Incompatible results of quantum measurements
... Various q u a n t u m " p a r a d o x e s " [ 1-5 ] are based on the a s s u m p t i o n that the result o f the m e a s u r e m e n t o f an o p e r a t o r A d e p e n d s only on A and on the state o f the q u a n t u m system being measured (here, the word " s t a t e " includes not only the wav ...
... Various q u a n t u m " p a r a d o x e s " [ 1-5 ] are based on the a s s u m p t i o n that the result o f the m e a s u r e m e n t o f an o p e r a t o r A d e p e n d s only on A and on the state o f the q u a n t u m system being measured (here, the word " s t a t e " includes not only the wav ...
Chapter 7 Many-Electron Atoms
... gives the z component of the spin angular momentum. See figure 7.2 for the two possible orientations of the spin angular momentum vector in a magnetic field. You can also calculate the spin magnetic moment of an electron, and its z component. Since we skipped corresponding section on magnetism in Ch ...
... gives the z component of the spin angular momentum. See figure 7.2 for the two possible orientations of the spin angular momentum vector in a magnetic field. You can also calculate the spin magnetic moment of an electron, and its z component. Since we skipped corresponding section on magnetism in Ch ...
A proof of Bell`s inequality in quantum mechanics using causal
... observed. The results of experiments that close this loophole by observing a higher fraction of the pairs should be available within the next several years. Nearly all physicists believe that the results of these experiments will be precisely as predicted by quantum mechanics and thus violate Bell’ ...
... observed. The results of experiments that close this loophole by observing a higher fraction of the pairs should be available within the next several years. Nearly all physicists believe that the results of these experiments will be precisely as predicted by quantum mechanics and thus violate Bell’ ...
Electronic structure_(download)
... All elements have the same set Atomic number dictates how many are filled – how many electrons are added Filling orbitals follows a fixed pattern: lowest energy ones first But need to know... how many electrons in an orbital? ...
... All elements have the same set Atomic number dictates how many are filled – how many electrons are added Filling orbitals follows a fixed pattern: lowest energy ones first But need to know... how many electrons in an orbital? ...
slides - University of Toronto Physics
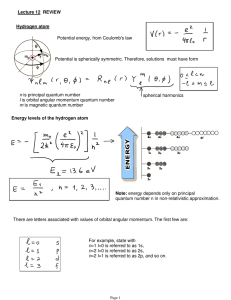
... An electron in a hydrogen atom is in a state with orbital angular momentum number ! = 1. If the total angular momentum quantum number is j=3/2, and the z component of total angular momentum is ! / 2 what is the probability of finding the electron with ms = +1 / 2 ? (next slides). See also problems 4 ...
... An electron in a hydrogen atom is in a state with orbital angular momentum number ! = 1. If the total angular momentum quantum number is j=3/2, and the z component of total angular momentum is ! / 2 what is the probability of finding the electron with ms = +1 / 2 ? (next slides). See also problems 4 ...
Erwin Schrodinger an Max Born and wavelength
... physical meaning of the wave function and in subsequent years repeatedly criticized the conventional Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics ...
... physical meaning of the wave function and in subsequent years repeatedly criticized the conventional Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics ...
3D simulation of a silicon quantum dot in
... semiconductor structures containing silicon quantum dots immersed in a magnetic field based on Current Spin Density Functional Theory (CSDFT) [7], in the framework of the NanoTCAD ViDES package. In this paper, we discuss the physical model and the numerical approach we adopt, and we present the simu ...
... semiconductor structures containing silicon quantum dots immersed in a magnetic field based on Current Spin Density Functional Theory (CSDFT) [7], in the framework of the NanoTCAD ViDES package. In this paper, we discuss the physical model and the numerical approach we adopt, and we present the simu ...
Is Anything Real? Have Physicists Lost Their Grip on Reality?
... Newton's theory leads to predictions that are very impressively verified. Does it explain gravity? What is gravity? What is the reality behind the name “gravity”? Newton: “I don't know. This just works.” Did Newton discover gravity or invent it? ...
... Newton's theory leads to predictions that are very impressively verified. Does it explain gravity? What is gravity? What is the reality behind the name “gravity”? Newton: “I don't know. This just works.” Did Newton discover gravity or invent it? ...
... possible values of the angular momentum. Calculate the energy eigenvalues. What is the energy difference between the ground state of zero angular momentum and the first rotational state? Show that this approaches infinity as N . Contrast this with the comparable energy for a “nicked” cylinder, wh ...
... possible values of the angular momentum. Calculate the energy eigenvalues. What is the energy difference between the ground state of zero angular momentum and the first rotational state? Show that this approaches infinity as N . Contrast this with the comparable energy for a “nicked” cylinder, wh ...
Many-Electron Atoms Thornton and Rex, Ch. 8
... A careful analysis involving L and S in multi-electron atoms is very complicated. Hund’s Rules (Empirical rules for filling a subshell, while minimizing the energy) 1) The total Spin should be maximized (without violating Pauli Exclusion Principle). 2) Without violating Rule 1, the Orbital Angular m ...
... A careful analysis involving L and S in multi-electron atoms is very complicated. Hund’s Rules (Empirical rules for filling a subshell, while minimizing the energy) 1) The total Spin should be maximized (without violating Pauli Exclusion Principle). 2) Without violating Rule 1, the Orbital Angular m ...
1. dia
... and by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, the uncertainty in simultaneously determining proton velocity and position is given as follows: ...
... and by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, the uncertainty in simultaneously determining proton velocity and position is given as follows: ...