Saccharomyces cerevisiae Metabolic engineering of for production
... the cost and complicate downstream processing (Benninga, 1990; Vaidya et al., 2005). Furthermore, these prokaryotic organisms are generally unable to grow and produce organic acids at the low pH values where these compounds occur predominantly in their undissociated form. Production at these lower p ...
... the cost and complicate downstream processing (Benninga, 1990; Vaidya et al., 2005). Furthermore, these prokaryotic organisms are generally unable to grow and produce organic acids at the low pH values where these compounds occur predominantly in their undissociated form. Production at these lower p ...
09LecturePresentation
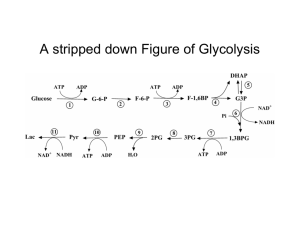
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP • Glycolysis can produce ATP with or without O2 (in aerobic or anaerobic conditions) • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produ ...
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP • Glycolysis can produce ATP with or without O2 (in aerobic or anaerobic conditions) • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produ ...
ID_4450_General principles of metaboli_English_sem_5
... Why is it undesirable to have high concentrations of free fatty acids and lysophosphoglycerides in cells? They are unstable, free radicals that can react to form toxic substances They polymerize easily and can cause the cytosol to become too gel-like They inhibit the uptake of pyruvate by mitochondr ...
... Why is it undesirable to have high concentrations of free fatty acids and lysophosphoglycerides in cells? They are unstable, free radicals that can react to form toxic substances They polymerize easily and can cause the cytosol to become too gel-like They inhibit the uptake of pyruvate by mitochondr ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Acid–Base
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
Support Vector Machine-based classification of protein folds using
... their accuracies remain low. This can be attributed to insufficient exploitation of fold discriminatory features. Results: We have developed a new method for protein fold recognition using structural information of amino acid residues and amino acid residue pairs. Since protein fold recognition can ...
... their accuracies remain low. This can be attributed to insufficient exploitation of fold discriminatory features. Results: We have developed a new method for protein fold recognition using structural information of amino acid residues and amino acid residue pairs. Since protein fold recognition can ...
FIGURE 21–6 Part 1
... stages: (1) synthesis of the 18-carbon amine sphinganine from palmitoyl-CoA and serine; (2) attachment of a fatty acid in amide linkage to yield N-acylsphinganine; (3) desaturation of the sphinganine moiety to form Nacylsphingosine (ceramide); and (4) attachment of a head group to produce a sphingol ...
... stages: (1) synthesis of the 18-carbon amine sphinganine from palmitoyl-CoA and serine; (2) attachment of a fatty acid in amide linkage to yield N-acylsphinganine; (3) desaturation of the sphinganine moiety to form Nacylsphingosine (ceramide); and (4) attachment of a head group to produce a sphingol ...
Caspaar Bijleveld and Math JH Geelen
... [lO,ll]. These difficulties can be circumvented by coupling the carboxylation reaction with the fatty acid synthase reaction. In this coupled system the rate of formation of labelled malonyl-CoA from radioactive acetyl-CoA is measured by determining the incorporation of 14C into long-chain fatty aci ...
... [lO,ll]. These difficulties can be circumvented by coupling the carboxylation reaction with the fatty acid synthase reaction. In this coupled system the rate of formation of labelled malonyl-CoA from radioactive acetyl-CoA is measured by determining the incorporation of 14C into long-chain fatty aci ...
Amino acids
... • Deficient in enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, therefore can not metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine and it accumulates • If left untreated can lead to brain damage, mental retardation, and seizures • Tested in newborns with blood test • Management is low PKU diet, no meat, dairy, eggs, starchy f ...
... • Deficient in enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, therefore can not metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine and it accumulates • If left untreated can lead to brain damage, mental retardation, and seizures • Tested in newborns with blood test • Management is low PKU diet, no meat, dairy, eggs, starchy f ...
I. ATP is Universal
... Critical concepts include: fermentation, energy production via fermentation, and the use of fermentation for food production. 7.7 When oxygen is in short supply, the cell switches to fermentation A. Fermentation produces two ATP per glucose molecule in the absence of O2. B. Pyruvate is used as final ...
