221_exam_2_2004
... What are some basic differences and similarities between fermentation and respiration using glucose as the carbon and energy source? ...
... What are some basic differences and similarities between fermentation and respiration using glucose as the carbon and energy source? ...
If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel
... like? Why do they begin to feel like that? ...
... like? Why do they begin to feel like that? ...
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) - LSU School of Medicine
... • OAA acts as carrier or acceptor of acetyl CoA units – is regenerated • “Burns” acetyl CoA to CO2 – during this oxidation eˉs from acetyl CoA are trapped in the form of: Pyruvate ...
... • OAA acts as carrier or acceptor of acetyl CoA units – is regenerated • “Burns” acetyl CoA to CO2 – during this oxidation eˉs from acetyl CoA are trapped in the form of: Pyruvate ...
Summary of Metabolic Pathways
... • In fatty acid oxidation, each acetyl-SCoA can pass carbons into the citric acid cycle, yielding 12 ATP. • Each of the FADH2 molecules can be oxidized via the electron transport chain to form a maximum of 2 ATP, and each NADH can result in formation of 3 ATP. • One mole of lauric acid weighs about ...
... • In fatty acid oxidation, each acetyl-SCoA can pass carbons into the citric acid cycle, yielding 12 ATP. • Each of the FADH2 molecules can be oxidized via the electron transport chain to form a maximum of 2 ATP, and each NADH can result in formation of 3 ATP. • One mole of lauric acid weighs about ...
Chapter 13: Carbohydrates
... molecules necessary for life as we know it However, most of these complex molecules are actually made of smaller, simpler units – they are biopolymers There are four main classes of biopolymers – lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids ...
... molecules necessary for life as we know it However, most of these complex molecules are actually made of smaller, simpler units – they are biopolymers There are four main classes of biopolymers – lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids ...
Alternative G-19
... nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] even if there are no changes. 2) Rank the 5 mutations you made to your own protein in order from the least aff ...
... nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] even if there are no changes. 2) Rank the 5 mutations you made to your own protein in order from the least aff ...
CARBOHYDRATE CHEMISTRY and MTABOLISM
... Carbohydrates containing 10 or more monosacchride units per molecule. • If the monosaccharide unit is of one-type, it is homopolysaccharide (both starch and glycogen are made of hundreds of glucose units, glucosans or glucans) . Dextrin, is similar to starch but of fewer glucosyl units, lower molecu ...
... Carbohydrates containing 10 or more monosacchride units per molecule. • If the monosaccharide unit is of one-type, it is homopolysaccharide (both starch and glycogen are made of hundreds of glucose units, glucosans or glucans) . Dextrin, is similar to starch but of fewer glucosyl units, lower molecu ...
Section II - School District 27J
... Write the letter of the most correct answer on your answer sheet. Do not write on this test. ...
... Write the letter of the most correct answer on your answer sheet. Do not write on this test. ...
Fermentation - mvhs
... Lactic Acid Fermentation • Occurs in certain fungi and bacteria, and humans • End products are lactate and NAD+ • Lactate is eventually converted back to pyruvate in the liver ...
... Lactic Acid Fermentation • Occurs in certain fungi and bacteria, and humans • End products are lactate and NAD+ • Lactate is eventually converted back to pyruvate in the liver ...
Honors Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide
... 4. Why is HFCS used in so many foods? What is it made of? What complaints have been blamed on HFCS? Are they justified? ...
... 4. Why is HFCS used in so many foods? What is it made of? What complaints have been blamed on HFCS? Are they justified? ...
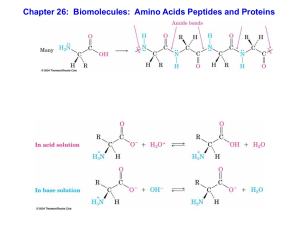
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
Fate of pyruvate
... Coenzymes of the complex are derived from water soluble vitamins: 1- Thiamine pyruphosphate, TPP (derived from thiamine, vitamin B1) 2- NAD+ (derived from niacin) 3- FAD (derived from riboflavin) 4- Lipoic acid 5- Coenzyme A (derived from pantothenic acid) ...
