Presentation Lesson 27 Quantum Physics
... • The radii of the electron orbits in the Bohr’s atomic model are determined by the amount of electric charge in the nucleus • As the positive charge in the nucleus increased, the negative electrons also increased. The inner orbits shrink in size due to stronger electric attraction. However, it won’ ...
... • The radii of the electron orbits in the Bohr’s atomic model are determined by the amount of electric charge in the nucleus • As the positive charge in the nucleus increased, the negative electrons also increased. The inner orbits shrink in size due to stronger electric attraction. However, it won’ ...
Chapter 2
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
CHEM_S1CourseReview_2011
... How does an electron act according to de Broglie’s wave-particle duality? What is a quantum? In what ways do the Bohr model and quantum mechanical model differ? How does the quantum mechanical model describe the arrangement of the electrons in atoms and their orbitals? What happens when electrons in ...
... How does an electron act according to de Broglie’s wave-particle duality? What is a quantum? In what ways do the Bohr model and quantum mechanical model differ? How does the quantum mechanical model describe the arrangement of the electrons in atoms and their orbitals? What happens when electrons in ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom that represents that charge it would have if it contained and ionic bond. Oxidation numbers are written as charge value, +4, -6, +2 Oxidation: Proces ...
... Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom that represents that charge it would have if it contained and ionic bond. Oxidation numbers are written as charge value, +4, -6, +2 Oxidation: Proces ...
Spectra and Atomic Structure
... • Solves problem of why electrons do not fall into nucleus. • Used quantized orbits with specific energies. • Electron can only move between orbits by getting or losing the exact amount of energy required. • It could not take ...
... • Solves problem of why electrons do not fall into nucleus. • Used quantized orbits with specific energies. • Electron can only move between orbits by getting or losing the exact amount of energy required. • It could not take ...
9/6/12 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... - An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. - Matter exists in many different forms but there are only 118+ types of atoms. - Atoms are joined together to make up all the different kinds of matter. Pure Substance - A pure substance is a sample of matte ...
... - An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. - Matter exists in many different forms but there are only 118+ types of atoms. - Atoms are joined together to make up all the different kinds of matter. Pure Substance - A pure substance is a sample of matte ...
Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom
... Quantum Mechanics • Predicts available energy states agreeing with Bohr. • Don’t have definite electron position, only a probability function. • Orbitals can have 0 angular momentum! • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, ...
... Quantum Mechanics • Predicts available energy states agreeing with Bohr. • Don’t have definite electron position, only a probability function. • Orbitals can have 0 angular momentum! • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, ...
Lecture 33 - Stimulated Absorption
... satisfies Eq. (1). However, this process is not a spontaneous one, because the atom is stimulated to absorb by the incident light field. a. ...
... satisfies Eq. (1). However, this process is not a spontaneous one, because the atom is stimulated to absorb by the incident light field. a. ...
Quantum Theory
... Heisenberg formally stated his principle by describing the relationship between the uncertainty in the measurement of a particle’s position and the uncertainty in the measurement of its momentum. Heisenberg said that the uncertainty in position (represented by Δx) times the uncertainty in momentum ...
... Heisenberg formally stated his principle by describing the relationship between the uncertainty in the measurement of a particle’s position and the uncertainty in the measurement of its momentum. Heisenberg said that the uncertainty in position (represented by Δx) times the uncertainty in momentum ...
Teacher text
... explain the results of Rutherford’s experiment: the empty atom with the tiny nucleus. The pictures in figure 2 are chemistry illustrations, used for depicting electronic orbitals. Figure 3 shows fuzzy ball atoms in a reaction in which a molecule is formed. From figure 3 one could move to a more quan ...
... explain the results of Rutherford’s experiment: the empty atom with the tiny nucleus. The pictures in figure 2 are chemistry illustrations, used for depicting electronic orbitals. Figure 3 shows fuzzy ball atoms in a reaction in which a molecule is formed. From figure 3 one could move to a more quan ...
