Download PDF
... electron capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and co ...
... electron capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and co ...
Fermentation - cloudfront.net
... • What happens? A) Glucose (from our food) is broken down into 2 pyruvates B) 2 ATP molecules released for cellular processes ...
... • What happens? A) Glucose (from our food) is broken down into 2 pyruvates B) 2 ATP molecules released for cellular processes ...
last year`s April exam
... b) Draw a picture that shows how water molecules can interact with an aldehyde through H-bonding, showing all possible interactions. ...
... b) Draw a picture that shows how water molecules can interact with an aldehyde through H-bonding, showing all possible interactions. ...
(PDF format, 1.73MB)
... • Complex I assembly is complex! • Sub-complexes (green) are assembled together via a number of discrete stages • Requires additional proteins (colour) that help the assembly process (assembly factors) – 12 known • Defects in the subunits (18) or assembly factors (9) can cause Mito disease ...
... • Complex I assembly is complex! • Sub-complexes (green) are assembled together via a number of discrete stages • Requires additional proteins (colour) that help the assembly process (assembly factors) – 12 known • Defects in the subunits (18) or assembly factors (9) can cause Mito disease ...
Review Sheet Key - Spring Branch ISD
... Pyruvic Acid ADP ATP NADH Carbon dioxide NADH ATP FAHD2 Citric Acid Water NAD+ FAD ATP Ethyl Alcohol Carbon dioxide NAD+ ...
... Pyruvic Acid ADP ATP NADH Carbon dioxide NADH ATP FAHD2 Citric Acid Water NAD+ FAD ATP Ethyl Alcohol Carbon dioxide NAD+ ...
Unit C - Topic 1.0 Notes
... Neutralization – a reaction where an acid and base come together to produce water and a salt. This reaction can be used to neutralize stomach acid or basic chemical spills, and can help combat the effects of acid rain. • In some parts of Canada, rain can have a pH as low as 3. Acid rain can have de ...
... Neutralization – a reaction where an acid and base come together to produce water and a salt. This reaction can be used to neutralize stomach acid or basic chemical spills, and can help combat the effects of acid rain. • In some parts of Canada, rain can have a pH as low as 3. Acid rain can have de ...
1. phylum: firmicutes - Fermentation-SN
... - These are the so-called acetone-butanol fermenters. Butanol is formed from butyrylCoA via butyrylaldehyde (see Figure 4). Acetone and isopropanol are formed from acetoacetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and subsequent reduction, respectively. These so-called butyric acid bacteria include Clostridium pas ...
... - These are the so-called acetone-butanol fermenters. Butanol is formed from butyrylCoA via butyrylaldehyde (see Figure 4). Acetone and isopropanol are formed from acetoacetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and subsequent reduction, respectively. These so-called butyric acid bacteria include Clostridium pas ...
Production of lactic acid
... Lactic acid is used as a humectant or moisturizer, in some cosmetics and as a mordant, a chemical that helps fabrics accept dyes, in textiles It is also used in making pickles and sauerkraut, foods for which a sour taste is desired. Lactic acid is used in the dairy industry not only in making yogurt ...
... Lactic acid is used as a humectant or moisturizer, in some cosmetics and as a mordant, a chemical that helps fabrics accept dyes, in textiles It is also used in making pickles and sauerkraut, foods for which a sour taste is desired. Lactic acid is used in the dairy industry not only in making yogurt ...
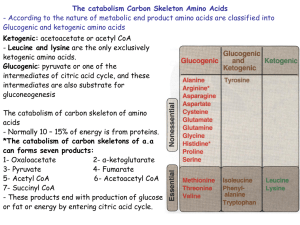
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Metabolic engineering Synthetic Biology
... for the production of valuable products Practice of optimizing genetic and regulatory processes within cells to increase the cells' production of a substance. Metabolic engineers commonly work to reduce cellular energy use (i.e, the energetic cost of cell reproduction or proliferation) and to re ...
... for the production of valuable products Practice of optimizing genetic and regulatory processes within cells to increase the cells' production of a substance. Metabolic engineers commonly work to reduce cellular energy use (i.e, the energetic cost of cell reproduction or proliferation) and to re ...
