FAS or PKS, lipid biosynthesis and stable carbon isotope
... Fatty acids are found in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Given the ubiquity of these important membrane components in biological systems, it is reasonable to assume that the biosynthetic pathway of fatty acids is relatively ancient [58]. Bacteria are known to synthesize fatty acids via the clas ...
... Fatty acids are found in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Given the ubiquity of these important membrane components in biological systems, it is reasonable to assume that the biosynthetic pathway of fatty acids is relatively ancient [58]. Bacteria are known to synthesize fatty acids via the clas ...
Topic 8 Acids and Bases File
... Salt hydrolysis: The process by which a salt is broken down by water. Strong: An acid or a base that dissociates completely into its ions. Ka >> 1. Some strong acids: hydrochloric, sulphuric, nitric (weaker than other two). Strong bases: hydroxides of alkali metals. ...
... Salt hydrolysis: The process by which a salt is broken down by water. Strong: An acid or a base that dissociates completely into its ions. Ka >> 1. Some strong acids: hydrochloric, sulphuric, nitric (weaker than other two). Strong bases: hydroxides of alkali metals. ...
Protein Metabolism
... The role of urea cycle “arg” has been discussed. A high protein diet increases the rate of synthesis of arginase in liver. Therefore, up-regulates the urea cycle. Notes: About 80% of nitrogen in human is excreted as urea, small amounts of ammonia, A.As., urate, creatinine and other nitrogenous ...
... The role of urea cycle “arg” has been discussed. A high protein diet increases the rate of synthesis of arginase in liver. Therefore, up-regulates the urea cycle. Notes: About 80% of nitrogen in human is excreted as urea, small amounts of ammonia, A.As., urate, creatinine and other nitrogenous ...
Dialene 4—Fat Loss You Can FEEL!
... have been outstanding. The first time I took Dialene 4 I noticed an increase in heart rate, body temperature, sweating, and a greater pump in the gym (perhaps due to increased blood flow). I also experienced an almost euphoric energy high and enhanced focus in the gym. There was no crash in energy a ...
... have been outstanding. The first time I took Dialene 4 I noticed an increase in heart rate, body temperature, sweating, and a greater pump in the gym (perhaps due to increased blood flow). I also experienced an almost euphoric energy high and enhanced focus in the gym. There was no crash in energy a ...
Lipid Metabolism
... resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP. Because one triglyceride molecule yields three fatty acid molecules with as much as 1 ...
... resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP. Because one triglyceride molecule yields three fatty acid molecules with as much as 1 ...
Electron-Transport Chain and ATP production
... Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the intermembrane s ...
... Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the intermembrane s ...
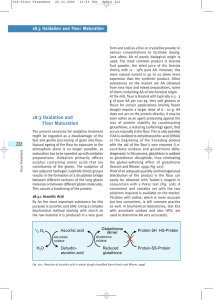
222 18.3 Oxidation and Flour Maturation
... various concentrations to facilitate dosing. Less often, AA of purely biological origin is used. The most common product is Acerola fruit powder, the dried juice of the Acerola cherry, with 17 - 19% pure AA. However, this more natural variant is up to 50 times more expensive than the synthetic produ ...
... various concentrations to facilitate dosing. Less often, AA of purely biological origin is used. The most common product is Acerola fruit powder, the dried juice of the Acerola cherry, with 17 - 19% pure AA. However, this more natural variant is up to 50 times more expensive than the synthetic produ ...
Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of
... pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pre-column derivatisation has gained wide acceptance and a number of different derivatisation reagents have been used.10–18 One of the most popular derivatisati ...
... pre-column derivatisation of amino acids, has become a very important method for the analysis of amino acids.9 It should be emphasized that pre-column derivatisation has gained wide acceptance and a number of different derivatisation reagents have been used.10–18 One of the most popular derivatisati ...
Metabolism: Introduction
... Many vitamins are "coenzymes" molecules that bring unusual chemistry to the enzyme active site Vitamins and coenzymes are classified as "water-soluble" and "fat-soluble" The water-soluble coenzymes exhibit the ...
... Many vitamins are "coenzymes" molecules that bring unusual chemistry to the enzyme active site Vitamins and coenzymes are classified as "water-soluble" and "fat-soluble" The water-soluble coenzymes exhibit the ...
1 - WordPress.com
... (E) does not require biotin 42. Which one of the following is a characteristic of the product of the fatty acid synthase complex in the liver? (A) May be elongated to stearic acid (B) May be reduced to form oleic acid (C) May be oxidized directly to palmitic acid (D) May be converted to arachidonic ...
... (E) does not require biotin 42. Which one of the following is a characteristic of the product of the fatty acid synthase complex in the liver? (A) May be elongated to stearic acid (B) May be reduced to form oleic acid (C) May be oxidized directly to palmitic acid (D) May be converted to arachidonic ...
Master Beekeeper Certification Course: Category #7
... Honeybees process nectar into honey by removing water biophysically and chemically by absorbing water and passing it from one bee to another and mechanically by fanning to evaporate the stored nectar. This raw honey is composed of a variety of sugars; mainly glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), ...
... Honeybees process nectar into honey by removing water biophysically and chemically by absorbing water and passing it from one bee to another and mechanically by fanning to evaporate the stored nectar. This raw honey is composed of a variety of sugars; mainly glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), ...
purine
... • Hydrolyzing a phosphate from ATP is relatively easy G°’= -30.5 kJ/mol – If exergonic reaction released energy into cell as heat energy, wouldn’t be useful – Must be coupled to an endergonic reaction ...
