Lone pairs
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
S1-2-02: What is the basic subatomic structure of an atom?
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
Charge Transfer in Collisions of Ions with atoms and - Indico
... But, while an adiabatic representation of the system allows us to visualize the collision process there are some conceptual difficulties (even leaving aside the problem of determining the adiabatic eigen energies and eigen functions). Electronic adiabatic states generated from the clamped nuclei app ...
... But, while an adiabatic representation of the system allows us to visualize the collision process there are some conceptual difficulties (even leaving aside the problem of determining the adiabatic eigen energies and eigen functions). Electronic adiabatic states generated from the clamped nuclei app ...
THE CONTINUOUS R.ADIATIVE .ABSORPTION CROSS SECTION
... It is found that about 0·4 of the total value of (QR)Av. comes from the low energy tail of the Maxwell distribution below an energy of 4 eV corresponding to ka <1/30. This is due to the rapid rise in the QRn'S towards infinite values as ka tends to zero, so that the value of QR.dN/dE, where dN is th ...
... It is found that about 0·4 of the total value of (QR)Av. comes from the low energy tail of the Maxwell distribution below an energy of 4 eV corresponding to ka <1/30. This is due to the rapid rise in the QRn'S towards infinite values as ka tends to zero, so that the value of QR.dN/dE, where dN is th ...
Chemistry Module 1- Basic Revision Notes 1.1a Atomic Structure 1.1
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
Broglie and Schrodinger Atomic Model
... particle duality theory of matter, this was also with the help of research that Albert Einstein had found. Broglie’s hypothesis was “Any moving particle or object has an associated wave”. His discovery of wave mechanics which merged the physics of light and matter earned him the nobel prize. Informa ...
... particle duality theory of matter, this was also with the help of research that Albert Einstein had found. Broglie’s hypothesis was “Any moving particle or object has an associated wave”. His discovery of wave mechanics which merged the physics of light and matter earned him the nobel prize. Informa ...
First Year - WordPress.com
... Q. 28. A 50.00 mL sample of a cough mixture prepared by a pharmacist was found to have a mass of 46.0g. what is the density (in g/mL) of this mixture. Stated to the correct number of ...
... Q. 28. A 50.00 mL sample of a cough mixture prepared by a pharmacist was found to have a mass of 46.0g. what is the density (in g/mL) of this mixture. Stated to the correct number of ...
discrete spectra - Project PHYSNET
... electron from an initially neutral atom, leaving a system consisting of a nucleus of charge +Ze and a single electron. • ionization: the process of adding electrons to, or removing electrons from, an initially neutral atom to form a charged particle called an “ion.” By removing all the electrons, th ...
... electron from an initially neutral atom, leaving a system consisting of a nucleus of charge +Ze and a single electron. • ionization: the process of adding electrons to, or removing electrons from, an initially neutral atom to form a charged particle called an “ion.” By removing all the electrons, th ...
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the ...
... They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the ...
Chapter 1
... A. Protons have an elementary positive charge of 1. B. Protons have one Dalton of mass. C. Protons are always found in the nucleus of the atom. D. Any atom found in nature always has the same number of protons as electrons. 2. Which of the following statements about electron orbitals is FALSE? A. Th ...
... A. Protons have an elementary positive charge of 1. B. Protons have one Dalton of mass. C. Protons are always found in the nucleus of the atom. D. Any atom found in nature always has the same number of protons as electrons. 2. Which of the following statements about electron orbitals is FALSE? A. Th ...
OKEMOS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... Write the kernal electronic configuration for the following elements and write the number of valence electrons each has in the space before the symbol. __1__ a) Rb [Kr]5s1 ...
... Write the kernal electronic configuration for the following elements and write the number of valence electrons each has in the space before the symbol. __1__ a) Rb [Kr]5s1 ...
Chemistry Readings
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
... the nucleus). The shells are also called energy levels or orbitals. We will use the term shell. Chemists use letters to name the shells around a nucleus. They use the letters "k, l, m, n, o, p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold ...
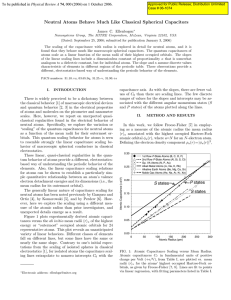
Neutral Atoms Behave Much Like Classical Spherical Capacitors
... for an isolated spherical conductor. The nonzero intercept does have an analog, though, in the equations for a classical spherical capacitor if ra+1 is not very much larger than ra , as in Eq. (2c), and if the sum there in square brackets is nearly linear or constant in ra . Such behaviors also are ...
... for an isolated spherical conductor. The nonzero intercept does have an analog, though, in the equations for a classical spherical capacitor if ra+1 is not very much larger than ra , as in Eq. (2c), and if the sum there in square brackets is nearly linear or constant in ra . Such behaviors also are ...
2nd Semester Chemistry Terms - Glancy 4TH PERIOD PHYSICAL
... into its component colors 20. Atomic spectrum- the pattern of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the atoms of an element, considered to be the element’s “fingerprint” 21. Quantum hypothesis- the idea that light energy is contained in discrete packets called quanta 22. Quantum- a sma ...
... into its component colors 20. Atomic spectrum- the pattern of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the atoms of an element, considered to be the element’s “fingerprint” 21. Quantum hypothesis- the idea that light energy is contained in discrete packets called quanta 22. Quantum- a sma ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.