AS Biology - TavistockCollegeScience
... Animal fats have a higher melting point and are generally solid at room temperature due to saturated fatty acids ...
... Animal fats have a higher melting point and are generally solid at room temperature due to saturated fatty acids ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... However, do not use the blank sheet for your final answers. If you need more space, use the back of pages 2-12. Write your name on top of each page! Petitions for re-grading will be considered only if you have used permanent ink, unless an addition error has occurred. ...
... However, do not use the blank sheet for your final answers. If you need more space, use the back of pages 2-12. Write your name on top of each page! Petitions for re-grading will be considered only if you have used permanent ink, unless an addition error has occurred. ...
High Alcohol Fermentations: How to Manage Primary and
... What to Know Before Restarting a Stuck Alcoholic Fermentation ...
... What to Know Before Restarting a Stuck Alcoholic Fermentation ...
Lipid Metabolism
... resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP. Because one triglyceride molecule yields three fatty acid molecules with as much as 1 ...
... resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP. Because one triglyceride molecule yields three fatty acid molecules with as much as 1 ...
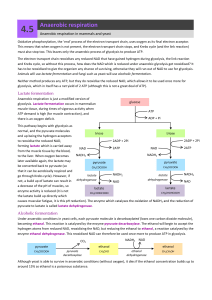
Anaerobic respiration
... Oxidative phosphorylation, the ‘end’ process of the electron transport chain, uses oxygen as its final electron acceptor. This means that when oxygen is not present, the electron transport chain stops, and Krebs cycle (and the link reaction) must also stop too. This leaves only the anaerobic process ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation, the ‘end’ process of the electron transport chain, uses oxygen as its final electron acceptor. This means that when oxygen is not present, the electron transport chain stops, and Krebs cycle (and the link reaction) must also stop too. This leaves only the anaerobic process ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... What is the biochemical reason for the different end products in the two tissues? (2 pts) Glucose-6-P phosphatase in the liver produces glucose from G6P, an intermediate of glycogen degradation. However, this enzyme (G6P phosphatase) is not present in skeletal muscles. Therefore, in skeletal muscles ...
... What is the biochemical reason for the different end products in the two tissues? (2 pts) Glucose-6-P phosphatase in the liver produces glucose from G6P, an intermediate of glycogen degradation. However, this enzyme (G6P phosphatase) is not present in skeletal muscles. Therefore, in skeletal muscles ...
lecture5
... referred to as lipolysis. The lipase of adipose tissue are activated on treatment of these cells with the hormones epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. In adipose cells, these hormones trigger 7TM receptors that activate adenylate cyclase (Section 15.1.3 ). The inc ...
... referred to as lipolysis. The lipase of adipose tissue are activated on treatment of these cells with the hormones epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. In adipose cells, these hormones trigger 7TM receptors that activate adenylate cyclase (Section 15.1.3 ). The inc ...
LESSON 2.5 WORKBOOK Blood glucose in sleep, a 5 mile
... **Exercise can act like insulin The act of using your muscles can trigger a response that is similar to the effects of insulin. We previously learned that insulin tells the liver to store extra energy. Insulin also has an important role in the muscles: to bring glucose into the cells so that it can ...
... **Exercise can act like insulin The act of using your muscles can trigger a response that is similar to the effects of insulin. We previously learned that insulin tells the liver to store extra energy. Insulin also has an important role in the muscles: to bring glucose into the cells so that it can ...
Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates
... All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an energy source. Proteins form part of a ...
... All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an energy source. Proteins form part of a ...
Lecture: Fatty Acids Synthesis Recall the physiological role of
... Recall triglyceride degradation in adipose tissue by hormone sensitive lipase, and identify the hormone that regulates the hormone sensitive lipase. o During fasting, adipose TG broken down (lipolysis) o Lipases cleave FAs from TG: hormone sensitive lipase starts process Signaled by decreasing ins ...
... Recall triglyceride degradation in adipose tissue by hormone sensitive lipase, and identify the hormone that regulates the hormone sensitive lipase. o During fasting, adipose TG broken down (lipolysis) o Lipases cleave FAs from TG: hormone sensitive lipase starts process Signaled by decreasing ins ...
Presentation
... glucose to pyruvate is much higher than under aerobic conditions (yeast cells produce more ethanol and muscle cells accumulate lactate) • The Pasteur Effect is the slowing of glycolysis in the presence of oxygen • More ATP is produced under aerobic conditions than under anaerobic conditions, therefo ...
... glucose to pyruvate is much higher than under aerobic conditions (yeast cells produce more ethanol and muscle cells accumulate lactate) • The Pasteur Effect is the slowing of glycolysis in the presence of oxygen • More ATP is produced under aerobic conditions than under anaerobic conditions, therefo ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... (aka Citric Acid Cycle, Krebs Cycle) • Pyruvate (actually acetate) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 • Some ATP is produced • More NADH is made • NADH goes on to make more ATP in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation ...
... (aka Citric Acid Cycle, Krebs Cycle) • Pyruvate (actually acetate) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 • Some ATP is produced • More NADH is made • NADH goes on to make more ATP in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • Glycolysis is the only process that can function • The NAD that has been reduced (Hydrogen added) has to be re-oxidised (Hydrogen removed) so that it can keep accepting Hydrogens in glycolysis • There are two ways that NAD can be reoxidised • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use ...
