- IMSA Digital Commons
... mutually inconsistent – knowledge of one invalidates knowledge of the other. For example, if you measure the x spin of a particle, then measure the y spin, then measure the x spin again, you may get a different answer Position and momentum are incompatible observables – hence, the Heisenberg uncerta ...
... mutually inconsistent – knowledge of one invalidates knowledge of the other. For example, if you measure the x spin of a particle, then measure the y spin, then measure the x spin again, you may get a different answer Position and momentum are incompatible observables – hence, the Heisenberg uncerta ...
Two-particle systems
... mechanics, you simply can't say which electron is which as you can not put any labels on them to tell them apart. There are two possible ways to deal with indistinguishable particles, i.e. to construct two-particle wave function that is non committal to which particle is in which state: ...
... mechanics, you simply can't say which electron is which as you can not put any labels on them to tell them apart. There are two possible ways to deal with indistinguishable particles, i.e. to construct two-particle wave function that is non committal to which particle is in which state: ...
Δk/k
... In the Bohr model, this quantization may pictorially be linked to the requirement that the rotating particle must form a standing matter wave: Moreover, as the Stern-Gerlach effect shows (and as the Dirac equation describes), particles may carry spin angular momentum s, quantized to s s(s 1) , ...
... In the Bohr model, this quantization may pictorially be linked to the requirement that the rotating particle must form a standing matter wave: Moreover, as the Stern-Gerlach effect shows (and as the Dirac equation describes), particles may carry spin angular momentum s, quantized to s s(s 1) , ...
Identical Particles
... The results that we have just obtained for the independent particle approximation to the helium atom illustrate a more general result, related to the Spin-Statistics Theorem and known as the Pauli Exclusion Principle which states No two identical fermions can be in the same quantum state For example ...
... The results that we have just obtained for the independent particle approximation to the helium atom illustrate a more general result, related to the Spin-Statistics Theorem and known as the Pauli Exclusion Principle which states No two identical fermions can be in the same quantum state For example ...
Particles and interactions
... By the end of this topic you should be able to: •state the meaning of the term elementary particle; •identify the three classes of elementary, the quarks, the leptons and the exchange particles; •understand the meaning of quantum numbers; •state the meaning of the term antiparticle; •classify partic ...
... By the end of this topic you should be able to: •state the meaning of the term elementary particle; •identify the three classes of elementary, the quarks, the leptons and the exchange particles; •understand the meaning of quantum numbers; •state the meaning of the term antiparticle; •classify partic ...
Lecture 29B - UCSD Department of Physics
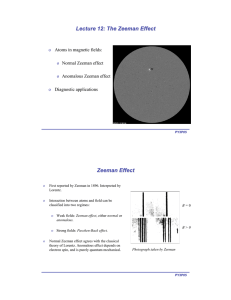
... Suppose a weak magnetic field is applied to an atom and its direction coincides with z axis. Then direction of the angular momentum vector relative to the z axis is quantized! ...
... Suppose a weak magnetic field is applied to an atom and its direction coincides with z axis. Then direction of the angular momentum vector relative to the z axis is quantized! ...
The Quantum Mechanics of MRI
... • Pauli’s exclusion principle ensures that many shells are filled. • Nuclei with uneven (even) atomic number have half-integer (integer) spin • Nuclei with even atomic and mass numbers have zero spin. • Unpaired neutrons/protons provide the spin for MRI. ...
... • Pauli’s exclusion principle ensures that many shells are filled. • Nuclei with uneven (even) atomic number have half-integer (integer) spin • Nuclei with even atomic and mass numbers have zero spin. • Unpaired neutrons/protons provide the spin for MRI. ...
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY AND GROUP THEORY(2) M.Sc. DEGREE
... To every observable in classical mechanics there corresponds a linear Hermitian operator in quantum mechanics. Any measurable dynamical variable is called an observable. The classical mechanical expressions for these observables can be written in terms of position co ordinates and momentum coordinat ...
... To every observable in classical mechanics there corresponds a linear Hermitian operator in quantum mechanics. Any measurable dynamical variable is called an observable. The classical mechanical expressions for these observables can be written in terms of position co ordinates and momentum coordinat ...
QUANTUM TUNNELING AND SPIN by Robert J
... 2. Two beams come out. This is really strange. Shouldn't the particles all remember their orientation exiting the first Stern-Gerlach experiment? They do not. This is yet another non-classical result, fundamental to quantum mechanics. ...
... 2. Two beams come out. This is really strange. Shouldn't the particles all remember their orientation exiting the first Stern-Gerlach experiment? They do not. This is yet another non-classical result, fundamental to quantum mechanics. ...
Coherent control of a single nuclear spin with an electric field
... with those electrons. In recent experiments at very low temperature (30 mK), we were able to show that the terbium’s nuclear spin can be manipulated purely by an oscillating electric field (the microwave field represented in Fig. 1). This is remarkable because the magnetic dipole associated with the ...
... with those electrons. In recent experiments at very low temperature (30 mK), we were able to show that the terbium’s nuclear spin can be manipulated purely by an oscillating electric field (the microwave field represented in Fig. 1). This is remarkable because the magnetic dipole associated with the ...