Exam 4, 2015 - Biochemistry at CSU, Stanislaus
... allosteric modulation, reversible covalent modification, protein-protein binding. ...
... allosteric modulation, reversible covalent modification, protein-protein binding. ...
the PDF for the Organix Test
... Carnitine helps your body use fatty acids. ! If carnitine is sufficient long-chain fatty acids go through beta-oxidation in the mitochondria. ! If there are inadequate amounts of carnitine, the long-chain fatty acids will get processed outside of the mitochondria ! Adipate and suberate are by-pro ...
... Carnitine helps your body use fatty acids. ! If carnitine is sufficient long-chain fatty acids go through beta-oxidation in the mitochondria. ! If there are inadequate amounts of carnitine, the long-chain fatty acids will get processed outside of the mitochondria ! Adipate and suberate are by-pro ...
Enantioselective -Hydroxylation of 2-Arylacetic Acid Derivatives and r
... hydroxylates long-chain fatty acids at the ω-1, ω-2, and ω-3 positions at high rates.9 BM-3 has provided an evolvable protein framework for obtaining modified or new activities. Rational design and directed evolution approaches have created BM-3 variants with activity on medium-chain fatty acids,10 ...
... hydroxylates long-chain fatty acids at the ω-1, ω-2, and ω-3 positions at high rates.9 BM-3 has provided an evolvable protein framework for obtaining modified or new activities. Rational design and directed evolution approaches have created BM-3 variants with activity on medium-chain fatty acids,10 ...
Metabolism: Dissimilatory (energy, catabolic) metabolism
... Distinction rarely absolute: ”autrotrophs” may require organic growth factors (vitamins). Usually refers to carbon source for assimilatory metabolism (autotrophs depend on C-1 compounds, that is CO2 or CH4). Photoautotrophs use light as energy source Chemoautotrophs depend on the oxidation of inorga ...
... Distinction rarely absolute: ”autrotrophs” may require organic growth factors (vitamins). Usually refers to carbon source for assimilatory metabolism (autotrophs depend on C-1 compounds, that is CO2 or CH4). Photoautotrophs use light as energy source Chemoautotrophs depend on the oxidation of inorga ...
第八章
... *synthesis of phospholipids. *synthesis of lipoprotein. *synthesis of ketone body. *degradation of fatty acid. *degradation of phospholipids. *removal of phospholipids and cholesterol from blood. *lengthening and shortening of fatty acids. *saturating and desaturating of fatty acids. *control of dep ...
... *synthesis of phospholipids. *synthesis of lipoprotein. *synthesis of ketone body. *degradation of fatty acid. *degradation of phospholipids. *removal of phospholipids and cholesterol from blood. *lengthening and shortening of fatty acids. *saturating and desaturating of fatty acids. *control of dep ...
Biochemistry II Test 2Q
... Fatty acid synthase has ___ enzymes and is dimer that contains an ___________ protein. To produce 1 palmitate you need __ AceCoA and __ malonyl CoA thus releasing _____. To produce Malonyl CoA you need an ATP, thus how may ATP are needed in Palmitate synth? 2NADPH are needed per Malonyl, thus how mu ...
... Fatty acid synthase has ___ enzymes and is dimer that contains an ___________ protein. To produce 1 palmitate you need __ AceCoA and __ malonyl CoA thus releasing _____. To produce Malonyl CoA you need an ATP, thus how may ATP are needed in Palmitate synth? 2NADPH are needed per Malonyl, thus how mu ...
Exam 1 454 Study Guide
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
Quiz8ch8.doc
... equation come from __________ during reactions of __________. a. O2, glycolysis b. O2, the electron transport system c. O2, the Krebs cycle d. C6H112O6, glycolysis e. C6H12O6, the Krebs cycle ...
... equation come from __________ during reactions of __________. a. O2, glycolysis b. O2, the electron transport system c. O2, the Krebs cycle d. C6H112O6, glycolysis e. C6H12O6, the Krebs cycle ...
Cellular Respiration
... steps loses 2C in 2 steps and changes back to same 4C acid. First formed acid is Citric Acid and at the end 4C acid is regenerated – so the name Citric Acid Cycle. It was discovered by Hans Kreb. Overall Reaction of Citric Acid Cycle: Acety CoA (2C) + 3NAD + FAD + ADP 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + FADH2 + ATP ...
... steps loses 2C in 2 steps and changes back to same 4C acid. First formed acid is Citric Acid and at the end 4C acid is regenerated – so the name Citric Acid Cycle. It was discovered by Hans Kreb. Overall Reaction of Citric Acid Cycle: Acety CoA (2C) + 3NAD + FAD + ADP 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + FADH2 + ATP ...
Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your
... a. light energy can be harnessed to produce more energy by plants; as disorder increase within a system, more heat is released into the surroundings b. Catabolic and anabolic reactions increase the disorder of the universe; light energy can be transformed into chemical energy within large molecules ...
... a. light energy can be harnessed to produce more energy by plants; as disorder increase within a system, more heat is released into the surroundings b. Catabolic and anabolic reactions increase the disorder of the universe; light energy can be transformed into chemical energy within large molecules ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... • Fats are degraded into fatty acids and glycerol in the cytoplasm • -oxidation of fatty acids occurs in mitochondria ...
... • Fats are degraded into fatty acids and glycerol in the cytoplasm • -oxidation of fatty acids occurs in mitochondria ...