... • Hydrolyzing a phosphate from ATP is relatively easy G°’= -30.5 kJ/mol – If exergonic reaction released energy into cell as heat energy, wouldn’t be useful – Must be coupled to an endergonic reaction ...
Lecture_6_TCA_Cycle
... Because the citric acid cycle provides precursors for biosynthesis, reactions to replenish the cycle components are required if the energy status of the cells changes. These replenishing reactions are called anaplerotic reactions. A prominent anaplerotic reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylas ...
... Because the citric acid cycle provides precursors for biosynthesis, reactions to replenish the cycle components are required if the energy status of the cells changes. These replenishing reactions are called anaplerotic reactions. A prominent anaplerotic reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylas ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... Once acetyl KSase and malonyl ACP have been formed, elongation can begin. First the acetyl group of acetyl ACP is transferred to a sulfhydryl residue of ketoacyl-ACP synthase also known as acyl-malonyl ACP condensing enzyme. The decarboxylation of malonyl ACP generates an enolate anion which is a g ...
... Once acetyl KSase and malonyl ACP have been formed, elongation can begin. First the acetyl group of acetyl ACP is transferred to a sulfhydryl residue of ketoacyl-ACP synthase also known as acyl-malonyl ACP condensing enzyme. The decarboxylation of malonyl ACP generates an enolate anion which is a g ...
video slide - Northwest Florida State College
... 2) All of these produce far less E for ATP production. ...
... 2) All of these produce far less E for ATP production. ...
9.3 student notes
... • To make ATP during glycolysis, NAD+ is converted to NADH. • Organisms must recycle NAD+ to continue making ATP through glycolysis. • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called ...
... • To make ATP during glycolysis, NAD+ is converted to NADH. • Organisms must recycle NAD+ to continue making ATP through glycolysis. • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called ...
Focus on Metabolism
... Glycolysis: Anaerobic Metabolism The first stage of cellular respiration takes place in the cytosol of the cell and is called glycolysis, meaning “glucose breakdown.” Because oxygen isn’t needed for this reaction, glycolysis is also called anaerobic metabolism. In glycolysis, the 6-carbon sugar gluc ...
... Glycolysis: Anaerobic Metabolism The first stage of cellular respiration takes place in the cytosol of the cell and is called glycolysis, meaning “glucose breakdown.” Because oxygen isn’t needed for this reaction, glycolysis is also called anaerobic metabolism. In glycolysis, the 6-carbon sugar gluc ...
Dynamic Modeling of Lactic Acid Fermentation Metabolism with
... 10 mM tributylamine aqueous solutions with their pH adjusted to 4.95 using 15 mM acetic acid and methanol, respectively. A binary gradient at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min was applied using an HPLC pump. The intracellular metabolite quantification method was adopted from Luo et al. [13]. Metabolic Pathw ...
... 10 mM tributylamine aqueous solutions with their pH adjusted to 4.95 using 15 mM acetic acid and methanol, respectively. A binary gradient at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min was applied using an HPLC pump. The intracellular metabolite quantification method was adopted from Luo et al. [13]. Metabolic Pathw ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA), Krebs Cycle
... multienzyme complex. pyr dehydrogenase complex is not part of TCA cycle proper, but is a mojor source of acetyl CoA. The irreversibility of the reaction explains why glucose can not be formed from acetyl CoA in gluconeogenesis. ...
... multienzyme complex. pyr dehydrogenase complex is not part of TCA cycle proper, but is a mojor source of acetyl CoA. The irreversibility of the reaction explains why glucose can not be formed from acetyl CoA in gluconeogenesis. ...
Document
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
1. Fatty acids may be synthesized from dietary glucose via pyruvate
... a. Hormone-sensitive lipase is activated by covalent phosphorylation of the lipase by a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase b. Epinephrine circulating in the blood in response to stress, or norepinephrine released by neural connections to adipose tissue, activates the cell ...
... a. Hormone-sensitive lipase is activated by covalent phosphorylation of the lipase by a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase b. Epinephrine circulating in the blood in response to stress, or norepinephrine released by neural connections to adipose tissue, activates the cell ...
Lecture 1 - Imperial College London
... e.g. polyacetylenes & ‘eicosanoids’ (prostaglandins, thromboxanes & leukotrienes) ...
... e.g. polyacetylenes & ‘eicosanoids’ (prostaglandins, thromboxanes & leukotrienes) ...
Bio-Organic Chemistry will Page | 1
... biological fluids. There will be more applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy in CHEM 122 and 220. Infra-Red (IR) Spectroscopy IR energy is long wavelength (hence low energy) light below visible red in the spectrum. It is the same as what you feel in your toaster and what you [don't] see in your toaster ...
... biological fluids. There will be more applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy in CHEM 122 and 220. Infra-Red (IR) Spectroscopy IR energy is long wavelength (hence low energy) light below visible red in the spectrum. It is the same as what you feel in your toaster and what you [don't] see in your toaster ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration • A catabolic, exergonic, oxygen (O2) requiring process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
... Cellular Respiration • A catabolic, exergonic, oxygen (O2) requiring process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
T. TRIOSE PHOSPHATE ISOMERASE Background
... second mechanism is a proton transfer mechanism, in which deprotonation of GAP leads to the formation of an enediolate intermediate which rearranges to form DHAP upon reprotonation (Figure T.4B). The strongest mechanistic evidence for proton transfer came through a chemical exchange experiment (rece ...
... second mechanism is a proton transfer mechanism, in which deprotonation of GAP leads to the formation of an enediolate intermediate which rearranges to form DHAP upon reprotonation (Figure T.4B). The strongest mechanistic evidence for proton transfer came through a chemical exchange experiment (rece ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.