New atom interferometry techniques for tests of fundamental
... tests of fundamental physics. Addressing these applications requires to push further the performances of cold atom inertial sensors, in particular for applications in fundamental physics (detection of gravitational waves or tests of the Einstein Equivalence Principle) or in geoscience (non-invasive ...
... tests of fundamental physics. Addressing these applications requires to push further the performances of cold atom inertial sensors, in particular for applications in fundamental physics (detection of gravitational waves or tests of the Einstein Equivalence Principle) or in geoscience (non-invasive ...
Electron interferometry - Fondation Louis de Broglie
... four photons. The explanation of this paradox is that, by interference, the interval of time between two consecutive photons becomes so much smaller that the mean photon current corresponds to the emission of four photons within a correspondingly shorter time interval. Destructive interference, acco ...
... four photons. The explanation of this paradox is that, by interference, the interval of time between two consecutive photons becomes so much smaller that the mean photon current corresponds to the emission of four photons within a correspondingly shorter time interval. Destructive interference, acco ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... Explaining the MOT with a different notation The quantum axis is now not an arbitrary axis in space like before but parallel to the local magnetic field or the photon propagation direction. Let look at the angular momentum conservation in a simplified J=1/2 system. Magnetic field in the MOT ...
... Explaining the MOT with a different notation The quantum axis is now not an arbitrary axis in space like before but parallel to the local magnetic field or the photon propagation direction. Let look at the angular momentum conservation in a simplified J=1/2 system. Magnetic field in the MOT ...
Wave Particle Duality - waiukucollegescience
... (b) What is the maximum velocity of photoelectrons liberated from a surface having a work function of 4.0 eV by ultra-violet radiation of wavelength 2.0 x 10-7m. (5) In an experiment on the photoelectric effect using radiation of wavelength 4.00 x 10-7m the maximum electron energy observed was 1.40 ...
... (b) What is the maximum velocity of photoelectrons liberated from a surface having a work function of 4.0 eV by ultra-violet radiation of wavelength 2.0 x 10-7m. (5) In an experiment on the photoelectric effect using radiation of wavelength 4.00 x 10-7m the maximum electron energy observed was 1.40 ...
Ms - cloudfront.net
... 11. Describe the following trend on the periodic table. a. Atomic Number b. Atomic Size c. Ionization Energy d. Electronegativy 12. Which atom is more electronegative, fluorine or lithium? 13. Which atom has a greater ionization energy, nitrogen or bismuth? 14. Which atom has a larger atomic radius, ...
... 11. Describe the following trend on the periodic table. a. Atomic Number b. Atomic Size c. Ionization Energy d. Electronegativy 12. Which atom is more electronegative, fluorine or lithium? 13. Which atom has a greater ionization energy, nitrogen or bismuth? 14. Which atom has a larger atomic radius, ...
Chem BIG REVIEW - Jones-wiki
... the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are arranged in atoms. Electrons enter the lowest energy first. At most there can be only 2 e ...
... the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are arranged in atoms. Electrons enter the lowest energy first. At most there can be only 2 e ...
Chemistry EOC Review
... In ionic bonds, the electrons are transferred from a __________ to a ________________. In covalent bonds, electrons are __________. Two non-metals join together by ___________ bonding. A metal and a non-metal join together by __________ bonding. Elements form ions which have the same valence electro ...
... In ionic bonds, the electrons are transferred from a __________ to a ________________. In covalent bonds, electrons are __________. Two non-metals join together by ___________ bonding. A metal and a non-metal join together by __________ bonding. Elements form ions which have the same valence electro ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... Chemical bonds A. Electron energy is shared or donated B. Only valence electrons involved in chemical bonds (Octet rule) C. Ionic bonds – electrons are transferred from one atom to another, forming ions. Ions of opposite charge attract forming an ionic bond D. Most ionic compounds are salts E. Coval ...
... Chemical bonds A. Electron energy is shared or donated B. Only valence electrons involved in chemical bonds (Octet rule) C. Ionic bonds – electrons are transferred from one atom to another, forming ions. Ions of opposite charge attract forming an ionic bond D. Most ionic compounds are salts E. Coval ...