Vitamins
... giving a person more energy. This is due to the fact that these vitamins each play different roles with energy metabolism in the body. When they are present in the body, they allow energy to be used more readily by the body. Since these vitamins are water soluble, they are not stored in the body li ...
... giving a person more energy. This is due to the fact that these vitamins each play different roles with energy metabolism in the body. When they are present in the body, they allow energy to be used more readily by the body. Since these vitamins are water soluble, they are not stored in the body li ...
The Basics of Cellular Respiration
... It takes place in the mitochondrion’s inner membrane. Electrons are carried and ATPs are produced. It is an aerobic process. ...
... It takes place in the mitochondrion’s inner membrane. Electrons are carried and ATPs are produced. It is an aerobic process. ...
Fermentation and Cellular Respiration 1. Define: Glycolysis
... glucose. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is split into two pyruvic acid molecules with the associated production of two molecules of ATP and the reduction of two molecules of NAD to form NADH + H+ (also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway). Fermentation – Fermentation is the anaerob ...
... glucose. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is split into two pyruvic acid molecules with the associated production of two molecules of ATP and the reduction of two molecules of NAD to form NADH + H+ (also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway). Fermentation – Fermentation is the anaerob ...
Name Due date ______ Strive for a 5 – AP Biology Review Unit 1
... Explain using the prompts below. Choice ____ is more water soluble because _________________________________. Choice ____ is less water soluble because __________________________________. 11. Number the un-numbered carbons and provide the names of each of these two monosaccharides. ...
... Explain using the prompts below. Choice ____ is more water soluble because _________________________________. Choice ____ is less water soluble because __________________________________. 11. Number the un-numbered carbons and provide the names of each of these two monosaccharides. ...
Bio-molecule
... Lipids are made mostly of carbon and hydrogen, and proteins contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. ...
... Lipids are made mostly of carbon and hydrogen, and proteins contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. ...
Energy Metabolism - 35-206-202
... cannot be completely broken down and form Ketones. Eventually our body can turn these ketones into Acetyl-CoA which can then finally enter the citric acid cycle. • This process is called ketogenesis • Ketosis in Diabetes Mellitus • Ketosis in semistarvation or fasting or very low/no ...
... cannot be completely broken down and form Ketones. Eventually our body can turn these ketones into Acetyl-CoA which can then finally enter the citric acid cycle. • This process is called ketogenesis • Ketosis in Diabetes Mellitus • Ketosis in semistarvation or fasting or very low/no ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... Occurs during starvation or prolonged exercise – result of elevated FFA • high HSL activity ...
... Occurs during starvation or prolonged exercise – result of elevated FFA • high HSL activity ...
Evening primrose oil
... In recent decades, much research has been conducted on the role of essential fatty acids in the formation and the barrier function of superficial skin layers. Some studies revealed that by applying linoleic acid (LA) and γ-linolenic acid (GLA) for some days, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) is reduc ...
... In recent decades, much research has been conducted on the role of essential fatty acids in the formation and the barrier function of superficial skin layers. Some studies revealed that by applying linoleic acid (LA) and γ-linolenic acid (GLA) for some days, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) is reduc ...
Cellular Respiration PPT
... This fermentation process, rather than producing lactic acid, produces ethanol commonly referred to as alcohol and CO2 from pyruvic acid. ...
... This fermentation process, rather than producing lactic acid, produces ethanol commonly referred to as alcohol and CO2 from pyruvic acid. ...
Document
... (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
role of respiration in glycolysis, co2 and h20 production
... from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the oxidation of one molecule and the reduction of another. ...
... from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the oxidation of one molecule and the reduction of another. ...
Water soluble Vit. Vit C: (Ascorbic Acid)
... A derivatives of folic acid is called folinic acid (5,6,7,8, tetrahydrofolate) (THF) is much more active than folic acid in stimulating erythrocyte formation. The conversion of folic acid to its active form folinic acid is catalysed by folinic ...
... A derivatives of folic acid is called folinic acid (5,6,7,8, tetrahydrofolate) (THF) is much more active than folic acid in stimulating erythrocyte formation. The conversion of folic acid to its active form folinic acid is catalysed by folinic ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.