Chemistry 11 – Course Outcomes
... for a missing element of hypothetical element of the same family. Distinguish between atoms and ions (cations and anions and their formation) ...
... for a missing element of hypothetical element of the same family. Distinguish between atoms and ions (cations and anions and their formation) ...
8.044s13 Excited State Helium, He
... is repulsive. The electrons will be less bound. But imagine that we made a first stab at approximating the increase in the energy by evaluating the coulomb energy of the electron cloud produced by taking the charge distribution resulting from our wavefunctions. The greatest contributions would come ...
... is repulsive. The electrons will be less bound. But imagine that we made a first stab at approximating the increase in the energy by evaluating the coulomb energy of the electron cloud produced by taking the charge distribution resulting from our wavefunctions. The greatest contributions would come ...
Review for Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... hybrid orbitals are employed. The inclusion of the d orbital enables “expanded octets” to occur. For octahedral molecules in which six pairs of electrons are arranged around a central atom, sp3d2 hybrid orbitals are used. 10. Sigma bonds are covalent bonds formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, ...
... hybrid orbitals are employed. The inclusion of the d orbital enables “expanded octets” to occur. For octahedral molecules in which six pairs of electrons are arranged around a central atom, sp3d2 hybrid orbitals are used. 10. Sigma bonds are covalent bonds formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff
... The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge by the electrons in lower energ ...
... The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge by the electrons in lower energ ...
Summer Assignment 2015
... 5. Give the complete chemical symbol for the atom that contains 82 protons, 82 electrons, and 126 neutrons. 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the ...
... 5. Give the complete chemical symbol for the atom that contains 82 protons, 82 electrons, and 126 neutrons. 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the ...
Document
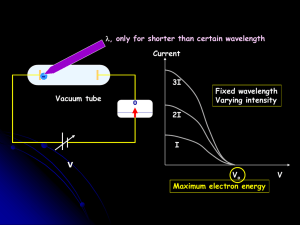
... Q. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron that has a kinetic energy of 100 eV? After an electron is accelerated in 100 V potential difference, its kinetic energy is 100 eV. eV unit has to be converted into SI unit, Joule. 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
... Q. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron that has a kinetic energy of 100 eV? After an electron is accelerated in 100 V potential difference, its kinetic energy is 100 eV. eV unit has to be converted into SI unit, Joule. 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom to
... Radiation can occur only when the electron jumps from one orbit to another. The atom will be completely stable in the state with the smallest orbit, since there is no orbit of lower energy into which the electron can jump. Bohr's starting point was to realize that classical mechanics by itself could ...
... Radiation can occur only when the electron jumps from one orbit to another. The atom will be completely stable in the state with the smallest orbit, since there is no orbit of lower energy into which the electron can jump. Bohr's starting point was to realize that classical mechanics by itself could ...
Honors Chemistry
... Sometimes light acts like a wave and some other times like a particle. To understand what light is one must take both characteristics into consideration. Neither the theory of particles (photons) nor the wave theory of light is correct if considered alone. Only combined does one get a full and prope ...
... Sometimes light acts like a wave and some other times like a particle. To understand what light is one must take both characteristics into consideration. Neither the theory of particles (photons) nor the wave theory of light is correct if considered alone. Only combined does one get a full and prope ...
Rutherford Model 1911 - University of St Andrews
... 1. Does well to describe hydrogen, but can be extended only to 1-electron atoms, i.e. hydrogen-like, with higher Z values. Can treat alkali atoms with some success, but only because they have 1 electron only outside closed shells. Fails to account for spectra of other atoms. 2. Theory does not expla ...
... 1. Does well to describe hydrogen, but can be extended only to 1-electron atoms, i.e. hydrogen-like, with higher Z values. Can treat alkali atoms with some success, but only because they have 1 electron only outside closed shells. Fails to account for spectra of other atoms. 2. Theory does not expla ...
e- are outside nucleus nucleus
... - quantized energy levels) • Difference: e- do not travel in fixed paths; they exist in an e- cloud e- cloud: region around the nucleus where the probability of finding an e- is about 90% ...
... - quantized energy levels) • Difference: e- do not travel in fixed paths; they exist in an e- cloud e- cloud: region around the nucleus where the probability of finding an e- is about 90% ...
1 Rutherford`s Nuclear Model of the atom A is the currently accepted
... The lowest orbital energy is reached when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized. This statement describes __________. A ...
... The lowest orbital energy is reached when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized. This statement describes __________. A ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... State any two postulates of quantum mechanics. Prove that the square of the angular momentum commutes with its components. What is meant by degeneracy of an energy level? What is an orthonormal basis? With an example explain simultaneous eigenfunctions. If A and B are two operators, then show that [ ...
... State any two postulates of quantum mechanics. Prove that the square of the angular momentum commutes with its components. What is meant by degeneracy of an energy level? What is an orthonormal basis? With an example explain simultaneous eigenfunctions. If A and B are two operators, then show that [ ...
Atomic Theory Notes Packet
... 1.) Period (row) corresponds to the ____________ ____________ Level being filled with electrons example: For Period 3, which Principal Energy Level is filling?_____ 2.) Electron configurations given in block for each element in _______________ corner. You need to know the filling order!! 3.) Blocks ...
... 1.) Period (row) corresponds to the ____________ ____________ Level being filled with electrons example: For Period 3, which Principal Energy Level is filling?_____ 2.) Electron configurations given in block for each element in _______________ corner. You need to know the filling order!! 3.) Blocks ...
Intro Biochemistry/Ecology
... The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because they have the same number of protons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. The main types of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Section 2-2: Properties of Water A water m ...
... The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because they have the same number of protons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. The main types of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Section 2-2: Properties of Water A water m ...
Environment Assisted Quantum Transport in Organic Molecules
... plays an essential role in exciton transport in photosynthesis 1–4 . One of the fundamental quantum effects there is the Environmentally Assisted Quantum Transport 5–7 (ENAQT). It applies to partially coherent quantum transport in disordered systems. At low temperatures transport is dominated by qua ...
... plays an essential role in exciton transport in photosynthesis 1–4 . One of the fundamental quantum effects there is the Environmentally Assisted Quantum Transport 5–7 (ENAQT). It applies to partially coherent quantum transport in disordered systems. At low temperatures transport is dominated by qua ...
Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure
... – The exact location of very small particles is not well known due to their wave-like properties – The probability to find a particle at a particular location depends on the amplitude (intensity) of the wave at this location ...
... – The exact location of very small particles is not well known due to their wave-like properties – The probability to find a particle at a particular location depends on the amplitude (intensity) of the wave at this location ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.