L6370Q
... In order to minimize the power dissipation when the output is shorted to grounded, an innovative, non dissipative short circuit protection (patent pending) is implemented, avoiding, thus the intervention of the thermal protection in most cases. Whenever the output is shorted to ground, or, generally ...
... In order to minimize the power dissipation when the output is shorted to grounded, an innovative, non dissipative short circuit protection (patent pending) is implemented, avoiding, thus the intervention of the thermal protection in most cases. Whenever the output is shorted to ground, or, generally ...
AD8133 - Analog Devices
... The AD8133 is a major advancement beyond using discrete op amps for driving differential RGB signals over twisted pair cable. The AD8133 is a triple, low cost differential or singleended input to differential output driver, and each amplifier has a fixed gain of 2 to compensate for the attenuation o ...
... The AD8133 is a major advancement beyond using discrete op amps for driving differential RGB signals over twisted pair cable. The AD8133 is a triple, low cost differential or singleended input to differential output driver, and each amplifier has a fixed gain of 2 to compensate for the attenuation o ...
HMC439QS16G
... detector intended for use in low noise phaselocked loop applications for inputs from 10 to 1300 MHz. Its combination of high frequency of operation along with its ultra low phase noise floor make possible synthesizers with wide loop bandwidth and low N resulting in fast switching and very low phase ...
... detector intended for use in low noise phaselocked loop applications for inputs from 10 to 1300 MHz. Its combination of high frequency of operation along with its ultra low phase noise floor make possible synthesizers with wide loop bandwidth and low N resulting in fast switching and very low phase ...
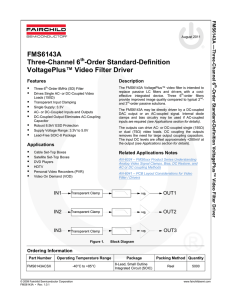
FMS6143A Three-Channel 6 -Order Standard-Definition VoltagePlus™ Video Filter Driver
... never operates. The internal pull-down resistance is 800kΩ ±20%, so the external resistance should be 7.5MΩ to set the DC level to 500mV: ...
... never operates. The internal pull-down resistance is 800kΩ ±20%, so the external resistance should be 7.5MΩ to set the DC level to 500mV: ...
NCP1030GEVB Isolated 2 W Bias Supply for Telecom Systems Using the
... The NCP1030 Power Switch Circuit is rated at 200 V, making it ideal for 48 V Telecom and 42 V automotive applications. In addition, this IC can operate from an existing 12 V supply. The NCP1030 includes an extensive set of features including: • On Board Power Switch: Eliminates the need for an exter ...
... The NCP1030 Power Switch Circuit is rated at 200 V, making it ideal for 48 V Telecom and 42 V automotive applications. In addition, this IC can operate from an existing 12 V supply. The NCP1030 includes an extensive set of features including: • On Board Power Switch: Eliminates the need for an exter ...
47000 SERIES 1W
... MYRRA encapsulated electronic transformers are Switched Mode Power Supplies based on Flyback topology. ...
... MYRRA encapsulated electronic transformers are Switched Mode Power Supplies based on Flyback topology. ...
AC/Synchro/Resolver/Phase Definitions
... Synchro/resolver devices (Cx/Rx) are designed to transmit their shaft angular position information (primary rotor windings) to the associated system by causing the amplitude of the signal on the secondary windings (stators) to be changed (Reference Figure 1 and Figure 2). The devices are limited to ...
... Synchro/resolver devices (Cx/Rx) are designed to transmit their shaft angular position information (primary rotor windings) to the associated system by causing the amplitude of the signal on the secondary windings (stators) to be changed (Reference Figure 1 and Figure 2). The devices are limited to ...
FMS6364A Four-Channel Standard- & High-Definition (SD & HD) VoltagePlus™ Video Filter Driver
... RL = channel load resistance. Board layout can also affect thermal characteristics. Refer to the Layout Considerations section for details. ...
... RL = channel load resistance. Board layout can also affect thermal characteristics. Refer to the Layout Considerations section for details. ...
design of transistor biasing circuits
... IZ(max) = Maximum zener current limited by maximum power dissipation. Since its reverse characteristics is not exactly vertical the diode posses some resistance called “Zener dynamic resistance’ given by ΔVZ ΔIZ ...
... IZ(max) = Maximum zener current limited by maximum power dissipation. Since its reverse characteristics is not exactly vertical the diode posses some resistance called “Zener dynamic resistance’ given by ΔVZ ΔIZ ...
Demystifying the Operational Transconductance Amplifier
... Figure 8. DC-Restore Circuit Example with the OPA615 In this example, the CHOLD capacitor is being charged by the sampling OTA (SOTA), triggered at the exact point of interest. The OTA provides a means to amplify the signal. Note that because of the very high input impedance of the OTA, a small CHOL ...
... Figure 8. DC-Restore Circuit Example with the OPA615 In this example, the CHOLD capacitor is being charged by the sampling OTA (SOTA), triggered at the exact point of interest. The OTA provides a means to amplify the signal. Note that because of the very high input impedance of the OTA, a small CHOL ...
powerlight 2 series powerlight 2 series
... for the touring and live sound professional. Four models range in power from 900 watts to 1850 watts per channel,all in two-rack space chassis that are only 14" deep and 21 lbs. Each of these models is available in two versions: a base model and an "A" version. Base ...
