset voltage drift (0.1 μV/°C, G ≥ 100), and high common-mode rejection (1 ...
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and
... circuits like ADC, DAC, LDO, Charge pump circuit. A voltage reference must be highly precise and stable with respect to temperature, supply, process and load variations. High power supply noise rejection ratio (PSRR) of LDOs which merits the noise immunity, since high PSRR of LDOs mostly depends on ...
... circuits like ADC, DAC, LDO, Charge pump circuit. A voltage reference must be highly precise and stable with respect to temperature, supply, process and load variations. High power supply noise rejection ratio (PSRR) of LDOs which merits the noise immunity, since high PSRR of LDOs mostly depends on ...
12 dBm OCP Millimeter-wave 28 nm CMOS Power
... A number of realizations of 60-GHz PAs in 65nm CMOS have been reported [5-9]. As a means of attaining high output power levels, parallel amplifying topologies including power combining structures are widely used. The drawback has been that most of these implementations have displayed a considerably ...
... A number of realizations of 60-GHz PAs in 65nm CMOS have been reported [5-9]. As a means of attaining high output power levels, parallel amplifying topologies including power combining structures are widely used. The drawback has been that most of these implementations have displayed a considerably ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... electric utility. It further converted to a DC voltage for various applications [3]. The inexpensive rectifiers with diodes convert AC to DC and the output voltage is uncontrolled. The controlled rectifiers are used for providing variable/ constant output voltage. The dc output voltage of a controll ...
... electric utility. It further converted to a DC voltage for various applications [3]. The inexpensive rectifiers with diodes convert AC to DC and the output voltage is uncontrolled. The controlled rectifiers are used for providing variable/ constant output voltage. The dc output voltage of a controll ...
ADA4311-1 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The ADA4311-1 is a dual-current feedback amplifier with high output current capability. With a current feedback amplifier, the current into the inverting input is the feedback signal, and the open-loop behavior is that of a transimpedance, dVO/dIIN or TZ. The open-loop transimpedance is analogous to ...
... The ADA4311-1 is a dual-current feedback amplifier with high output current capability. With a current feedback amplifier, the current into the inverting input is the feedback signal, and the open-loop behavior is that of a transimpedance, dVO/dIIN or TZ. The open-loop transimpedance is analogous to ...
MAX2644 2.4GHz SiGe, High IP3 Low-Noise Amplifier General Description
... Standby mode is achieved by disconnecting BIAS as shown in Figure 1. Avoid capacitance at the BIAS pin by connecting the bias resistor from BIAS to the switch. ...
... Standby mode is achieved by disconnecting BIAS as shown in Figure 1. Avoid capacitance at the BIAS pin by connecting the bias resistor from BIAS to the switch. ...
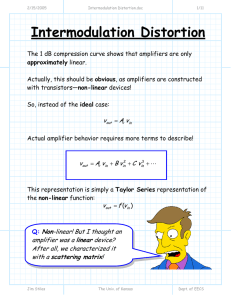
Intermodulation Distortion
... * Radio engineers specify the intermodulation distortion performance of a specific amplifier in terms of the intercept points, rather than values G2 and G3. * Generally, only the third-order intercept point is provided by amplifier manufactures (we’ll see why later). * Typical values of P3int for a ...
... * Radio engineers specify the intermodulation distortion performance of a specific amplifier in terms of the intercept points, rather than values G2 and G3. * Generally, only the third-order intercept point is provided by amplifier manufactures (we’ll see why later). * Typical values of P3int for a ...
Low Power, 350 MHz Voltage Feedback Amplifiers AD8038/AD8039
... is the voltage between the supply pins (VS) multiplied by the quiescent current (IS). Assuming the load (RL) is referenced to midsupply, then the total drive power is VS/2 × IOUT, some of which is dissipated in the package and some in the load (VOUT × IOUT). The difference between the total drive po ...
... is the voltage between the supply pins (VS) multiplied by the quiescent current (IS). Assuming the load (RL) is referenced to midsupply, then the total drive power is VS/2 × IOUT, some of which is dissipated in the package and some in the load (VOUT × IOUT). The difference between the total drive po ...
MAX2754 1.2GHz VCO with Linear Modulation Input General Description
... a ground connection separate from the oscillator core to minimize load-pulling effects. The amplifier boosts the oscillator signal to a level suitable for driving most RF mixers. ...
... a ground connection separate from the oscillator core to minimize load-pulling effects. The amplifier boosts the oscillator signal to a level suitable for driving most RF mixers. ...
Experiment 13: Op-Amp / Controlled Voltage Source
... and can be ignored. The op-amp’s input resistance is assumed to be infinite and its output resistance is assumed to be zero. The op-amp can be modeled as a voltage controlled voltage source whose output voltage is controlled by its input voltage. Refer to the model diagram on the right. A typical (d ...
... and can be ignored. The op-amp’s input resistance is assumed to be infinite and its output resistance is assumed to be zero. The op-amp can be modeled as a voltage controlled voltage source whose output voltage is controlled by its input voltage. Refer to the model diagram on the right. A typical (d ...
AN-346 High-Performance Audio Applications
... amplifier cannot have a gain of less than unity, which means that the high frequency gain cannot roll off continuously above the 2122 Hz breakpoint as it is supposed to. Instead, a new breakpoint is introduced at the unity gain frequency. In addition to the amplitude response errors (which can be ma ...
... amplifier cannot have a gain of less than unity, which means that the high frequency gain cannot roll off continuously above the 2122 Hz breakpoint as it is supposed to. Instead, a new breakpoint is introduced at the unity gain frequency. In addition to the amplitude response errors (which can be ma ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.