PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 15
... Planck derived a formula that described the distribution of ...
... Planck derived a formula that described the distribution of ...
Cl Cl and
... 27. Why don’t elements of group 4 form ions of charge 4+? Why don’t they form ions of charge 4–? Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do eleme ...
... 27. Why don’t elements of group 4 form ions of charge 4+? Why don’t they form ions of charge 4–? Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do eleme ...
Diapositiva 1 - people@roma2
... nanoscopic objects are considered, and this requires new intriguing concepts and funny mathematical methods, many of which involve the Berry phase too. Here I just recall some. The subject is in rapid evolution, and new applications are also under way. Ballistic conduction, nonlinear magnetic behavi ...
... nanoscopic objects are considered, and this requires new intriguing concepts and funny mathematical methods, many of which involve the Berry phase too. Here I just recall some. The subject is in rapid evolution, and new applications are also under way. Ballistic conduction, nonlinear magnetic behavi ...
Chapter 4 Bohr`s model of the atom
... Chapter 4 Bohr’s model of the atom 4.5 Bohr’s postulate Bohr’s postulate (1913): (1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb attraction between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. (2) An electron move i ...
... Chapter 4 Bohr’s model of the atom 4.5 Bohr’s postulate Bohr’s postulate (1913): (1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb attraction between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. (2) An electron move i ...
Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... • Very good at showing what can and cannot form! • Predicts directionality. • Works very well with organic compounds. • Exceptions are interesting and will be discussed later! ...
... • Very good at showing what can and cannot form! • Predicts directionality. • Works very well with organic compounds. • Exceptions are interesting and will be discussed later! ...
Practice exam - Dynamic Science
... 31) Which one of the following is a renewable energy source? a) Natural gas b) Ethanol c) Uranium d) all of the above 32) Which of the following are carbon neutral fuels? a) Ethanol b) Coal and bio-diesel c) Bio-diesel and natural gas d) Ethanol and coal ...
... 31) Which one of the following is a renewable energy source? a) Natural gas b) Ethanol c) Uranium d) all of the above 32) Which of the following are carbon neutral fuels? a) Ethanol b) Coal and bio-diesel c) Bio-diesel and natural gas d) Ethanol and coal ...
answer
... Only the cis isomer is biologically active - it is a potent anti-cancer drug. The cis chloride ligands are easily replaced, allowing Pt(II) to bind to DNA and stop cell replication. It appears that the cis-geometry of the Pt-DNA bonds is important in this. The flat nature of the complex means it can ...
... Only the cis isomer is biologically active - it is a potent anti-cancer drug. The cis chloride ligands are easily replaced, allowing Pt(II) to bind to DNA and stop cell replication. It appears that the cis-geometry of the Pt-DNA bonds is important in this. The flat nature of the complex means it can ...
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... –the highest occupied energy level Core electrons – are those in the energy levels below. ...
... –the highest occupied energy level Core electrons – are those in the energy levels below. ...
1 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
... Heisenberg’s Measurement Uncertainty The above discussion does not say a word about measurements. It is instead a limit on the possible properties of a given state. Roughly, if < x|Ψ > has a narrow distribution, then < p|Ψ > will have a spread out distribution and vice versa. Heisenberg’s original p ...
... Heisenberg’s Measurement Uncertainty The above discussion does not say a word about measurements. It is instead a limit on the possible properties of a given state. Roughly, if < x|Ψ > has a narrow distribution, then < p|Ψ > will have a spread out distribution and vice versa. Heisenberg’s original p ...
fn1_1h_qm2_cr
... Quantum Information and Computers Qubits – consist of logical storage that can be 0, 1 or indeterminant between 0 and 1 Writing data: Excite an electron from E0 to E1 Reading data: Excite with energy E2-E1and analyze the photons given off Quantum entanglement Quantum error correction codes The answ ...
... Quantum Information and Computers Qubits – consist of logical storage that can be 0, 1 or indeterminant between 0 and 1 Writing data: Excite an electron from E0 to E1 Reading data: Excite with energy E2-E1and analyze the photons given off Quantum entanglement Quantum error correction codes The answ ...