... for the touring and live sound professional. Four models range in power from 900 watts to 1850 watts per channel,all in two-rack space chassis that are only 14" deep and 21 lbs. Each of these models is available in two versions: a base model and an "A" version. Base ...
A022e-External Current Limiting Circuit
... Two diodes between the output of the circuit and the base of the pass transistor provide the current limiting function. When the circuit is operating within its normal operating range, a small voltage exists across the sense resistor. The sense voltage plus the base emitter voltage is less than the ...
... Two diodes between the output of the circuit and the base of the pass transistor provide the current limiting function. When the circuit is operating within its normal operating range, a small voltage exists across the sense resistor. The sense voltage plus the base emitter voltage is less than the ...
Power Factor Control..
... The UC1854 uses average current-mode control to accomplish fixedfrequency current control with stability and low distortion. Unlike peak current-mode, average current control accurately maintains sinusoidal line current without slope compensation and with minimal response to noise transients. The UC ...
... The UC1854 uses average current-mode control to accomplish fixedfrequency current control with stability and low distortion. Unlike peak current-mode, average current control accurately maintains sinusoidal line current without slope compensation and with minimal response to noise transients. The UC ...
Diode-connected BJT
... Differential Amplifiers: Active Loads • The output in this example is single-sided, but behaves sort of differentially • The output is a current, proportional to vd --- transconductance amplifier VCC ...
... Differential Amplifiers: Active Loads • The output in this example is single-sided, but behaves sort of differentially • The output is a current, proportional to vd --- transconductance amplifier VCC ...
- Orion Car Audio
... Avoid installing the unit where: -It would be subject to high temperatures, such as from direct sunlight or hot air from the heater. -It would be exposed to rain or moisture. -It would be subject to dust or dirt. If your car is parked in direct sunlight and there is a considerable rise in temperatur ...
... Avoid installing the unit where: -It would be subject to high temperatures, such as from direct sunlight or hot air from the heater. -It would be exposed to rain or moisture. -It would be subject to dust or dirt. If your car is parked in direct sunlight and there is a considerable rise in temperatur ...
Document
... A 3-stage staggered tuned amplifier for 2 GHz, having a voltage gain of 40 dB and a Chebyshev type frequency characteristic with 0.5 dB ripple and 380 MHz band width will be designed. The design will be made for a technology similar to the 0.35 micron AMS technology, but with an additional thick met ...
... A 3-stage staggered tuned amplifier for 2 GHz, having a voltage gain of 40 dB and a Chebyshev type frequency characteristic with 0.5 dB ripple and 380 MHz band width will be designed. The design will be made for a technology similar to the 0.35 micron AMS technology, but with an additional thick met ...
L298N datasheet
... Turn-On and Turn-Off : Before to Turn-ON the Supand its outputs can drive an inductive load in comply Voltageand beforeto Turnit OFF, the Enableinmon or differenzialmode, dependingon the state of put must be driven to the Low state. the inputs. The current that flows through the load 3. APPLICATIONS ...
... Turn-On and Turn-Off : Before to Turn-ON the Supand its outputs can drive an inductive load in comply Voltageand beforeto Turnit OFF, the Enableinmon or differenzialmode, dependingon the state of put must be driven to the Low state. the inputs. The current that flows through the load 3. APPLICATIONS ...
4. SIGNAL PROCESSING CIRCUITRY 4.1. INTRODUCTION
... signal path by proper design. Since each additional stage in an operational amplifier adds at least one pole, the number of stages must be minimized and thus results in low voltage gain and/or limited output swings. The second approach maintains low frequency gain and output swing but reduces bandwi ...
... signal path by proper design. Since each additional stage in an operational amplifier adds at least one pole, the number of stages must be minimized and thus results in low voltage gain and/or limited output swings. The second approach maintains low frequency gain and output swing but reduces bandwi ...
Article - I
... In 2011, a relatively new active building block, the so-called differential difference current conveyor transconductance amplifier (DDCCTA), was introduced [1]. The DDCCTA device is conceptually combination of the differential difference current conveyor (DDCC) [2] and the transconductance amplifier ...
... In 2011, a relatively new active building block, the so-called differential difference current conveyor transconductance amplifier (DDCCTA), was introduced [1]. The DDCCTA device is conceptually combination of the differential difference current conveyor (DDCC) [2] and the transconductance amplifier ...
Pendulum MDP-1 Operating Manual
... vacuum tube Mic/DI preamp designed to be the ultimate way to get your mic or source directly to tape or hard disk. Unlike vintage or hybrid designs, the MDP-1 uses a pure tube, class A high voltage circuit topology with a transformerless output stage to deliver an open, intimate sound with a level o ...
... vacuum tube Mic/DI preamp designed to be the ultimate way to get your mic or source directly to tape or hard disk. Unlike vintage or hybrid designs, the MDP-1 uses a pure tube, class A high voltage circuit topology with a transformerless output stage to deliver an open, intimate sound with a level o ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.