LIPID METABOLISM - Orange Coast College
... oxidation state than glucose metabolism of fats yields ~9 kcal/gram ...
... oxidation state than glucose metabolism of fats yields ~9 kcal/gram ...
Nonenzymatic, Self-Elimination Degradation
... sodium phosphate buffer). We found that the rate of hydrolysis was unaffected in all three cases of pH (Fig. 4, d – f, and Fig. 5, b). To study the effect of the ionic strength on degradation, similar studies were performed using 20 mm sodium phosphate buffer. It was observed that different ionic st ...
... sodium phosphate buffer). We found that the rate of hydrolysis was unaffected in all three cases of pH (Fig. 4, d – f, and Fig. 5, b). To study the effect of the ionic strength on degradation, similar studies were performed using 20 mm sodium phosphate buffer. It was observed that different ionic st ...
Amino Acids: An Introduction to Their Structure, Functions and
... the precursor for the synthesis of serotonin (aka “nature's downer”). Serotonin from the health food store will NOT cross the blood brain barrier; trp is required for this to occur. Turkey and milk have high levels of trp. There seems to be some controversy as to whether or not there is enough trp i ...
... the precursor for the synthesis of serotonin (aka “nature's downer”). Serotonin from the health food store will NOT cross the blood brain barrier; trp is required for this to occur. Turkey and milk have high levels of trp. There seems to be some controversy as to whether or not there is enough trp i ...
Cyclooxygenase mechanisms Lawrence J Marnett
... which reduces fatty acid hydroperoxides [33–35]. Once the Tyr385 radical is generated, each enzyme molecule catalyzes several hundred cycles of arachidonic acid oxygenation. Although the tyrosyl radical is reduced to tyrosine when it oxidizes arachidonic acid, the radical is regenerated in the last ...
... which reduces fatty acid hydroperoxides [33–35]. Once the Tyr385 radical is generated, each enzyme molecule catalyzes several hundred cycles of arachidonic acid oxygenation. Although the tyrosyl radical is reduced to tyrosine when it oxidizes arachidonic acid, the radical is regenerated in the last ...
Defelipe, L.A, Dolghih E, Roitberg A.E., Nouzova M., Mayoral
... in a hydrophobic pocket formed by Ile-151, Ile-154, Tyr 155, Leu158, Val-221 and Val-224 (Fig. 4A). Docking results indicated a clear difference in the interaction of (10R)-JHA and (10S)-JHA with the hydrophobic pocket of the binding site of AeJHAMT. Specifically, while the epoxide ring of (10S)-JHA ...
... in a hydrophobic pocket formed by Ile-151, Ile-154, Tyr 155, Leu158, Val-221 and Val-224 (Fig. 4A). Docking results indicated a clear difference in the interaction of (10R)-JHA and (10S)-JHA with the hydrophobic pocket of the binding site of AeJHAMT. Specifically, while the epoxide ring of (10S)-JHA ...
Lab Module 7 - philipdarrenjones.com
... In Lab Module 1, we applied the scientific method to test factors that affect reaction time. This week, we will again use the scientific method, this time to test factors that affect the rate of fermentation by baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as fermentation in humans. Fermentation i ...
... In Lab Module 1, we applied the scientific method to test factors that affect reaction time. This week, we will again use the scientific method, this time to test factors that affect the rate of fermentation by baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as fermentation in humans. Fermentation i ...
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... where most of the Krebs cycle reactions take place and the intermembrane space is where protons are pumped as they are produced by the electron transport chain. These protons are used to create the electrochemical gradient that stores free energy, which is necessary to create ATP. The inner membrane ...
... where most of the Krebs cycle reactions take place and the intermembrane space is where protons are pumped as they are produced by the electron transport chain. These protons are used to create the electrochemical gradient that stores free energy, which is necessary to create ATP. The inner membrane ...
Digestible carbohydrates
... It is the major source of lactic acid that is gluconeogenic. 8. Reversal of glycolysis is gluconeogenesis, an important source of glucose. 9. Main pathway of metabolism of fructose from the diet. 10. A small number of genetic diseases occur due to deficiency in activity of enzymes of glycolysis, are ...
... It is the major source of lactic acid that is gluconeogenic. 8. Reversal of glycolysis is gluconeogenesis, an important source of glucose. 9. Main pathway of metabolism of fructose from the diet. 10. A small number of genetic diseases occur due to deficiency in activity of enzymes of glycolysis, are ...
The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATP
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly • It breaks the large free-energy drop from food to O2 ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly • It breaks the large free-energy drop from food to O2 ...
Development of a novel analytical approach combining the quantification of
... A simple, rapid, sensitive and selective procedure based on the combination of HPLC-UV-Vis and HPLC-MS has been developed and single laboratory partially validated for the determination of a set of 13 analytes present in a commercially available IVF medium utilising small sample volumes (20–30 mL). ...
... A simple, rapid, sensitive and selective procedure based on the combination of HPLC-UV-Vis and HPLC-MS has been developed and single laboratory partially validated for the determination of a set of 13 analytes present in a commercially available IVF medium utilising small sample volumes (20–30 mL). ...
Acids, Bases and Salts
... For thousands of years people have known that vinegar, lemon juice and many other foods taste ...
