Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of
... a. When necessary to exceed the octet rule for one of several third row elements, assume that the extra electrons be placed on the central atom 8.12 Resonance A. Nitrate ion 1. Experiments show that all N-O bonds are equal 2. A single Lewis structure cannot represent the nitrate ion 3. A resonance s ...
... a. When necessary to exceed the octet rule for one of several third row elements, assume that the extra electrons be placed on the central atom 8.12 Resonance A. Nitrate ion 1. Experiments show that all N-O bonds are equal 2. A single Lewis structure cannot represent the nitrate ion 3. A resonance s ...
AP Unit 1 Test Review
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 6: Quantum mechanics and spectroscopy
... p = mv Prediction: particles (electrons, neutrons, etc.) should diffract like light under appropriate conditions ...
... p = mv Prediction: particles (electrons, neutrons, etc.) should diffract like light under appropriate conditions ...
Double-Slit Experiment
... Curved (accelerated) motion means that electron should do what? = ASSUMPTIONS BASED IN CLASSICAL PHYSICS!!! Quantum physics: ...
... Curved (accelerated) motion means that electron should do what? = ASSUMPTIONS BASED IN CLASSICAL PHYSICS!!! Quantum physics: ...
Document
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
2A Final Exam Review Worksheet
... o Temperature is proportional to kinetic energy. Two molecules at the same temperature will have the same average kinetic energy. o If two molecules are under the same conditions, the heavier molecule will travel slower ...
... o Temperature is proportional to kinetic energy. Two molecules at the same temperature will have the same average kinetic energy. o If two molecules are under the same conditions, the heavier molecule will travel slower ...
CHM134 General Chemistry I Semester Review – Dr. Steel This list
... 10. What is the mass percent of fluorine in PF5? 11. Balance this equation: C3H8 + O2 Æ CO2 + H2O. What is the coefficient of O2? 12. Calculate the number of molecules in 2.50 grams of CO2. 13. Calculate the mass of 8.60×1024 atoms of Neon, Ne. 14. Balance the equation: P4O10 + H2O Æ H3PO4. How many ...
... 10. What is the mass percent of fluorine in PF5? 11. Balance this equation: C3H8 + O2 Æ CO2 + H2O. What is the coefficient of O2? 12. Calculate the number of molecules in 2.50 grams of CO2. 13. Calculate the mass of 8.60×1024 atoms of Neon, Ne. 14. Balance the equation: P4O10 + H2O Æ H3PO4. How many ...
Modern Physics Important Concepts for AP Test
... When electron jumps back to a lower level it emits a photon of energy, ΔE. The wavelength is found using ΔE = hf. (Another commonly asked problem on AP test.) o Quantum Numbers The allowed orbital states for an electron in all atoms are specified by 4 quantum numbers. Pauli Exclusion Principle ...
... When electron jumps back to a lower level it emits a photon of energy, ΔE. The wavelength is found using ΔE = hf. (Another commonly asked problem on AP test.) o Quantum Numbers The allowed orbital states for an electron in all atoms are specified by 4 quantum numbers. Pauli Exclusion Principle ...
final exam practice test - Clayton State University
... 35. Consider the following atoms and ions: Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2, O, O2-, F, F- Which ones of the following groups includes only isoelectronic species? a.) Na, Mg, O, F b.) Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2 c.) O, O-2, F, F-1 d.) Na+, Mg+2, O-2, Fe.) none of these 36. Arrange the following set of ions in order of incr ...
... 35. Consider the following atoms and ions: Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2, O, O2-, F, F- Which ones of the following groups includes only isoelectronic species? a.) Na, Mg, O, F b.) Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2 c.) O, O-2, F, F-1 d.) Na+, Mg+2, O-2, Fe.) none of these 36. Arrange the following set of ions in order of incr ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
Vocabulary Notes
... The rule that atoms are most stable when there is a filled outer shell configuration. 8 electrons consist of a filled shell. This is the outer shell configuration of noble gases which are very stable. ...
... The rule that atoms are most stable when there is a filled outer shell configuration. 8 electrons consist of a filled shell. This is the outer shell configuration of noble gases which are very stable. ...
CHEMISTRY – UNITS 3 and 4 REVIEW PACKET Name Date
... 4) What is the word that describes two atoms that have the same # of protons but different numbers of neutrons? _____________________________ 5) Are these pictures an example of isotopes? ____________________________ VALENCE ELECTRONS / ELECTRON SHELL DIAGRAMS / LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS What is a valence ...
... 4) What is the word that describes two atoms that have the same # of protons but different numbers of neutrons? _____________________________ 5) Are these pictures an example of isotopes? ____________________________ VALENCE ELECTRONS / ELECTRON SHELL DIAGRAMS / LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS What is a valence ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms.
... Section. 6.8 Electron Configurations. The way in which the electrons are distributed among the various orbitals of the atom is know as the electron configuration. The orbitals are filled in order of increasing energy, two electrons of opposite spin per orbital. This is known as an orbital diagram: ...
... Section. 6.8 Electron Configurations. The way in which the electrons are distributed among the various orbitals of the atom is know as the electron configuration. The orbitals are filled in order of increasing energy, two electrons of opposite spin per orbital. This is known as an orbital diagram: ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... • Dry ice subliming into Carbon dioxide • Salt or sugar dissolving in water ...
... • Dry ice subliming into Carbon dioxide • Salt or sugar dissolving in water ...
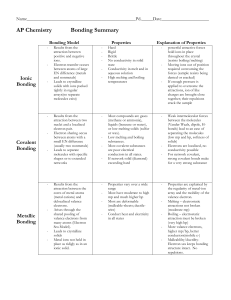
Types of Bonding Summary
... hold ions in place throughout the crystal (resists boiling/melting) Moving ions out of position required overcoming the forces (sample resists being dented or cracked) If enough pressure is applied to overcome the attractions, ion of like charges are brought close together; their repulsions crack th ...
... hold ions in place throughout the crystal (resists boiling/melting) Moving ions out of position required overcoming the forces (sample resists being dented or cracked) If enough pressure is applied to overcome the attractions, ion of like charges are brought close together; their repulsions crack th ...
Module 8 - Brookville Local Schools
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
Chapter 8 - Chemistry
... - energy depends primarily on n, increasing with its value - energies of orbitals with same n increase with the l quantum number - that is, 3p orbital has slightly greater energy than 3s orbital - exception: when subshells have nearly same energy, building- up order is not strictly determined by ord ...
... - energy depends primarily on n, increasing with its value - energies of orbitals with same n increase with the l quantum number - that is, 3p orbital has slightly greater energy than 3s orbital - exception: when subshells have nearly same energy, building- up order is not strictly determined by ord ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.