Quantum Theory
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
Electronic Structure Calculations of InP
... InAs/InGaAs/InGaAlAs/InP material systems [7] have been already considered for TIS and even further modifications have been proposed [8]. The general microscopic mechanisms of carrier transfer in the dot–well structures are, however, far from being well understood [9]. In this paper we do not resear ...
... InAs/InGaAs/InGaAlAs/InP material systems [7] have been already considered for TIS and even further modifications have been proposed [8]. The general microscopic mechanisms of carrier transfer in the dot–well structures are, however, far from being well understood [9]. In this paper we do not resear ...
H 2 O
... (all the atoms have the same number of protons). • Molecule: a unit composed of two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds • Compound: a substance composed of 2 or more elements that have been joined by chemical bonds • Mixture: a combination of 2 or more substances that do ...
... (all the atoms have the same number of protons). • Molecule: a unit composed of two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds • Compound: a substance composed of 2 or more elements that have been joined by chemical bonds • Mixture: a combination of 2 or more substances that do ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... o *electrons gain energy (heated) they may jump into next level o *once electron emits this energy, falls back down o -electrons move b/w energy levels by losing or gaining energy (usually that is a specific amount of energy) o -Electrons can’t exist in-between levels -Atoms have nucleus and elect ...
... o *electrons gain energy (heated) they may jump into next level o *once electron emits this energy, falls back down o -electrons move b/w energy levels by losing or gaining energy (usually that is a specific amount of energy) o -Electrons can’t exist in-between levels -Atoms have nucleus and elect ...
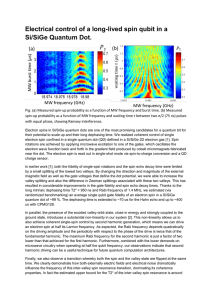
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a
... In earlier work [1], both the fidelity of single-spin rotations and the spin echo decay time were limited by a small splitting of the lowest two valleys. By changing the direction and magnitude of the external magnetic field as well as the gate voltages that define the dot potential, we were able to ...
... In earlier work [1], both the fidelity of single-spin rotations and the spin echo decay time were limited by a small splitting of the lowest two valleys. By changing the direction and magnitude of the external magnetic field as well as the gate voltages that define the dot potential, we were able to ...
Model Visualization of Atomic Quantum Numbers Three
... they are required to be able to interpret the physics knowledge appropriately and not vague or ambiguous. Such situation is further compounded again by the use of learning methods that are not appropriate physics. Students will be able to learn more easily about the concepts that are real and can be ...
... they are required to be able to interpret the physics knowledge appropriately and not vague or ambiguous. Such situation is further compounded again by the use of learning methods that are not appropriate physics. Students will be able to learn more easily about the concepts that are real and can be ...
CHAPTER 1-MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIES The
... 18. In order to seperate iron powder and pellicle components from a mixture we use the method of ____Floating and Precipitation______ 19. If a heterogenous mixture comprises solid and liquid components with different densities, than a further precipitation process is applied in order to seperate the ...
... 18. In order to seperate iron powder and pellicle components from a mixture we use the method of ____Floating and Precipitation______ 19. If a heterogenous mixture comprises solid and liquid components with different densities, than a further precipitation process is applied in order to seperate the ...
Statistical Mechanics Introduction:- The subject which deals with the
... This gives complete dynamics of the system. Here we have 3- position coordinates & 3- momentum coordinates. Phase space is represented as f (x, y, z, p x , p y , p z ) It represents the positions and momenta of all molecules at given time. Ensemble:- A collection of large number of essentially indep ...
... This gives complete dynamics of the system. Here we have 3- position coordinates & 3- momentum coordinates. Phase space is represented as f (x, y, z, p x , p y , p z ) It represents the positions and momenta of all molecules at given time. Ensemble:- A collection of large number of essentially indep ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.