Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Multivalent: some transition metals have more than one charge. Roman numerals are used after the metal name to indicate which ion was used Ex. 1 What is the formula manganese(III) sulphide? This manganese is Mn3+ Sulphur is S2– Lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is 6 2 Mn3+ ions and 3 S2– i ...
... Multivalent: some transition metals have more than one charge. Roman numerals are used after the metal name to indicate which ion was used Ex. 1 What is the formula manganese(III) sulphide? This manganese is Mn3+ Sulphur is S2– Lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is 6 2 Mn3+ ions and 3 S2– i ...
Periodic Table
... protons) will appear at the __________ • The mass number (number of protons plus neutrons will appear at the __________ • The element symbol will appear to the __________ • The different number of neutrons has NO bearing on chemical reactivity ...
... protons) will appear at the __________ • The mass number (number of protons plus neutrons will appear at the __________ • The element symbol will appear to the __________ • The different number of neutrons has NO bearing on chemical reactivity ...
Chapter 7. The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom 100
... Use de Broglie’s relation to interconvert wavelength, mass, and velocity. Know the complementarity of position and velocity through Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Know the similarities and differences in classica ...
... Use de Broglie’s relation to interconvert wavelength, mass, and velocity. Know the complementarity of position and velocity through Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Know the similarities and differences in classica ...
Chemistry Outcomes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... properties for a missing element of hypothetical element of the same family. Distinguish between atoms and ions (cations and anions and their formation) ...
... properties for a missing element of hypothetical element of the same family. Distinguish between atoms and ions (cations and anions and their formation) ...
Activity 17 Follow-up
... very reactive. When the sodium reacts with the water it takes the place of one of the hydrogen atoms. This happens because sodium is more reactive than the hydrogen it is replacing. Reactivity is largely due to the atomic radius of an element and the valence. Larger metals lose their outer electrons ...
... very reactive. When the sodium reacts with the water it takes the place of one of the hydrogen atoms. This happens because sodium is more reactive than the hydrogen it is replacing. Reactivity is largely due to the atomic radius of an element and the valence. Larger metals lose their outer electrons ...
stable structure - Rothschild Science
... Octet rule- atoms in compounds tend to have the electron configuration of ...
... Octet rule- atoms in compounds tend to have the electron configuration of ...
Electrons in Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle ...
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle ...
1,0-,1,2 + ½
... To Write Ground State Electron Configurations… 1. Lowest energy is the most stable 2. 3 principals or rules to follow—Pauli Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle, and Hund’s Rule ...
... To Write Ground State Electron Configurations… 1. Lowest energy is the most stable 2. 3 principals or rules to follow—Pauli Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle, and Hund’s Rule ...
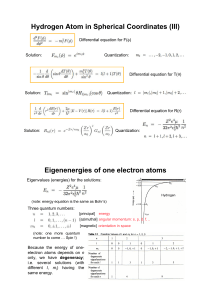
Hydrogen Atom in Spherical Coordinates (III) Eigenenergies of one
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
Problem Set 11: Chemistry Graduate Quantum I Physics 6572
... (Hint: the main feature of this plot will be that larger A have larger nuclear masses.) The semi-empirical mass formula treats the nucleus primarily as a drop of liquid, with a ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucl ...
... (Hint: the main feature of this plot will be that larger A have larger nuclear masses.) The semi-empirical mass formula treats the nucleus primarily as a drop of liquid, with a ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucl ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Quantum
... l=0 → spherical shape with nucles at the center → s orbital for H atom's ground state → the electron probability density is highest at the nucleus (Fig. 7.17A) Fig. 7.17B → Because the 2s orbital is larger than the 1s, an electron in 2s spend more time farther from the nucleus than when it occupies ...
... l=0 → spherical shape with nucles at the center → s orbital for H atom's ground state → the electron probability density is highest at the nucleus (Fig. 7.17A) Fig. 7.17B → Because the 2s orbital is larger than the 1s, an electron in 2s spend more time farther from the nucleus than when it occupies ...
chapt02_lecture from text
... Electron arrangement • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can co ...
... Electron arrangement • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can co ...
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms 1 Section 5.1: Light and Quantized
... All orbitals related to an energy sublevel have equal energy (ex. all three 2p orbitals have equal energy) Energy sublevels within a principal energy level have different energies (ex. three 2 p orbitals have higher energy than the 2s orbital) o energy increases as the level changes In order of incr ...
... All orbitals related to an energy sublevel have equal energy (ex. all three 2p orbitals have equal energy) Energy sublevels within a principal energy level have different energies (ex. three 2 p orbitals have higher energy than the 2s orbital) o energy increases as the level changes In order of incr ...
Topic 3.1: Chemical Elements and Water
... 96% of living matter ( Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen,and Nitrogen). The rest are called trace elements. These are required in minute amounts( Zinc, Cobalt, Iron, Magnesium). Molecules: Two or more different atoms combined. Atomic Number: The total number of protons or electrons in an atom. Atomic Mass: T ...
... 96% of living matter ( Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen,and Nitrogen). The rest are called trace elements. These are required in minute amounts( Zinc, Cobalt, Iron, Magnesium). Molecules: Two or more different atoms combined. Atomic Number: The total number of protons or electrons in an atom. Atomic Mass: T ...
Name: Date: Chemistry Enriched Per. ______ Midterm Review
... split the logs and let them “season” (dry out) for at least 6 months. You then burn the firewood in your highly efficient, “clean” burning wood stove. Describe the chemical and physical processes taking place…and describe how you know the difference… ...
... split the logs and let them “season” (dry out) for at least 6 months. You then burn the firewood in your highly efficient, “clean” burning wood stove. Describe the chemical and physical processes taking place…and describe how you know the difference… ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.