PracticeFinalSP2003
... 14. Triglyceride fats can be made (and indeed, your body does this) by reacting fatty acids with glycerol in a ester hydrolysis reaction similar to the ones you studied in lab. Draw a mechaism for this type of reaction to form a triglyceride fat. 15. Soaps are made from triglyceride fats, how is thi ...
... 14. Triglyceride fats can be made (and indeed, your body does this) by reacting fatty acids with glycerol in a ester hydrolysis reaction similar to the ones you studied in lab. Draw a mechaism for this type of reaction to form a triglyceride fat. 15. Soaps are made from triglyceride fats, how is thi ...
Ch.24Pt.4_000
... One glycerol formed for each TAG hydrolyzed. Enter bloodstream & go to liver or kidneys for processing. Converted in 2 steps to Dihydroxyacetone phosphate ...
... One glycerol formed for each TAG hydrolyzed. Enter bloodstream & go to liver or kidneys for processing. Converted in 2 steps to Dihydroxyacetone phosphate ...
chapter 6 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Harvest of Food Energy Student Misconceptions and Concerns 1. Some students might expect that fermentation produces alcohol and maybe even carbon dioxide. Care should be taken to clarify the different possible products of fermentation in muscle cells and alcoholic fermentatio ...
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Harvest of Food Energy Student Misconceptions and Concerns 1. Some students might expect that fermentation produces alcohol and maybe even carbon dioxide. Care should be taken to clarify the different possible products of fermentation in muscle cells and alcoholic fermentatio ...
Structure and properties of N,O - donor bicyclic derivatives
... Structure and properties of N,O-donor bicyclic derivatives of imidazoleacetic acid and their complexes with selected d-block metal ions In the last decades bicyclic imidazole derivatives had been gaining substantial interest both in the field of modern organic synthesis, as well as their potential a ...
... Structure and properties of N,O-donor bicyclic derivatives of imidazoleacetic acid and their complexes with selected d-block metal ions In the last decades bicyclic imidazole derivatives had been gaining substantial interest both in the field of modern organic synthesis, as well as their potential a ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Catabolic: break down compounds into smaller units; weight loss or wasting c. In general, balance exists between anabolism and catabolism ...
... Catabolic: break down compounds into smaller units; weight loss or wasting c. In general, balance exists between anabolism and catabolism ...
8.1 Condensation Polymers
... Each monomer in a condensation polymer must have at least two functional groups. LO: I know the structure of starch. ...
... Each monomer in a condensation polymer must have at least two functional groups. LO: I know the structure of starch. ...
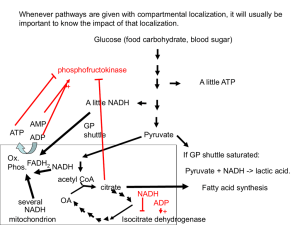
Slide 1
... Liver cells have a responsibility to support blood glucose levels by first releasing glucose from their internal glycogen stores, and if necessary synthesizing glucose from amino acids. They will shut down glycolysis and rely on other energy sources for their own needs under these conditions. Liver ...
... Liver cells have a responsibility to support blood glucose levels by first releasing glucose from their internal glycogen stores, and if necessary synthesizing glucose from amino acids. They will shut down glycolysis and rely on other energy sources for their own needs under these conditions. Liver ...
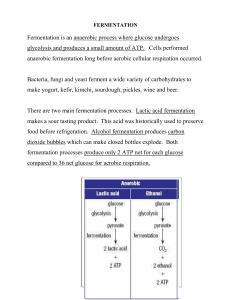
FERMENTATION
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
Additional Information on the Synthesis of Esters
... 3-Methyl-1-butanol (isoamyl alcohol) is an irritant. Avoid breathing vapors. Butyric acid is corrosive and toxic. Propionic acid is corrosive and toxic. Glacial acetic acid is poisonous if swallowed. Both the liquid and vapour are irritating to the skin and eyes and can cause burns and ulcers. Flamm ...
... 3-Methyl-1-butanol (isoamyl alcohol) is an irritant. Avoid breathing vapors. Butyric acid is corrosive and toxic. Propionic acid is corrosive and toxic. Glacial acetic acid is poisonous if swallowed. Both the liquid and vapour are irritating to the skin and eyes and can cause burns and ulcers. Flamm ...
chapter3_part2
... C A peptide bond forms between the alanine and leucine. Tryptophan (trp) will be next. The chain is starting to twist and fold as atoms swivel around some bonds and attract or ...
... C A peptide bond forms between the alanine and leucine. Tryptophan (trp) will be next. The chain is starting to twist and fold as atoms swivel around some bonds and attract or ...
Cellular Respiration
... time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane H+ build up in the intermembrane space, making it ...
... time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane H+ build up in the intermembrane space, making it ...
MMG 301, Lecture 19 Fermentation
... (-917 kJ/mol)(-182 kJ/mol)(-394 kJ/mol) ∆Go’ = ∆Gof (products) - ∆Gof (subtrates) [2(-182) + 2(-394)] – (-917) = -235 kJ/mol What about ATP? ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi Pi + ADP → ATP + H2O ...
... (-917 kJ/mol)(-182 kJ/mol)(-394 kJ/mol) ∆Go’ = ∆Gof (products) - ∆Gof (subtrates) [2(-182) + 2(-394)] – (-917) = -235 kJ/mol What about ATP? ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi Pi + ADP → ATP + H2O ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.