... • Glycolysis is the only process that can function • The NAD that has been reduced (Hydrogen added) has to be re-oxidised (Hydrogen removed) so that it can keep accepting Hydrogens in glycolysis • There are two ways that NAD can be reoxidised • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use ...
Document
... (from oxaloacetate), which crosses the membrane and gives them back to NAD to generate NADH (and oxaloacetate). Oxaloacetate is converted into aspartate, which crosses back to the cytosol and is metabolized to oxaloacetate to begin the process all over again. [Students may get this confused or mixed ...
... (from oxaloacetate), which crosses the membrane and gives them back to NAD to generate NADH (and oxaloacetate). Oxaloacetate is converted into aspartate, which crosses back to the cytosol and is metabolized to oxaloacetate to begin the process all over again. [Students may get this confused or mixed ...
Energy Metabolism - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... illustrated by the speed with which aerobic cells, tissues, and organisms die if deprived of oxygen! An even more striking example is given by the elite marathon runner who, it has been calculated, uses a colossal 60kg of ATP during a race12. Moreover, an increase in the steady state level of ATP co ...
... illustrated by the speed with which aerobic cells, tissues, and organisms die if deprived of oxygen! An even more striking example is given by the elite marathon runner who, it has been calculated, uses a colossal 60kg of ATP during a race12. Moreover, an increase in the steady state level of ATP co ...
Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain
... • Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane • allows H+ gradient to rush through using energy to make ATP ADP + P ATP ATP Conversions • 1 cytosolic NADH = 2 ATP • 1 mitochondrial NADH = 3 ATP • 1 mitochondrial FADH = 2 ATP Net ATP from 1 Glucose • 2 ATP (G) • 2 NADH2 (G) = 2 FADH2 (transport) • 2N ...
... • Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane • allows H+ gradient to rush through using energy to make ATP ADP + P ATP ATP Conversions • 1 cytosolic NADH = 2 ATP • 1 mitochondrial NADH = 3 ATP • 1 mitochondrial FADH = 2 ATP Net ATP from 1 Glucose • 2 ATP (G) • 2 NADH2 (G) = 2 FADH2 (transport) • 2N ...
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Ceramide and
... Measurement of free fatty acid and glycerol Assessment of fatty acid is through a coupled reaction involving acyl-CoA synthetase and acyl-CoA oxidase by measuring optical density at 540-550nm (Zenbio, NC). Detection of free glycerol involves phosphorylation to glycerol phosphate, which is oxidized b ...
... Measurement of free fatty acid and glycerol Assessment of fatty acid is through a coupled reaction involving acyl-CoA synthetase and acyl-CoA oxidase by measuring optical density at 540-550nm (Zenbio, NC). Detection of free glycerol involves phosphorylation to glycerol phosphate, which is oxidized b ...
CHAPTER 6
... • Energy transduction and energy storage in the adenylate system – ATP, ADP, and AMP – lie at the very heart of metabolism – The regulation of metabolism by adenylates in turn requires close control of the relative concentrations of ATP, ADP, and AMP – ATP, ADP, and AMP are all important effectors i ...
... • Energy transduction and energy storage in the adenylate system – ATP, ADP, and AMP – lie at the very heart of metabolism – The regulation of metabolism by adenylates in turn requires close control of the relative concentrations of ATP, ADP, and AMP – ATP, ADP, and AMP are all important effectors i ...
2. Microbial Growth Kinetics
... Conversion of ethanol to acetic acid, sorbitol to sorbose, synthesis of steroid hormones and certain amino acids Structurally related compounds in one or few enzymatic reactions Can use resting cells, spores or even killed cells. Mixed cultures can also be used, use of immobilized cells at low cost ...
... Conversion of ethanol to acetic acid, sorbitol to sorbose, synthesis of steroid hormones and certain amino acids Structurally related compounds in one or few enzymatic reactions Can use resting cells, spores or even killed cells. Mixed cultures can also be used, use of immobilized cells at low cost ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... process when no oxygen is consumed or no change in the concentration of NAD+ or NADH during energy extraction. ...
... process when no oxygen is consumed or no change in the concentration of NAD+ or NADH during energy extraction. ...
AMINO ACID DEGRADATION
... acetyl CoA are called KETOGENIC AMINO ACIDS because they can be converted into ketone bodies. The amino acids that are converted in the remaining of the seven molecules are called GLUCOGENIC AMINO ACIDS becaause they can be converted into phosphoenol pyruvate and then in glucose. • Some amino acids ...
... acetyl CoA are called KETOGENIC AMINO ACIDS because they can be converted into ketone bodies. The amino acids that are converted in the remaining of the seven molecules are called GLUCOGENIC AMINO ACIDS becaause they can be converted into phosphoenol pyruvate and then in glucose. • Some amino acids ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... To calculate the energy released by lipid breakdown, there are two steps. Step One: beta-oxidation step that converts a long chain of carbons into a series of acetyl-CoA The oxidation of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules requires the breaking of bonds, always one less bond that the number of ac ...
... To calculate the energy released by lipid breakdown, there are two steps. Step One: beta-oxidation step that converts a long chain of carbons into a series of acetyl-CoA The oxidation of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules requires the breaking of bonds, always one less bond that the number of ac ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.