ACID BASE - Union City High School
... To classify a soluble substance as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte, we simply use the following table: ...
... To classify a soluble substance as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte, we simply use the following table: ...
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ion
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
supporting information
... Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Raymond Zeng at ...
... Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Raymond Zeng at ...
VEN 124 Section IV
... • Creates an intensely bitter taste when combined with phenolic compounds ...
... • Creates an intensely bitter taste when combined with phenolic compounds ...
Note 17 - South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School
... (1) the change of _____________________ into acetyl-CoA (2-C) [this is not a part of the Krebs cycle] The products are NADH, acetyl-CoA, CO2 (carbon dioxide). ...
... (1) the change of _____________________ into acetyl-CoA (2-C) [this is not a part of the Krebs cycle] The products are NADH, acetyl-CoA, CO2 (carbon dioxide). ...
221_exam_2_2003
... Approximately 20% of bacterial proteins are exported to the cytoplasmic membrane and beyond. The translocation of many of these proteins involves a signal peptide. Briefly explain the four different mechanisms by which signal peptide containing proteins can get from the ribosome to the cytoplasmic m ...
... Approximately 20% of bacterial proteins are exported to the cytoplasmic membrane and beyond. The translocation of many of these proteins involves a signal peptide. Briefly explain the four different mechanisms by which signal peptide containing proteins can get from the ribosome to the cytoplasmic m ...
III: Cells Utilizing Oxygen to Form Lipid Regulators and
... 3) Flurbiprofen - slow binding (salt bridge) competitive inhibition by binding in the hydrophobic channel Indomethacin - non-selective - binds deepest in hydrophobic channel (incr. risk of hypertension,congestive heart failure unlike Celecoxib) COX-2 inhibitors – much less GI toxicity ...
... 3) Flurbiprofen - slow binding (salt bridge) competitive inhibition by binding in the hydrophobic channel Indomethacin - non-selective - binds deepest in hydrophobic channel (incr. risk of hypertension,congestive heart failure unlike Celecoxib) COX-2 inhibitors – much less GI toxicity ...
Fall 2009 Chem 306 Exam II KEY
... head group of a detergent is a sulfate group instead of a carboxylate group. b. Detergents do not form an insoluble solid with the magnesium and calcium ions found in tap water. c. A common detergent found in shampoos and hand-washing formulations is sodium lauryl sulfate. d. The mechanism of the cl ...
... head group of a detergent is a sulfate group instead of a carboxylate group. b. Detergents do not form an insoluble solid with the magnesium and calcium ions found in tap water. c. A common detergent found in shampoos and hand-washing formulations is sodium lauryl sulfate. d. The mechanism of the cl ...
Anaerobic metabolism is the production of ATP with oxygen
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
III. Neutralization
... D12 - Explain the chemical composition of acids and bases, and explain the change of pH in neutralization reactions. ...
... D12 - Explain the chemical composition of acids and bases, and explain the change of pH in neutralization reactions. ...
Fatty Acids - National Lipid Association
... Triglycerides (TG) should actually be called triacylglycerols (TAG). TG or TAG are molecules with a glycerol (a carbohydrate) backbone to which are attached three acyl groups. They represent a concentrated source of metabolic energy contributing 9 kcal/gm. Phospholipids (PL) are also derived from gl ...
... Triglycerides (TG) should actually be called triacylglycerols (TAG). TG or TAG are molecules with a glycerol (a carbohydrate) backbone to which are attached three acyl groups. They represent a concentrated source of metabolic energy contributing 9 kcal/gm. Phospholipids (PL) are also derived from gl ...
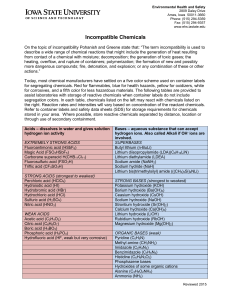
Incompatible Chemicals
... Segregate oxidizing acids (nitric, perchloric and chromic) from all other materials. Store water reactives away from water sources or aqueous solutions. Examples include metals such as sodium and potassium; acid anhydrides and acid chlorides; and fine metal powders such as zinc. Store pyrophoric che ...
