Atomic Concepts
... 21. Ground state electron configuration matches periodic table; excited state does not 22. Lewis dot structure; a dot represents a valence electron (# dots = # valence electrons) 23. *** be able to calculate the atomic mass of an element, given masses and ratios of isotopes (% ÷ 100 * mass and add t ...
... 21. Ground state electron configuration matches periodic table; excited state does not 22. Lewis dot structure; a dot represents a valence electron (# dots = # valence electrons) 23. *** be able to calculate the atomic mass of an element, given masses and ratios of isotopes (% ÷ 100 * mass and add t ...
Chapter 31 Atomic Physics
... The electron was discovered in 1897, and was observed to be much smaller than the atom. It was known that atoms are electrically neutral; the first modern model of the atom was therefore the “plum pudding” model – tiny electrons embedded in a mass of positive ...
... The electron was discovered in 1897, and was observed to be much smaller than the atom. It was known that atoms are electrically neutral; the first modern model of the atom was therefore the “plum pudding” model – tiny electrons embedded in a mass of positive ...
ramsauer - UT Relativity Group
... the potential. If the Ramsauer-Townsend effect was not occurring then one would expect the two graphs to be approximately the same, however it is clear that the graph of the plate current at room temperature deviates tremendously due to the effect. (see graph I(p*) and I(p) v.s. root Va next page). ...
... the potential. If the Ramsauer-Townsend effect was not occurring then one would expect the two graphs to be approximately the same, however it is clear that the graph of the plate current at room temperature deviates tremendously due to the effect. (see graph I(p*) and I(p) v.s. root Va next page). ...
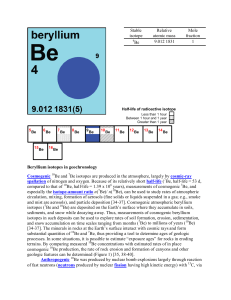
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...
Practice MSL Multiple Choice 1. Compared to the charge and mass
... lose electrons and form negative ions lose electrons and form positive ions gain electrons and from negative ions gain electrons and form positive ions ...
... lose electrons and form negative ions lose electrons and form positive ions gain electrons and from negative ions gain electrons and form positive ions ...
doc
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
The Atomic Emission Spectra of Hydrogen, Deuterium
... A Russell-‐Saunders term symbol can be written for each electronic energy level of an atom. It has the form n(2S +1)LJ where n is the principle quantum number. Define the other elements (S, ...
... A Russell-‐Saunders term symbol can be written for each electronic energy level of an atom. It has the form n(2S +1)LJ where n is the principle quantum number. Define the other elements (S, ...
Quantum Physics
... proposed was that electrons normally came in pairs, so that their magnetic effects cancelled out. This would be the case if, in addition to movement in an “orbit”, the electrons were also spinning on their axes. Each electron would then be a magnet. A pair of electrons in the same orbit would cancel ...
... proposed was that electrons normally came in pairs, so that their magnetic effects cancelled out. This would be the case if, in addition to movement in an “orbit”, the electrons were also spinning on their axes. Each electron would then be a magnet. A pair of electrons in the same orbit would cancel ...
photoelectric-effect-qrg
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Brochure
... Order Online - http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3048746/ Order by Fax - using the form below Order by Post - print the order form below and send to Research and Markets, ...
... Order Online - http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3048746/ Order by Fax - using the form below Order by Post - print the order form below and send to Research and Markets, ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... • is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of the element • as they occur naturally • taking their abundances into account • expressed on a scale in which the atoms of carbon 12 isotope have a mass of exactly 12 units. AG ...
... • is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of the element • as they occur naturally • taking their abundances into account • expressed on a scale in which the atoms of carbon 12 isotope have a mass of exactly 12 units. AG ...
Solute
... Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... formula of the compound Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant tha ...
... formula of the compound Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant tha ...
Laboratory 1
... 1. Plot the window function for the phonon transport 2 at different temperatures. k T ...
... 1. Plot the window function for the phonon transport 2 at different temperatures. k T ...
1 - Academics
... region of space centered about the nucleus, but not always. (C) the electron is most likely to be found in a spherical region of space centered about the nucleus, but not always. (D) the electron is most likely to be found in a single-dumb-bell region of space centered about the nucleus, but not alw ...
... region of space centered about the nucleus, but not always. (C) the electron is most likely to be found in a spherical region of space centered about the nucleus, but not always. (D) the electron is most likely to be found in a single-dumb-bell region of space centered about the nucleus, but not alw ...
king fahd university of petroleum and minerals
... If you miss a major exam, you should come and see me with your official excuse within three days after the exam. Personal excuses are not allowed. If you miss the exam without a valid excuse, you get a ZERO score for that exam. Attendance: Attendance will be enforced and evaluated according to curre ...
... If you miss a major exam, you should come and see me with your official excuse within three days after the exam. Personal excuses are not allowed. If you miss the exam without a valid excuse, you get a ZERO score for that exam. Attendance: Attendance will be enforced and evaluated according to curre ...
Thermodynamic Properties of Hydrated and Ammoniated Electrons
... in the first solvation layer have a larger number of degrees of freedom than in the bulk. It thus seems reasonable that So,- should be smaller in ammonia at higher temperature, when there is already more freedom in the bulk and still be smaller in water, where the first conduction shell is more tigh ...
... in the first solvation layer have a larger number of degrees of freedom than in the bulk. It thus seems reasonable that So,- should be smaller in ammonia at higher temperature, when there is already more freedom in the bulk and still be smaller in water, where the first conduction shell is more tigh ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.