Metabolic Interactions of aPurple Sulfur Bacterium and a Facultative
... (sugars, fatty acids, and different concentrations of supernata nt from ACMO1) and the optical density of the enrichments was measured after two days (Figure 3) Enrichments with fatty acid additions showed enhanced growth over the control, as did enrichments with sugars and supernatant. However, the ...
... (sugars, fatty acids, and different concentrations of supernata nt from ACMO1) and the optical density of the enrichments was measured after two days (Figure 3) Enrichments with fatty acid additions showed enhanced growth over the control, as did enrichments with sugars and supernatant. However, the ...
Cellular Respiration
... A total of 1 ATP, 3NADH, and 1 FADH2 are produced for each turn 2 molecules of CO2 is released as waste per turn ...
... A total of 1 ATP, 3NADH, and 1 FADH2 are produced for each turn 2 molecules of CO2 is released as waste per turn ...
Chemical Inactivation of the Cinnamate 4
... A single branch point at CA is reported in the upstream phenylpropanoid pathway, which leads to benzoic acids such as the defense signal SA by a mechanism that is not yet elucidated (Chong et al., 2001). Preliminary experiments have suggested that PIP inhibition of C4H activity promotes the accumula ...
... A single branch point at CA is reported in the upstream phenylpropanoid pathway, which leads to benzoic acids such as the defense signal SA by a mechanism that is not yet elucidated (Chong et al., 2001). Preliminary experiments have suggested that PIP inhibition of C4H activity promotes the accumula ...
No Slide Title
... Encodes a protein that activates a specific E3 enzyme in ubiquitination process. E3 Ub the tumor suppressor p53 and other proteins that control DNA repair, when are then destroyed. E3 activation is observed in 90% of cervical carcinoma. NF-kB (transcription factor) initiates the expression o ...
... Encodes a protein that activates a specific E3 enzyme in ubiquitination process. E3 Ub the tumor suppressor p53 and other proteins that control DNA repair, when are then destroyed. E3 activation is observed in 90% of cervical carcinoma. NF-kB (transcription factor) initiates the expression o ...
Preparation of pyruvate for the citric acid cycle Recap 1. We have
... 3. It is converted to Lactate (animal muscles) 4. It is converted to ethanol (yeast; alcohol fermantation) Pyruvate enters the Citric acid cycle First, we need to get pyruvate to the correct location: Glycolyis occurs in the ______________ TCA cycle occurs in the ______________ ...
... 3. It is converted to Lactate (animal muscles) 4. It is converted to ethanol (yeast; alcohol fermantation) Pyruvate enters the Citric acid cycle First, we need to get pyruvate to the correct location: Glycolyis occurs in the ______________ TCA cycle occurs in the ______________ ...
Detoxikace endogenních a exogenních látek
... A portion of Gln can be taken up by the kidney; another portion of Gln is produced by the kidney itself ...
... A portion of Gln can be taken up by the kidney; another portion of Gln is produced by the kidney itself ...
Ch16
... used as the starting molecules for several amino acid biosynthesis and pyrole (heme) biosynthesis. This drains CAC intermediates away which could slow down CAC (CAC can only move if there is sufficient oxaloacetate OAA). So when OAA or malate were added to pigeon muscle preps, their oxygen uptake in ...
... used as the starting molecules for several amino acid biosynthesis and pyrole (heme) biosynthesis. This drains CAC intermediates away which could slow down CAC (CAC can only move if there is sufficient oxaloacetate OAA). So when OAA or malate were added to pigeon muscle preps, their oxygen uptake in ...
Purification and amino acid sequence of a bacteriocins produced by
... chemicals used as preservatives in food because of their side effects. Therefore, natural antibiotics have been considered as alternatives (Soomro et al., 2002). Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are commonly found in many foods such as meat, vegetable and milk, sometimes as dominating microflora (Atrih et ...
... chemicals used as preservatives in food because of their side effects. Therefore, natural antibiotics have been considered as alternatives (Soomro et al., 2002). Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are commonly found in many foods such as meat, vegetable and milk, sometimes as dominating microflora (Atrih et ...
Effect of nitrogen fertilization on metabolisms of essential and non
... such as seeds of annual crops. High leaf carbohydrate to nitrogen (C:N) ratios were implicated in the induction or acceleration of the senescence process (Parrott et al. 2010). During seed production the aleurone layer is formed which contains very interesting proteins, i.e. metallothionein-like pro ...
... such as seeds of annual crops. High leaf carbohydrate to nitrogen (C:N) ratios were implicated in the induction or acceleration of the senescence process (Parrott et al. 2010). During seed production the aleurone layer is formed which contains very interesting proteins, i.e. metallothionein-like pro ...
Acids and Bases
... Now let’s see how we knew that water acts as a base in the first reaction in Section 2.1 and as an acid in the second reaction. To determine which of the reactants will be the acid, we need to compare their pKa values: The pKa of hydrogen chloride is -7 and the pKa of water is 15.7. Because hydrogen ...
... Now let’s see how we knew that water acts as a base in the first reaction in Section 2.1 and as an acid in the second reaction. To determine which of the reactants will be the acid, we need to compare their pKa values: The pKa of hydrogen chloride is -7 and the pKa of water is 15.7. Because hydrogen ...
Vitamins B6 and B12 (Final).
... 1-Cyanocobalamin 2-Hydroxycobalamin These 2 forms which is given to patient as supplement + it can be converted into active coenzymes with help of different enzymes 3-Adenosylcobalamin (major storage form in the liver) 4-Methylcobalamin (mostly found in blood circulation) *Coenzymes for metabolic re ...