... Coenzymes of the complex are derived from water soluble vitamins: 1- Thiamine pyruphosphate, TPP (derived from thiamine, vitamin B1) 2- NAD+ (derived from niacin) 3- FAD (derived from riboflavin) 4- Lipoic acid 5- Coenzyme A (derived from pantothenic acid) ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... a. Equation for lactic acid fermentation-b. Equation for alcoholic fermentation-2. Compare lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation by describing what pyruvic acid is changed in to. Be sure to include what type of organism each one takes place in. In the absence of oxygen pyruvate (3 suga ...
... a. Equation for lactic acid fermentation-b. Equation for alcoholic fermentation-2. Compare lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation by describing what pyruvic acid is changed in to. Be sure to include what type of organism each one takes place in. In the absence of oxygen pyruvate (3 suga ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Citrate activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Fatty acyl-CoAs inhibit acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Hormones regulate ACC • Glucagon activates lipases/inhibits ACC • Insulin inhibits lipases/activates ACC ...
... • Citrate activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Fatty acyl-CoAs inhibit acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Hormones regulate ACC • Glucagon activates lipases/inhibits ACC • Insulin inhibits lipases/activates ACC ...
Chapter 16 (Part 3)
... • Citrate activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Fatty acyl-CoAs inhibit acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Hormones regulate ACC • Glucagon activates lipases/inhibits ACC • Insulin inhibits lipases/activates ACC ...
... • Citrate activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Fatty acyl-CoAs inhibit acetyl-CoA carboxylase • Hormones regulate ACC • Glucagon activates lipases/inhibits ACC • Insulin inhibits lipases/activates ACC ...
Classification of Enzymes - Lectures For UG-5
... • Every enzyme code consists of the letters "EC" followed by four numbers separated by periods. Those numbers represent a progressively finer classification of the enzyme. • For example, the tripeptide aminopeptidases have the code "EC 3.4.11.4", whose components indicate the following groups of ...
... • Every enzyme code consists of the letters "EC" followed by four numbers separated by periods. Those numbers represent a progressively finer classification of the enzyme. • For example, the tripeptide aminopeptidases have the code "EC 3.4.11.4", whose components indicate the following groups of ...
CELL RESPIRATION
... • Cells that contain mitochondria (Eukaryotes) normally carry out Aerobic Cell Respiration. • Pyruvate produced by Glycolysis enters the mitochondria and is catabolised by the Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. • The latter process requires the presence of free oxygen. ...
... • Cells that contain mitochondria (Eukaryotes) normally carry out Aerobic Cell Respiration. • Pyruvate produced by Glycolysis enters the mitochondria and is catabolised by the Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. • The latter process requires the presence of free oxygen. ...
Biosynthesis of Nucleotides 1 - University of Alabama at Birmingham
... – Begins with their metabolic precursors: amino acids, ribose-5-phosphate, and CO2 – The free bases A, T, G, C, and U are not intermediates – Appears to be present in identical form in nearly all living organisms ...
... – Begins with their metabolic precursors: amino acids, ribose-5-phosphate, and CO2 – The free bases A, T, G, C, and U are not intermediates – Appears to be present in identical form in nearly all living organisms ...
ACID - SchoolNotes
... slippery in water solution, turn red litmus to blue, and react with acids to form salts. • NEUTRAL - These are items that are neither acids or bases. There are 4 main ways to determine if a substance is and acid or a base. They are: Red litmus paper, Blue litmus paper, pH, and Red Cabbage Juice. ...
... slippery in water solution, turn red litmus to blue, and react with acids to form salts. • NEUTRAL - These are items that are neither acids or bases. There are 4 main ways to determine if a substance is and acid or a base. They are: Red litmus paper, Blue litmus paper, pH, and Red Cabbage Juice. ...
labmuscle
... energy demands this process is unavoidable. Nevertheless, there are factors that might prolong muscle fatigue and enable one to perform more diligently while exercising. When one works out the blood vessels in the muscle dilate and the blood flow rate increases because more oxygen is needed to quic ...
... energy demands this process is unavoidable. Nevertheless, there are factors that might prolong muscle fatigue and enable one to perform more diligently while exercising. When one works out the blood vessels in the muscle dilate and the blood flow rate increases because more oxygen is needed to quic ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.