... For thousands of years people have known that vinegar, lemon juice and many other foods taste ...
Some Properties of a Gram-Negative Heterotrophic
... action on monosaccharides. It is a polar flagellate, has limited acid tolerance, consistent with its inability to produce acid from sugars and has no constitutive system for metabolizing glucose. A weak inducible system was available, however, which enabled adapted organisms to grow on glucose and u ...
... action on monosaccharides. It is a polar flagellate, has limited acid tolerance, consistent with its inability to produce acid from sugars and has no constitutive system for metabolizing glucose. A weak inducible system was available, however, which enabled adapted organisms to grow on glucose and u ...
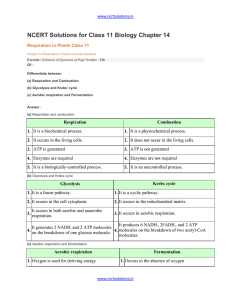
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
Teacher`s Guide - American Chemical Society
... technology are based largely on traditional processes, yet are extremely advanced and sophisticated. The main use of molds has been in the process of making koji (mold-fermented grains and/or soybeans). The koji making process has been unique to East Asia, where it has been used in the preparation o ...
... technology are based largely on traditional processes, yet are extremely advanced and sophisticated. The main use of molds has been in the process of making koji (mold-fermented grains and/or soybeans). The koji making process has been unique to East Asia, where it has been used in the preparation o ...
Cellular Respiration
... from glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle into ATP Occurs in inner membrane of mitochondrion The energy in each NADH molecule moves enough protons (H+) into the mitochondrial matrix to create 3 ATP 1 FADH2 2 ATP ...
... from glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle into ATP Occurs in inner membrane of mitochondrion The energy in each NADH molecule moves enough protons (H+) into the mitochondrial matrix to create 3 ATP 1 FADH2 2 ATP ...
Integration of Metabolism
... iii. Won’t have to draw structures, identify structures, or know historical facts b. Today: Integration of Metabolism c. Metabolic pathways separated for teaching, but these different pathways are all going on at the same time d. All of them involve ATP, but there is only one pool of ATP i. So if on ...
... iii. Won’t have to draw structures, identify structures, or know historical facts b. Today: Integration of Metabolism c. Metabolic pathways separated for teaching, but these different pathways are all going on at the same time d. All of them involve ATP, but there is only one pool of ATP i. So if on ...
Determination and changes of free amino acids in royal
... of the derivatized free amino acids Although performing ion exchange chromatography, the eluate was rich in short chain free fatty acids, which represented 80% of the lipid fraction of RJ. The efficiency of ion exchange chromatography was evaluated by using a standard mixture of sebacic acid and hom ...
... of the derivatized free amino acids Although performing ion exchange chromatography, the eluate was rich in short chain free fatty acids, which represented 80% of the lipid fraction of RJ. The efficiency of ion exchange chromatography was evaluated by using a standard mixture of sebacic acid and hom ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
Egg Components Dong Ahn Animal Science Department Iowa State University
... been isolated from some plants, bacteria and bacteriophages • The chicken egg white is a rich and easily available source of lysozyme • The lysozyme content of a laying hen’s blood is 10‐fold higher than in mammals because it is being transferred to the egg ...
... been isolated from some plants, bacteria and bacteriophages • The chicken egg white is a rich and easily available source of lysozyme • The lysozyme content of a laying hen’s blood is 10‐fold higher than in mammals because it is being transferred to the egg ...
Hydrogen peroxide production regulates the mitochondrial
... were the first to propose that under high exposure to fatty acids, glucose utilization is substantially reduced in different tissues including skeletal muscle. The mechanism behind this biochemical process was known as the glucose–fatty acid cycle. Under such condition, the elevated content of acetyl ...
... were the first to propose that under high exposure to fatty acids, glucose utilization is substantially reduced in different tissues including skeletal muscle. The mechanism behind this biochemical process was known as the glucose–fatty acid cycle. Under such condition, the elevated content of acetyl ...
2chap9guidedreadingVideo
... 2. What is the currency for biological energy? 3. What do you need to know about the three phosphate groups of ATP? ...
... 2. What is the currency for biological energy? 3. What do you need to know about the three phosphate groups of ATP? ...
(18 , 19)
... • There must be a mechanism by which Ammonia is moved from peripheral tissues to the liver for disposal as urea While at the same time Ammonia must be maintained at low levels in blood. ...
... • There must be a mechanism by which Ammonia is moved from peripheral tissues to the liver for disposal as urea While at the same time Ammonia must be maintained at low levels in blood. ...
Chapter 9
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
Chem 32 Solutions to Section 15.4 – 15.6 Homework Problems
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
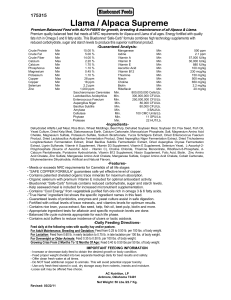
Llama / Alpaca Supreme
... - Kelp seaweed meal is included for increased micronutrient supplementation. - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeas ...
... - Kelp seaweed meal is included for increased micronutrient supplementation. - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeas ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.