Matter: a Material World
... • How can we use spectra to determine the composition of a distant object? • How can we use spectra to determine the temperature of distant objects? • How can we use spectra to tell us how fast something is moving? ...
... • How can we use spectra to determine the composition of a distant object? • How can we use spectra to determine the temperature of distant objects? • How can we use spectra to tell us how fast something is moving? ...
Chapter 6
... Symbolized by ms Indicates the fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital Values are + ½ and -1/2 ...
... Symbolized by ms Indicates the fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital Values are + ½ and -1/2 ...
Structure of atoms and solids
... their atoms. We shall see how quantum theory of the atom can be extended to account for the electrical properties of solids and how this has led to the computer, mobile phones and the internet revolution now happening. The basic building blocks (computer chips, microchips, microprocessors, etc) perf ...
... their atoms. We shall see how quantum theory of the atom can be extended to account for the electrical properties of solids and how this has led to the computer, mobile phones and the internet revolution now happening. The basic building blocks (computer chips, microchips, microprocessors, etc) perf ...
Atomic Structure - Winona State University
... White light can be separated into a continuous spectrum of colors. Note that there are no dark spots on the continuous spectrum that would correspond to different lines. ...
... White light can be separated into a continuous spectrum of colors. Note that there are no dark spots on the continuous spectrum that would correspond to different lines. ...
LEWIS DOT STRUCTURES , MOLECULAR SHAPES, AND
... 1. Determine the type and number of atoms present in the molecule 2. Determine the number of valence electrons each atom will supply (you may wish to draw the electron dot diagram for that atom) If you are asked to do the structure of a polyatomic ion: add to the total number of electrons if the ion ...
... 1. Determine the type and number of atoms present in the molecule 2. Determine the number of valence electrons each atom will supply (you may wish to draw the electron dot diagram for that atom) If you are asked to do the structure of a polyatomic ion: add to the total number of electrons if the ion ...
2013.9.23
... Si Conduction-Band Structure in wave vector k-space (Constant-Energy Surfaces in k-space)Effective mass approximation: Kinetic energy ...
... Si Conduction-Band Structure in wave vector k-space (Constant-Energy Surfaces in k-space)Effective mass approximation: Kinetic energy ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 17. State the Variation Theorem and prove it with a suitable example. ...
... 17. State the Variation Theorem and prove it with a suitable example. ...
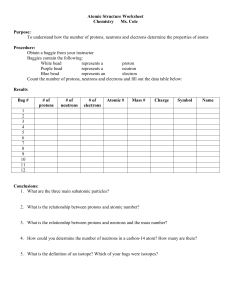
Atomic Structure Mini Lab
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Chapter 9 – Many Electron Atoms
... The exchange interaction is the reason that if orbitals are degenerate, it is preferable to align spins parallel. It maximizes the number of “ -‐ k ab ” like-‐spin contributions. See Hund’s rules for ...
... The exchange interaction is the reason that if orbitals are degenerate, it is preferable to align spins parallel. It maximizes the number of “ -‐ k ab ” like-‐spin contributions. See Hund’s rules for ...
Eighth Grade Review - PAMS-Doyle
... have the original element in any form. Now you have a different element! ...
... have the original element in any form. Now you have a different element! ...
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... there are. THE SPIN QUANTUM NUMBER. ms The SPIN QUANTUM NUMBER, ms, represents electron spin. Since there are only two possible spins —- clockwise and counterclockwise — for an electron, ms can have two values: ─½ or +½. The spin quantum number led to the PAULI'S EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE. In a given atom ...
... there are. THE SPIN QUANTUM NUMBER. ms The SPIN QUANTUM NUMBER, ms, represents electron spin. Since there are only two possible spins —- clockwise and counterclockwise — for an electron, ms can have two values: ─½ or +½. The spin quantum number led to the PAULI'S EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE. In a given atom ...
Electron Configuration (You will have to read this more than once to
... just like a 3-D Cartesian Coordinate system. Do that 3 times. And on each one put a p-orbital that is going either up and down, left to right, or front and back. Label them 2px, 2py and 2pz. Depending on which axis they are on. ...
... just like a 3-D Cartesian Coordinate system. Do that 3 times. And on each one put a p-orbital that is going either up and down, left to right, or front and back. Label them 2px, 2py and 2pz. Depending on which axis they are on. ...
Chapter 2
... b) is found only in molecules containing oxygen c) shares electrons equally between atoms d) ionizes e) has shared electrons pulled closer to the more electronegative atom 15. When the proton number and electron number are unequal, the atom or molecule _____. (Concept 2.3 ) a) forms a covalent bond ...
... b) is found only in molecules containing oxygen c) shares electrons equally between atoms d) ionizes e) has shared electrons pulled closer to the more electronegative atom 15. When the proton number and electron number are unequal, the atom or molecule _____. (Concept 2.3 ) a) forms a covalent bond ...
Chapter 4 - Tolland High School
... Energy States of Atoms/Electrons • Ground State- lowest energy level of an electron within an atom • Excited State- a higher energy level within an atom that an electron may exist in – Energy must be absorbed for an electron to go from ground to excited state – Energy is given off as visible light ...
... Energy States of Atoms/Electrons • Ground State- lowest energy level of an electron within an atom • Excited State- a higher energy level within an atom that an electron may exist in – Energy must be absorbed for an electron to go from ground to excited state – Energy is given off as visible light ...
n = 2. - Cloudfront.net
... wave of single-frequency light is produced. As intensity increases, photons pass through a partially reflective end in intense pulses of coherent red light. ...
... wave of single-frequency light is produced. As intensity increases, photons pass through a partially reflective end in intense pulses of coherent red light. ...
1. Define each of the following terms: a.Alkaline earth metals
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
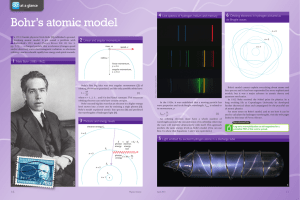
Bohr`s atomic model
... n 1913 Danish physicist Niels Bohr (1) published a groundbreaking atomic model. It got round a problem with Rutherford’s 1911 model (P HYSICS R EVIEW Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 2–5) — a charged particle that accelerates (changes speed and/or direction) emits electromagnetic radiation, so electrons orbitin ...
... n 1913 Danish physicist Niels Bohr (1) published a groundbreaking atomic model. It got round a problem with Rutherford’s 1911 model (P HYSICS R EVIEW Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 2–5) — a charged particle that accelerates (changes speed and/or direction) emits electromagnetic radiation, so electrons orbitin ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... - If a new alkaline earth were created, its ato number would most probably be (9) . ...
... - If a new alkaline earth were created, its ato number would most probably be (9) . ...
Problem set #1 - U.C.C. Physics Department
... 4) Let us assume that a light bulb emits a monochromatic yellow light, at wavelength λ = 600 nm. You are standing 3 meters away from a 60 W light bulb, and looks at it. Calculate the number of photons that enter your eyes each second. You can assume that the light bulb’s emission is spherical, and t ...
... 4) Let us assume that a light bulb emits a monochromatic yellow light, at wavelength λ = 600 nm. You are standing 3 meters away from a 60 W light bulb, and looks at it. Calculate the number of photons that enter your eyes each second. You can assume that the light bulb’s emission is spherical, and t ...
The Periodic Table
... the core of an atom, called the nucleus The number of protons and neutrons add together to give the mass of the atom – each is designated a mass of 1 amu ...
... the core of an atom, called the nucleus The number of protons and neutrons add together to give the mass of the atom – each is designated a mass of 1 amu ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.