Q 2
... (Frequently, physicists set c = 1 and quote mass and/or momentum in “GeV” units, as in the graph of the proton electric form factor, lecture 4. This is just a form of shorthand – they really mean GeV/c for momentum and GeV/c2 for mass.... numerically these have the same value because the value of c ...
... (Frequently, physicists set c = 1 and quote mass and/or momentum in “GeV” units, as in the graph of the proton electric form factor, lecture 4. This is just a form of shorthand – they really mean GeV/c for momentum and GeV/c2 for mass.... numerically these have the same value because the value of c ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... Arrangement of the Periodic table Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
... Arrangement of the Periodic table Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
Problems
... b. How the two boundary conditions reduce the number of acceptable solutions from two to one and limit the values of E that can be “allowed”. c. How the wave function is continuous even at the box boundaries, but dΨ/dx is not. In general dΨ/dx, which relates to the momentum because – i h d/dx is the ...
... b. How the two boundary conditions reduce the number of acceptable solutions from two to one and limit the values of E that can be “allowed”. c. How the wave function is continuous even at the box boundaries, but dΨ/dx is not. In general dΨ/dx, which relates to the momentum because – i h d/dx is the ...
Lecture 1 Review of hydrogen atom Heavy proton (put at the origin
... 3. If it is degenerate, how many states have the same energy and what are their quantum numbers ? (ignore spin) Answers ...
... 3. If it is degenerate, how many states have the same energy and what are their quantum numbers ? (ignore spin) Answers ...
down
... • With s orbitals, only σ MO exists. • With 2p orbitals, 2 MOs exist. 1) axis of the 2p orbital lies on the intermolecular axis(by convention, z axis) : σ orbital generated. It called as 3σg or σg(2pz) orbital. 2) combining 2px or 2py orbitals, π orbital generated because of nodal plane containing t ...
... • With s orbitals, only σ MO exists. • With 2p orbitals, 2 MOs exist. 1) axis of the 2p orbital lies on the intermolecular axis(by convention, z axis) : σ orbital generated. It called as 3σg or σg(2pz) orbital. 2) combining 2px or 2py orbitals, π orbital generated because of nodal plane containing t ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • It’s not hard to solve equations for the various wafefunctions if they are all alone (like H) • The problem is what happens in the presence of other electrons • The electron interactions problem • Electron interaction so complex, exact solutions are ...
... • It’s not hard to solve equations for the various wafefunctions if they are all alone (like H) • The problem is what happens in the presence of other electrons • The electron interactions problem • Electron interaction so complex, exact solutions are ...
Density functional theory
... potential which I will later introduce as exchange and correlation. It proposed an expected value of the kinetic term in the H operator that depends solely on the density. This approach is acceptable only in high electron density metals where the quantum corrections to the Couloumb potential can be ...
... potential which I will later introduce as exchange and correlation. It proposed an expected value of the kinetic term in the H operator that depends solely on the density. This approach is acceptable only in high electron density metals where the quantum corrections to the Couloumb potential can be ...
Miroir quantique pour les électrons
... Manoharan. "But we must make significant improvements before this method becomes useful in actual circuits. Making each ellipse with the STM is currently impractically slow. They would have to be easily and rapidly produced, connections to other components would also have to be devised and a rapid a ...
... Manoharan. "But we must make significant improvements before this method becomes useful in actual circuits. Making each ellipse with the STM is currently impractically slow. They would have to be easily and rapidly produced, connections to other components would also have to be devised and a rapid a ...
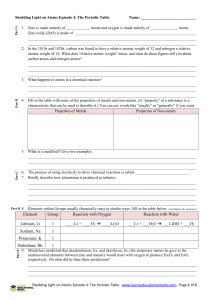
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
1AMQ, Part II Quantum Mechanics
... Deficiencies of the Bohr Model • No proper account of quantum mechanics (de Boglie waves etc.) • It is planar and the `real world’ is three dimensional . • It is for single electron atoms only. • It gets all the angular momenta wrong by one unit of h/2. ...
... Deficiencies of the Bohr Model • No proper account of quantum mechanics (de Boglie waves etc.) • It is planar and the `real world’ is three dimensional . • It is for single electron atoms only. • It gets all the angular momenta wrong by one unit of h/2. ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.