Lecture 5
... How does the average moment of an assemblage of particles come into equilibrium with an applied field (so that net M is proportional to B and the direction is parallel ...
... How does the average moment of an assemblage of particles come into equilibrium with an applied field (so that net M is proportional to B and the direction is parallel ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... Electronegativity -the attraction to electrons involved in a chemical bond Two Types of Covalent Bonds 1. Polar Covalent Bond -one atom in a molecule is significantly more electronegative -This causes a slight positive and negative charge on a molecule. 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shar ...
... Electronegativity -the attraction to electrons involved in a chemical bond Two Types of Covalent Bonds 1. Polar Covalent Bond -one atom in a molecule is significantly more electronegative -This causes a slight positive and negative charge on a molecule. 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shar ...
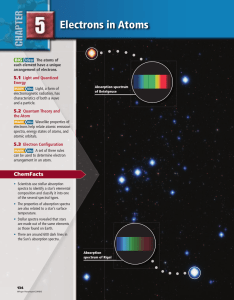
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms
... The Particle Nature of Light While considering light as a wave explains much of its everyday behavior, it fails to adequately describe important aspects of light’s interactions with matter. The wave model of light cannot explain why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at a given t ...
... The Particle Nature of Light While considering light as a wave explains much of its everyday behavior, it fails to adequately describe important aspects of light’s interactions with matter. The wave model of light cannot explain why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at a given t ...
Atom The smallest part of an element that can exist on its own
... Dibasic acid One which has 2 replaceable H atoms per molecule Isotopes Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers - As the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons increases relatively faster, so small atoms have proton and neutron numbers which are comparable whereas ...
... Dibasic acid One which has 2 replaceable H atoms per molecule Isotopes Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers - As the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons increases relatively faster, so small atoms have proton and neutron numbers which are comparable whereas ...
Unit 4 - Dorman High School
... V. Ionic Bonding and Structures of Ionic Compounds When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can ...
... V. Ionic Bonding and Structures of Ionic Compounds When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can ...
File
... hand, the Hamilton-Jacobi theory pointed somewhat in that direction, for it can be applied to particles and, in addition, it represents a geometrical optics; on the other hand, in quantum phenomena one obtains quantum numbers, which are rarely found in mechanics but occur very frequently in wave phe ...
... hand, the Hamilton-Jacobi theory pointed somewhat in that direction, for it can be applied to particles and, in addition, it represents a geometrical optics; on the other hand, in quantum phenomena one obtains quantum numbers, which are rarely found in mechanics but occur very frequently in wave phe ...
r - Purdue Physics
... c.) Photons are emitted or absorbed in the transitions between these stable orbits d.) Electrons do not radiate when move in stable orbits Periodic Table and Rutherford’s Experiment Nuclear structure and radioactivity ...
... c.) Photons are emitted or absorbed in the transitions between these stable orbits d.) Electrons do not radiate when move in stable orbits Periodic Table and Rutherford’s Experiment Nuclear structure and radioactivity ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... 1. What is the molar mass of the following compounds? a. Pb(C2O4)2 b. Ni(OH)2 c. Tin (IV) acetate pentahydrate d. CH3COOH 2. Calculate the mass of the following: a. 7.01 mol of SiF4 b. 6.59 x 10-4 mol H3PO4 c. 0.0765 mol Li2HSO4 d. 6.85 mol CH3CH2 CH2 CH2CH3 3. Calculate the number of moles of the f ...
... 1. What is the molar mass of the following compounds? a. Pb(C2O4)2 b. Ni(OH)2 c. Tin (IV) acetate pentahydrate d. CH3COOH 2. Calculate the mass of the following: a. 7.01 mol of SiF4 b. 6.59 x 10-4 mol H3PO4 c. 0.0765 mol Li2HSO4 d. 6.85 mol CH3CH2 CH2 CH2CH3 3. Calculate the number of moles of the f ...
Kondo effect of an antidot in the integer quantum Hall regime: a
... those expected in the experiment [8] of large-size realistic antidots and the results of the capacitive interaction model [12]. In large-size antidots, it is naturally expected that the spin polarization would show a periodic oscillation with Aharonov–Bohm period in a wide range of magnetic 2eld (at ...
... those expected in the experiment [8] of large-size realistic antidots and the results of the capacitive interaction model [12]. In large-size antidots, it is naturally expected that the spin polarization would show a periodic oscillation with Aharonov–Bohm period in a wide range of magnetic 2eld (at ...
Notes matter energy
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 49) Identify the number of main groups on the periodic table and the name of each one. 50) How many periods are on the periodic table? 51) Groups are __________________ columns and periods are _________________ rows on the periodic table. 52) Elements within the same _________________ have similar c ...
... 49) Identify the number of main groups on the periodic table and the name of each one. 50) How many periods are on the periodic table? 51) Groups are __________________ columns and periods are _________________ rows on the periodic table. 52) Elements within the same _________________ have similar c ...
Chapter 12 Multiple Particle States
... The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two fermions may occupy the same quantum state. This principle is absolutely crucial to life as we know it; without it, we would not have the Periodic Table of chemistry, nor would we have a lot of the rest of the structure of matter. This doesn’t mean, h ...
... The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two fermions may occupy the same quantum state. This principle is absolutely crucial to life as we know it; without it, we would not have the Periodic Table of chemistry, nor would we have a lot of the rest of the structure of matter. This doesn’t mean, h ...
the zeeman effect
... additional energy just as a bar magnet does and consequently the original energy level is shifted. The energy shift may be positive, zero, or even negative, depending on the angle between the electron magnetic dipole moment and the field. Due to Zeeman effect, some degenerate energy levels will spli ...
... additional energy just as a bar magnet does and consequently the original energy level is shifted. The energy shift may be positive, zero, or even negative, depending on the angle between the electron magnetic dipole moment and the field. Due to Zeeman effect, some degenerate energy levels will spli ...
Chemical formula Chemistry Subscript Subscript
... subscripts; A way of describing the number of atoms Chemical formula that makes up one molecule of a compound ...
... subscripts; A way of describing the number of atoms Chemical formula that makes up one molecule of a compound ...
Chapter 3- sec 1- the atom
... contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with ...
... contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
2. Covalent network
... [A]^j x [B]^k 3. K is the equilibrium constant and varies depending on temperature and the coefficients of the balanced equation. Concentration does NOT effect k. ...
... [A]^j x [B]^k 3. K is the equilibrium constant and varies depending on temperature and the coefficients of the balanced equation. Concentration does NOT effect k. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.