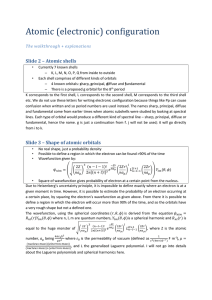
energy levels
... The 2p orbitals are lower in energy than the 3s orbital, so they will be completely filled before any electrons will be found in the 3s orbital. ...
... The 2p orbitals are lower in energy than the 3s orbital, so they will be completely filled before any electrons will be found in the 3s orbital. ...
Atomic structure review
... Atomic structure review - H People Thompson – discovered electrons Rutherford – discovered the nucleus – small dense positive nucleus, volume empty space Bohr – electrons have quantized (specific) energy, shell model Heisenberg – due to wave nature of electrons you can’t know the position and moment ...
... Atomic structure review - H People Thompson – discovered electrons Rutherford – discovered the nucleus – small dense positive nucleus, volume empty space Bohr – electrons have quantized (specific) energy, shell model Heisenberg – due to wave nature of electrons you can’t know the position and moment ...
stationary state
... jump, from one stationary state to another. During this transition it does emit radiation. When an electron makes a transition from one stationary state to another, the energy difference ∆E is released as a single photon of frequency ν= ∆E /h ( or h ν= Ei-Ef ). • In the limit of large orbits and lar ...
... jump, from one stationary state to another. During this transition it does emit radiation. When an electron makes a transition from one stationary state to another, the energy difference ∆E is released as a single photon of frequency ν= ∆E /h ( or h ν= Ei-Ef ). • In the limit of large orbits and lar ...
Application of Quantum Theory 1- Particle in 1
... maximum value. (why) e. Node = the point where wave function passes through zero, or the position where probability of finding particle = 0 (No. of nodes = n-1) f. The probability of finding the particle between two points x 1 and x2 are different when n have small values, while as n increases (n >1 ...
... maximum value. (why) e. Node = the point where wave function passes through zero, or the position where probability of finding particle = 0 (No. of nodes = n-1) f. The probability of finding the particle between two points x 1 and x2 are different when n have small values, while as n increases (n >1 ...
Quiz 8
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
File
... When investigators passed electric current through hydrgoen gas in a vacuum tube. A pinkish glow was emitted. When the beam was shined through a prism, it was separated into a series of visible light bars with different frequencies. (wavelength*frequency= speed of light(constant)). Therefore, these ...
... When investigators passed electric current through hydrgoen gas in a vacuum tube. A pinkish glow was emitted. When the beam was shined through a prism, it was separated into a series of visible light bars with different frequencies. (wavelength*frequency= speed of light(constant)). Therefore, these ...
CHEM 121
... 5. Calculate the energy in kJ/mol of photons of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 3.72 x 1017 s-1. 6. How did the study of blackbody radiation and the ultraviolet catastrophe contribute to the development of quantum mechanics? 7. A minimum frequency of 5.56 x 1014 Hz is needed for ob ...
... 5. Calculate the energy in kJ/mol of photons of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 3.72 x 1017 s-1. 6. How did the study of blackbody radiation and the ultraviolet catastrophe contribute to the development of quantum mechanics? 7. A minimum frequency of 5.56 x 1014 Hz is needed for ob ...
Chapter 7 Many-Electron Atoms
... Electrons within a shell generally have lower total energies (bigger negative energies, and therefore larger binding energies) when they have lower l. Electrons having the same l are said to occupy the same subshell. We write electronic configurations showing shells and subshells. For example, magne ...
... Electrons within a shell generally have lower total energies (bigger negative energies, and therefore larger binding energies) when they have lower l. Electrons having the same l are said to occupy the same subshell. We write electronic configurations showing shells and subshells. For example, magne ...
Quantum Numbers Quiz
... 1. _____ describes the orientation of the orbitals in space 2. _____ describes the spin of an electron 3. _____ describes the shape of the orbital occupied by the electron 4. _____ describes the main energy level of the electron ...
... 1. _____ describes the orientation of the orbitals in space 2. _____ describes the spin of an electron 3. _____ describes the shape of the orbital occupied by the electron 4. _____ describes the main energy level of the electron ...
chemistry i
... Note: This set of problems does NOT cover all of the concepts that will be on the midterm. Remember to study your class notes and handouts for a full review! 1. Which sequence represents a correct order of historical developments leading to the modern model of the atom? A. The atom is a hard sphere ...
... Note: This set of problems does NOT cover all of the concepts that will be on the midterm. Remember to study your class notes and handouts for a full review! 1. Which sequence represents a correct order of historical developments leading to the modern model of the atom? A. The atom is a hard sphere ...
Final “Intro Quantum Mechanics”
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...
7. In CCl 4 carbon is the “central atom”. In NF3 nitrogen is the
... 13. Considering questions 11 and 12, we can formulate a rule: For each negative charge on a polyatomic ion, we must ______________ an electron and for each positive charge we must add or subtract ...
... 13. Considering questions 11 and 12, we can formulate a rule: For each negative charge on a polyatomic ion, we must ______________ an electron and for each positive charge we must add or subtract ...
Ch05ElectronConfig - Journigan-wiki
... The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines upon it. If the light frequency was below a certain level, no electrons were emitted. The wave theory of light predicted that light of any frequency could supply enough energy to eject an electron. Scientists could not explain why a certain ...
... The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines upon it. If the light frequency was below a certain level, no electrons were emitted. The wave theory of light predicted that light of any frequency could supply enough energy to eject an electron. Scientists could not explain why a certain ...
$doc.title
... Note for He2 (4 electrons), Pauli principle means two e’s in antibonding state as well as bonding state so no overall energy saving (inert gases – no bond - no He2) Mid-periodic table elements (half-filled orbitals) tend to have strongest bonds (e.g. melting points. etc.) ...
... Note for He2 (4 electrons), Pauli principle means two e’s in antibonding state as well as bonding state so no overall energy saving (inert gases – no bond - no He2) Mid-periodic table elements (half-filled orbitals) tend to have strongest bonds (e.g. melting points. etc.) ...
VIII. Other Types of Notations or Configurations
... – 4. Orientation of sublevels in space •s • px, py, pz •d ...
... – 4. Orientation of sublevels in space •s • px, py, pz •d ...
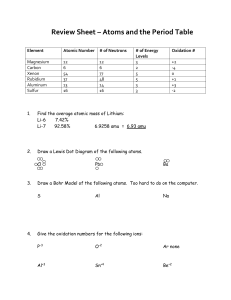
Review Sheet Filled Out
... Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside the nucleus Can’t tell where an electron is at any ...
... Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside the nucleus Can’t tell where an electron is at any ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms.
... permitted 2. An electron in a specific orbit has an allowed energy 3. Energy is emitted or absorbed only when it changes from one state to another. ...
... permitted 2. An electron in a specific orbit has an allowed energy 3. Energy is emitted or absorbed only when it changes from one state to another. ...
Problem set #1 - U.C.C. Physics Department
... and let kx = 6π/L; ky = 4π/L. Draw out (i) for t = 0 and (ii) for t = π/ω, the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assumi ...
... and let kx = 6π/L; ky = 4π/L. Draw out (i) for t = 0 and (ii) for t = π/ω, the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assumi ...
Document
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
... numbers also result in small energy differences • Pauli exclusion principle: no two electrons in the same atom can be in the same quantum state • Electrons are grouped into shells and subshells • Periodic table reflects shell structure •Atoms with the same number of electrons in their outer shells h ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.