... 1-Cyanocobalamin 2-Hydroxycobalamin These 2 forms which is given to patient as supplement + it can be converted into active coenzymes with help of different enzymes 3-Adenosylcobalamin (major storage form in the liver) 4-Methylcobalamin (mostly found in blood circulation) *Coenzymes for metabolic re ...
H 3 O +
... – His has a side chain pKa of 6.0 and is only 10% protonated at pH 7 – Because His has a pKa near neutral, it plays important roles as a proton donor or acceptor in many enzymes. – His containing peptides are important biological buffers ...
... – His has a side chain pKa of 6.0 and is only 10% protonated at pH 7 – Because His has a pKa near neutral, it plays important roles as a proton donor or acceptor in many enzymes. – His containing peptides are important biological buffers ...
Nutritional Requirements of Streptococcus salivarius
... The close overall similarity between Streptococcus bovis and S. salivarius (Carlsson, 1968) and the similarity in nutritional requirements of these species suggest that ammonia and carbon dioxide are assimilated in similar ways in these streptococci. Streptococcus salivarius could utilize cysteine, ...
... The close overall similarity between Streptococcus bovis and S. salivarius (Carlsson, 1968) and the similarity in nutritional requirements of these species suggest that ammonia and carbon dioxide are assimilated in similar ways in these streptococci. Streptococcus salivarius could utilize cysteine, ...
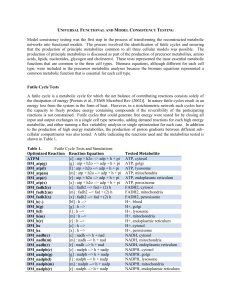
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... reactions that are catalyzed by the NADP dependent malic enzyme are included to be reversible, based on the previous experimental evidence generated using various types of mammalian cell types and tissues. In this case, cytosolic NADP-dependent malic enzyme performs in the reverse direction allowing ...
... reactions that are catalyzed by the NADP dependent malic enzyme are included to be reversible, based on the previous experimental evidence generated using various types of mammalian cell types and tissues. In this case, cytosolic NADP-dependent malic enzyme performs in the reverse direction allowing ...
Estimation of the dietary essential amino acid requirements
... composition (Mitchell, 1950), the ideal protein concept that uses the relationships of each essential amino acid profile in relation to lysine has been developed as a basis to formulate diets for fish (Furuya et al., 2004a; Kaushik & Seiliez, 2010; NRC, 2011). The advantage of this concept is that i ...
... composition (Mitchell, 1950), the ideal protein concept that uses the relationships of each essential amino acid profile in relation to lysine has been developed as a basis to formulate diets for fish (Furuya et al., 2004a; Kaushik & Seiliez, 2010; NRC, 2011). The advantage of this concept is that i ...
CELLULAR ENERGY METABOLISM DURING FETAL
... In view of the importance of fatty acids as substrates for the mature heart, fatty acid oxidation by fetal and calf heart mitochondria has been investigated . Free fatty acids of 10 carbon units or less which exhibit carnitine-independent transport into mitochondria were effective substrates for oxi ...
... In view of the importance of fatty acids as substrates for the mature heart, fatty acid oxidation by fetal and calf heart mitochondria has been investigated . Free fatty acids of 10 carbon units or less which exhibit carnitine-independent transport into mitochondria were effective substrates for oxi ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Slide 1
... dinucleotide) to carry e– Another coenzyme that functions like NAD+ is FAD – They “carry” e- from glucose to a series of proteins found along the cristae of the mitochondrion called the electron transport chain or ETC ...
... dinucleotide) to carry e– Another coenzyme that functions like NAD+ is FAD – They “carry” e- from glucose to a series of proteins found along the cristae of the mitochondrion called the electron transport chain or ETC ...
electron transport chain
... to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Energy Transformation — Cellular Respiration
... has to appear to supply a bulk of ATP (almost 90%) to the body cells. Hence, most cells of multicellular organisms cannot live long without oxygen, especially the human brain cells which cannot undergo glycolysis. 2. Lack of oxygen is not the only factor that interferes with the electron transport s ...
... has to appear to supply a bulk of ATP (almost 90%) to the body cells. Hence, most cells of multicellular organisms cannot live long without oxygen, especially the human brain cells which cannot undergo glycolysis. 2. Lack of oxygen is not the only factor that interferes with the electron transport s ...
Poster
... inhibitors as drug leads Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) are generated from arachidonic acid by epoxygenases of the cytochrome P450 superfamily. In humans, EETs promote vasodilation and angiogenesis, and act to inhibit systemic antiinflammatory response (1). The enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sE ...
... inhibitors as drug leads Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) are generated from arachidonic acid by epoxygenases of the cytochrome P450 superfamily. In humans, EETs promote vasodilation and angiogenesis, and act to inhibit systemic antiinflammatory response (1). The enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sE ...
interaction analysis of aspirin with selective amino acids
... Abstract: This study was conducted to assess the compatibility of aspirin with selective amino acids by studying the effect of amino acids on the solubility of aspirin, so that the attention could be paid towards the use of proteinous foods along with aspirin. Two different types of dissolution medi ...
... Abstract: This study was conducted to assess the compatibility of aspirin with selective amino acids by studying the effect of amino acids on the solubility of aspirin, so that the attention could be paid towards the use of proteinous foods along with aspirin. Two different types of dissolution medi ...
General Biology I (BIOLS 102)
... However, hydrogen atoms must be combined with oxygen to make water If O2 is not present, NADH cannot release H+ No longer recycled back to NAD+ ...
... However, hydrogen atoms must be combined with oxygen to make water If O2 is not present, NADH cannot release H+ No longer recycled back to NAD+ ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.