Unit 16 Worksheet - Jensen Chemistry
... 1. When do electrons release photons(packets of energy)? When the electrons: a. move to higher levels of energy b. return to their original energy level c increase orbital speed around the nucleus d. are released by the atom 2. Helium was discovered on the sun in 1868, almost 30 years before it was ...
... 1. When do electrons release photons(packets of energy)? When the electrons: a. move to higher levels of energy b. return to their original energy level c increase orbital speed around the nucleus d. are released by the atom 2. Helium was discovered on the sun in 1868, almost 30 years before it was ...
3.3 Why do atoms radiate light?
... description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady change in the dipole moment. • Each state, which is not an Eigenstate of the Hamiltonian has a non infin ...
... description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady change in the dipole moment. • Each state, which is not an Eigenstate of the Hamiltonian has a non infin ...
Chapter 5: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The
... Analyzing the light given off by H2 gas in a discharge tube. ...
... Analyzing the light given off by H2 gas in a discharge tube. ...
Chem1101 – Semester 1
... Recognise the consequences of Hund’s rule on the detailed electronic configuration of an atom Having one electron in each p-‐orbital will keep the electrons as far from each other as possible to accoun ...
... Recognise the consequences of Hund’s rule on the detailed electronic configuration of an atom Having one electron in each p-‐orbital will keep the electrons as far from each other as possible to accoun ...
Physics 30 Lesson 34 – Quantum Mechanics
... To summarise, a shell is a group of states that have the same principal quantum number. A subshell is a smaller group of states that has both the same value of n and l. An orbital is specified by the three quantum numbers n, l and ml, and it can contain two electrons; one spin-up, one spin-down. And ...
... To summarise, a shell is a group of states that have the same principal quantum number. A subshell is a smaller group of states that has both the same value of n and l. An orbital is specified by the three quantum numbers n, l and ml, and it can contain two electrons; one spin-up, one spin-down. And ...
Chapter 7 NotesAA
... Electrons coming from excited to ground state which gives off a photon of light (h) ...
... Electrons coming from excited to ground state which gives off a photon of light (h) ...
POWERPOINT JEOPARDY
... Write the equation relating the speed of light with frequency and wavelength. Write the equation relating energy and frequency. Label the variables in each. The speed of light always equals ____________. Answer questions #11-14 on p. 157. Which has more energy, a radio wave or a gamma ray? ...
... Write the equation relating the speed of light with frequency and wavelength. Write the equation relating energy and frequency. Label the variables in each. The speed of light always equals ____________. Answer questions #11-14 on p. 157. Which has more energy, a radio wave or a gamma ray? ...
Untitled - Washington County Schools
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
Chapter 7(Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Introduction to Atomic
... Bohr model was built on classical Newtonian mechanics -- a new kind of mecha nics was developed to treat small particles like electrons that traveled at high speeds approaching the speed of light … From Bohr to Schrödinger … Quantum Mechanics (QM) … QM treated electrons like waves of energy instead ...
... Bohr model was built on classical Newtonian mechanics -- a new kind of mecha nics was developed to treat small particles like electrons that traveled at high speeds approaching the speed of light … From Bohr to Schrödinger … Quantum Mechanics (QM) … QM treated electrons like waves of energy instead ...
homework answers - SPHS Devil Physics
... f. What is this pattern of black lines called? g. What is the Balmer formula for the wavelengths in the hydrogen spectra? ...
... f. What is this pattern of black lines called? g. What is the Balmer formula for the wavelengths in the hydrogen spectra? ...
Quantum Theory of the Atom
... absorb enough energy, they become “excited”. In this state it is actually the electrons that become excited. When these electrons release this energy to go back down to “ground” state, they release it in the form of radiation (light). Each element will display a particular emission spectrum, so ...
... absorb enough energy, they become “excited”. In this state it is actually the electrons that become excited. When these electrons release this energy to go back down to “ground” state, they release it in the form of radiation (light). Each element will display a particular emission spectrum, so ...
lecture slides of chap8
... When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always removed first from the ns orbital and then from the (n – 1)d orbitals. ...
... When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always removed first from the ns orbital and then from the (n – 1)d orbitals. ...
III. Quantum Model of the Atom
... • Relative Size of the orbital • n = # of sublevels in that energy level • n2 = # of orbitals in the energy level • 2n2 = total # of electrons in that energy level ...
... • Relative Size of the orbital • n = # of sublevels in that energy level • n2 = # of orbitals in the energy level • 2n2 = total # of electrons in that energy level ...
AP Review – Life and Chemistry Name: Date: ___B_ 1. The atomic
... ___B__ 2. Which of the following statements concerning electrons is not correct? a. b. c. d. ...
... ___B__ 2. Which of the following statements concerning electrons is not correct? a. b. c. d. ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... - A chemical bond exists between two atoms or group of atoms when the force acting between them lead to the formation of stable aggregate. - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quant ...
... - A chemical bond exists between two atoms or group of atoms when the force acting between them lead to the formation of stable aggregate. - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quant ...
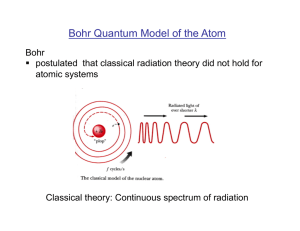
Bohr Quantum Model of the Atom
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
File
... TUESDAY: Atoms, Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures (worth 33 percent) True or False: Identify if the following statements are true or false. 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two ...
... TUESDAY: Atoms, Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures (worth 33 percent) True or False: Identify if the following statements are true or false. 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.