... Critical concepts include: fermentation, energy production via fermentation, and the use of fermentation for food production. 7.7 When oxygen is in short supply, the cell switches to fermentation A. Fermentation produces two ATP per glucose molecule in the absence of O2. B. Pyruvate is used as final ...
Amino acids
... • Deficient in enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, therefore can not metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine and it accumulates • If left untreated can lead to brain damage, mental retardation, and seizures • Tested in newborns with blood test • Management is low PKU diet, no meat, dairy, eggs, starchy f ...
... • Deficient in enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, therefore can not metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine and it accumulates • If left untreated can lead to brain damage, mental retardation, and seizures • Tested in newborns with blood test • Management is low PKU diet, no meat, dairy, eggs, starchy f ...
Control of cytoplasmic pH under anoxic
... improved understanding of intracellular pH regulation, yet despite the many splendid reports and reviews (Smith and Raven, 1979; Roberts et al, 1984a, b; Raven, 1986; Davies, 1986; Fox and Ratcliffe, 1990; Guern et al, 1991) our understanding remains limited. In part, this may arise from the fact th ...
... improved understanding of intracellular pH regulation, yet despite the many splendid reports and reviews (Smith and Raven, 1979; Roberts et al, 1984a, b; Raven, 1986; Davies, 1986; Fox and Ratcliffe, 1990; Guern et al, 1991) our understanding remains limited. In part, this may arise from the fact th ...
artículo - Anales de la Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia
... like signaling pathways (22). But there are others like Agtr1a–/– (Angiotensine II type 1 receptors targeted disrupted) mice (23) and AC5KO (adenylyl cyclase 5 Knockout) mice (1) that also ...
... like signaling pathways (22). But there are others like Agtr1a–/– (Angiotensine II type 1 receptors targeted disrupted) mice (23) and AC5KO (adenylyl cyclase 5 Knockout) mice (1) that also ...
video slide
... are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: ...
... are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: ...
1 - WordPress.com
... (D) Fatty acids from adipose stores are the major source of fuel for red blood cells (E) noneof them 5-A. After 3-5 days of starvation, the brain begins to use ketone bodies, in addition to glucose, as a fuel source. Glycogen stores in the liver are depleted during the first 30 hours of fasting. In ...
... (D) Fatty acids from adipose stores are the major source of fuel for red blood cells (E) noneof them 5-A. After 3-5 days of starvation, the brain begins to use ketone bodies, in addition to glucose, as a fuel source. Glycogen stores in the liver are depleted during the first 30 hours of fasting. In ...
Classification of amino acids: -
... j) Methionine acts as active Methionine (δ – adensyl – Methionine) to transfer methyl group to various substances by transmethylation. Note: Cys and Met are source of sulphur for the sulphur compound in the body. ...
... j) Methionine acts as active Methionine (δ – adensyl – Methionine) to transfer methyl group to various substances by transmethylation. Note: Cys and Met are source of sulphur for the sulphur compound in the body. ...
Micro 2 transcripts to be made into flashcards
... NOTE: Know which wells have what color of a positive test: Brown, Orange or Red, Blue, Yellow, Diffused black pigment, Pink ring on top, etc. CATALASE TEST (Control: positive = Staph aureus) Some facultative aerobes have the enzyme called catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into har ...
... NOTE: Know which wells have what color of a positive test: Brown, Orange or Red, Blue, Yellow, Diffused black pigment, Pink ring on top, etc. CATALASE TEST (Control: positive = Staph aureus) Some facultative aerobes have the enzyme called catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into har ...
Bacteroides macacae - International Journal of Systematic and
... have trypsin-like activity but do not produce lipase. P. macacae ATCC 3314lTcontains 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (iso-C1s:o acid) as a major cellular fatty acid, and malate, glutamate, glucose-6-phosphate, and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases are present. Strains have been isolated from oral caviti ...
... have trypsin-like activity but do not produce lipase. P. macacae ATCC 3314lTcontains 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (iso-C1s:o acid) as a major cellular fatty acid, and malate, glutamate, glucose-6-phosphate, and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases are present. Strains have been isolated from oral caviti ...