... Segregate oxidizing acids (nitric, perchloric and chromic) from all other materials. Store water reactives away from water sources or aqueous solutions. Examples include metals such as sodium and potassium; acid anhydrides and acid chlorides; and fine metal powders such as zinc. Store pyrophoric che ...
ws bubbles new 1213 with answers
... 5. Use Table B to identify the protein coded for by that strand of DNA 6. Identify the kind of mutation that makes each pair of proteins different ...
... 5. Use Table B to identify the protein coded for by that strand of DNA 6. Identify the kind of mutation that makes each pair of proteins different ...
Organic Molecules - Dublin City Schools
... #16 Certain fatty acids are said to be essential because the body cannot make them itself; they must be obtained in the diet. If you diet were deficient in these essential fatty acids, you would not be able to tame certain? a. fats b. glycerol molecules c. monosaccharides d. proteins e. You would n ...
... #16 Certain fatty acids are said to be essential because the body cannot make them itself; they must be obtained in the diet. If you diet were deficient in these essential fatty acids, you would not be able to tame certain? a. fats b. glycerol molecules c. monosaccharides d. proteins e. You would n ...
Biochemistry_of_Cells abridged
... Plant cells store starch for energy Potatoes and grains are major sources of starch in the human diet ...
... Plant cells store starch for energy Potatoes and grains are major sources of starch in the human diet ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
... 21.Nucleic acids carry genetic information in a molecule called DNA or Deoxyribo nucleic acid. 22. Nucleotides are the subunits making up nucleic acid. 23. The 3 parts of a nucleotide are a 5 carbon sugar , a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. 24. Give the symbols for the elements that make up each of ...
... 21.Nucleic acids carry genetic information in a molecule called DNA or Deoxyribo nucleic acid. 22. Nucleotides are the subunits making up nucleic acid. 23. The 3 parts of a nucleotide are a 5 carbon sugar , a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. 24. Give the symbols for the elements that make up each of ...
Hariri High School II
... The percentage by mass of oxygen in an organic compound (E) of general formula CnH2n O2 is 24.61 %. (H=1 , C=12 , O=16) A. Show that the molecular formula of (E) is C7H14O2. B. The compound (E) may be an acid or an ester . What is the nature of ( E ),knowing that its aqueous solution has a PH = 7 . ...
... The percentage by mass of oxygen in an organic compound (E) of general formula CnH2n O2 is 24.61 %. (H=1 , C=12 , O=16) A. Show that the molecular formula of (E) is C7H14O2. B. The compound (E) may be an acid or an ester . What is the nature of ( E ),knowing that its aqueous solution has a PH = 7 . ...
PPT 4
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
Lipids - Cloudfront.net
... The “tail” end is scared of water and is given the name HYDROPHOBIC You will see why this is so important when we talk about ...
... The “tail” end is scared of water and is given the name HYDROPHOBIC You will see why this is so important when we talk about ...
File - Wk 1-2
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
lq 17.5 Lipid composition of cell membrones
... It is possible to break cells,empty them of their contents, and isolate the cell membranes.The cellmembrane is the "snck"that holds the contentsof cells and actsas a selectiuebarrier for the passageofcertain substancesin and out of the cell. The interior of cells also contains membrane structures, a ...
... It is possible to break cells,empty them of their contents, and isolate the cell membranes.The cellmembrane is the "snck"that holds the contentsof cells and actsas a selectiuebarrier for the passageofcertain substancesin and out of the cell. The interior of cells also contains membrane structures, a ...
Response to Review of ANS 495 595
... Next, students cannot, at present, enroll in a course entitled “Physiological Chemistry” at Oregon State University. This is what was meant by “physiological chemistry is a subject that is not taught at OSU.” This statement was made within the context of a course proposal as opposed to a summary of ...
... Next, students cannot, at present, enroll in a course entitled “Physiological Chemistry” at Oregon State University. This is what was meant by “physiological chemistry is a subject that is not taught at OSU.” This statement was made within the context of a course proposal as opposed to a summary of ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.