Chapter 2
... Since some particles were deflected at large angles, Thompson’s model could not be correct. ...
... Since some particles were deflected at large angles, Thompson’s model could not be correct. ...
Atomic Theory
... Hydrogen spectrum- it consists of discrete lines that converge towards the high energy end of the spectrum. The lines converge as the shells are getting closer together. Energy levels increase because we get a higher frequency and a smaller wavelength. ( E V ) ...
... Hydrogen spectrum- it consists of discrete lines that converge towards the high energy end of the spectrum. The lines converge as the shells are getting closer together. Energy levels increase because we get a higher frequency and a smaller wavelength. ( E V ) ...
An Introduction to Matter
... – A chemical change is a change that does alter the identity of the matter. – A compound is a pure substance that can be decomposed by a chemical change into simpler substances – An element is a pure substance which cannot be broken down into anything simpler by either physical or chemical means. ...
... – A chemical change is a change that does alter the identity of the matter. – A compound is a pure substance that can be decomposed by a chemical change into simpler substances – An element is a pure substance which cannot be broken down into anything simpler by either physical or chemical means. ...
Table of Contents - Free Coursework for GCSE, IGCSE, A Level, IB
... Hydrogen spectrum- it consists of discrete lines that converge towards the high energy end of the spectrum. The lines converge as the shells are getting closer together. Energy levels increase because we get a higher frequency and a smaller wavelength. ( E V ) ...
... Hydrogen spectrum- it consists of discrete lines that converge towards the high energy end of the spectrum. The lines converge as the shells are getting closer together. Energy levels increase because we get a higher frequency and a smaller wavelength. ( E V ) ...
Derivation of Bohr`s Equations for the One
... Since ao is a constant, equation (6) predicts that the radius increases in direct proportion to the square of the quantum number, n2, and decreases in inverse proportion to the atomic number, Z. Thus, the sizes of the orbits in hydrogen are predicted to be ao, 4ao, 9ao, 16ao, 25ao, etc. Furthermore, ...
... Since ao is a constant, equation (6) predicts that the radius increases in direct proportion to the square of the quantum number, n2, and decreases in inverse proportion to the atomic number, Z. Thus, the sizes of the orbits in hydrogen are predicted to be ao, 4ao, 9ao, 16ao, 25ao, etc. Furthermore, ...
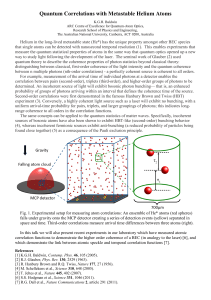
Quantum Correlations with Metastable Helium Atoms
... experiment (3). Conversely, a highly coherent light source such as a laser will exhibit no bunching, with a uniform arrival-time probability for pairs, triplets, and larger groupings of photons; this indicates longrange coherence to all orders in the correlation functions. The same concepts can be a ...
... experiment (3). Conversely, a highly coherent light source such as a laser will exhibit no bunching, with a uniform arrival-time probability for pairs, triplets, and larger groupings of photons; this indicates longrange coherence to all orders in the correlation functions. The same concepts can be a ...
Lecture_19-Energy Levels in the Bohr model of the atom
... electron (accelerating charge) would emit electromagnetic radiation and fall into the nucleus. So classical physics could not explain why atoms are stable. ...
... electron (accelerating charge) would emit electromagnetic radiation and fall into the nucleus. So classical physics could not explain why atoms are stable. ...
Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... • Any successful model for the bonding in metals must be able to explain: – Good thermal and electrical conductivity – Reflectivity ...
... • Any successful model for the bonding in metals must be able to explain: – Good thermal and electrical conductivity – Reflectivity ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
... All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
The Weird World of Quantum Information
... Single electron states are labeled by quantum numbers: n, l, ml, s, ms Rule: In an atoms, all electrons have to differ in at least one quantum number Electrons are fermions and have to be in different states – remember that this leads to electron degeneracy pressure in white dwarfs. n is principal q ...
... Single electron states are labeled by quantum numbers: n, l, ml, s, ms Rule: In an atoms, all electrons have to differ in at least one quantum number Electrons are fermions and have to be in different states – remember that this leads to electron degeneracy pressure in white dwarfs. n is principal q ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.