Introduction into Metabolism and Energy Exchange in Human
... enzymes: E1-TPP (vitamin B1 –derivative); E2: CoASH (vitamin B3derivative), Amine of Lipoic acid; E3: FAD (vitamin B2-derivative, NAD+ (vitamin PP-derivative). It catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of αketoglutarate to form three products: succinyl~SCoA, carbon dioxide and NADH. Allosteric Inhi ...
... enzymes: E1-TPP (vitamin B1 –derivative); E2: CoASH (vitamin B3derivative), Amine of Lipoic acid; E3: FAD (vitamin B2-derivative, NAD+ (vitamin PP-derivative). It catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of αketoglutarate to form three products: succinyl~SCoA, carbon dioxide and NADH. Allosteric Inhi ...
histidine and cysteine can enhance the metabolic reaction rates in
... The cycle produces many starting substrates converting to amino acids, nucleotides, and lipids later. The results in my previous letter [2] showed that histidine acts as pyruvate carboxylase (ligase) to form oxalacetate from pyruvate and carbonate with ATP , as oxalacetate decarboxylase (lyase) to c ...
... The cycle produces many starting substrates converting to amino acids, nucleotides, and lipids later. The results in my previous letter [2] showed that histidine acts as pyruvate carboxylase (ligase) to form oxalacetate from pyruvate and carbonate with ATP , as oxalacetate decarboxylase (lyase) to c ...
TCA Cycle - eCurriculum
... Catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase, enzyme directly linked to the electron transport chain. )G 0 ’= 0. Uses FAD because the free energy change is not enough to generate NADH. 7) fumarate + H2O ↔ malate Catalyzed by fumarase. )G 0 ’= 0. 8) malate + NAD + ↔ oxaloacetate + NADH Catalyzed ...
... Catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase, enzyme directly linked to the electron transport chain. )G 0 ’= 0. Uses FAD because the free energy change is not enough to generate NADH. 7) fumarate + H2O ↔ malate Catalyzed by fumarase. )G 0 ’= 0. 8) malate + NAD + ↔ oxaloacetate + NADH Catalyzed ...
Determination of free amino acids in cheeses from the Czech market
... in the metabolism. The substances are quickly and easily absorbed by the body. Cheese is easily digestible and constitutes an important source of vitamins, but also calcium, magnesium, phosphor, and other trace elements as well as amino acids and proteins (Fox 1993). The presence of amino acids, vit ...
... in the metabolism. The substances are quickly and easily absorbed by the body. Cheese is easily digestible and constitutes an important source of vitamins, but also calcium, magnesium, phosphor, and other trace elements as well as amino acids and proteins (Fox 1993). The presence of amino acids, vit ...
Water Soluble Vitamins
... Decreases uric acid reabsorption resulting in increased risk of gout Affects diagnostic tests in feces and ...
... Decreases uric acid reabsorption resulting in increased risk of gout Affects diagnostic tests in feces and ...
Respiration and Lipid Metabolism - Roberto Cezar | Fisiologista
... classic glycolytic and fermentative pathways in plants are almost identical with those of animal cells (Figure 11.3). However, plant glycolysis has unique regulatory features, as well as a parallel partial glycolytic pathway in plastids and alternative enzymatic routes for several cytosolic steps. I ...
... classic glycolytic and fermentative pathways in plants are almost identical with those of animal cells (Figure 11.3). However, plant glycolysis has unique regulatory features, as well as a parallel partial glycolytic pathway in plastids and alternative enzymatic routes for several cytosolic steps. I ...
lecture1
... units. The molecular weight may vary from 1 million to 4 million Formation of glycogen occur mostly in the liver and muscles and in small traces in every tissue of the body. Liver glycogen replenishes blood glucose when it is lowered while muscle glycogen acts as a readily available source of hexose ...
... units. The molecular weight may vary from 1 million to 4 million Formation of glycogen occur mostly in the liver and muscles and in small traces in every tissue of the body. Liver glycogen replenishes blood glucose when it is lowered while muscle glycogen acts as a readily available source of hexose ...
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skele ...
... by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skele ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.