Nearly Free Electron Approximation
... cannot be a net change into any particular direction or particular set of them. So then the material cannot conduct electricity, (no net momentum in a particular direction) In a metal however, even at 0K, there is not a problem because in the case of the alkali metals and noble metals there are alwa ...
... cannot be a net change into any particular direction or particular set of them. So then the material cannot conduct electricity, (no net momentum in a particular direction) In a metal however, even at 0K, there is not a problem because in the case of the alkali metals and noble metals there are alwa ...
Atom and Light
... gas occur at exactly the same wavelengths as the emission lines in the emission line spectrum of the same gas. ...
... gas occur at exactly the same wavelengths as the emission lines in the emission line spectrum of the same gas. ...
The Bohr model for the electrons
... Couldn’t explain why orbits were allowed Only successful agreement with experiment was with the H atom Introduced connection between spectra and electron structure Concept of allowed orbits is developed further with new knowledge Nonetheless, an important contribution, worthy of the Nobel prize ...
... Couldn’t explain why orbits were allowed Only successful agreement with experiment was with the H atom Introduced connection between spectra and electron structure Concept of allowed orbits is developed further with new knowledge Nonetheless, an important contribution, worthy of the Nobel prize ...
Chapter 11: Electromagnetic Waves
... The wave model cannot account for the spectrum of light emitted by hot objects (like stars) The photoelectric effect – the emission of an electron from a metal surface when subjected to ultraviolet radiation. • In an effort to explain these two issues, physicists developed the quantum theory Qua ...
... The wave model cannot account for the spectrum of light emitted by hot objects (like stars) The photoelectric effect – the emission of an electron from a metal surface when subjected to ultraviolet radiation. • In an effort to explain these two issues, physicists developed the quantum theory Qua ...
Atomic Theory Notes
... Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. They make up everything around us; Your desk, the board, your body, everything is made of atoms! Atoms are too small to see without powerful microscopes. ...
... Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. They make up everything around us; Your desk, the board, your body, everything is made of atoms! Atoms are too small to see without powerful microscopes. ...
File - Rogers` Rocket Science
... An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a ________ or _________ charge. Remember that atoms are neutral because the # of protons = # of electrons. Some compounds are composed of particles called ions. Positive and negative ions are formed when __________ are __________ (lost or gained) ...
... An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a ________ or _________ charge. Remember that atoms are neutral because the # of protons = # of electrons. Some compounds are composed of particles called ions. Positive and negative ions are formed when __________ are __________ (lost or gained) ...
chem 1411- chapter 7
... Radiations like visible light, X-rays, UV radiations, IR radiations, cosmic rays etc are called electromagnetic radiations. They are associated with electric and magnetic fields. They are produced by the oscillation or vibration of charged particles. . All electromagnetic radiations travel with the ...
... Radiations like visible light, X-rays, UV radiations, IR radiations, cosmic rays etc are called electromagnetic radiations. They are associated with electric and magnetic fields. They are produced by the oscillation or vibration of charged particles. . All electromagnetic radiations travel with the ...
OCR Document
... Some atoms or molecules in their neutral gaseous state have an affinity to acquire a free electron and form a stable negative ion. This property of negative ion formation is known as 'electron attachment' or 'electron affinity'. It has been proved that the atomic or molecular gases having electron a ...
... Some atoms or molecules in their neutral gaseous state have an affinity to acquire a free electron and form a stable negative ion. This property of negative ion formation is known as 'electron attachment' or 'electron affinity'. It has been proved that the atomic or molecular gases having electron a ...
Multi-Particle States 31.1 Multi
... isolation. Indeed, we can establish the relative correctness of an electron in isolation only by considering its relation to other electrons and particles. This is the task we now undertake: A description of wavefunctions of systems. Particles in isolation is itself a classical concept – fundamental ...
... isolation. Indeed, we can establish the relative correctness of an electron in isolation only by considering its relation to other electrons and particles. This is the task we now undertake: A description of wavefunctions of systems. Particles in isolation is itself a classical concept – fundamental ...
chapter 7 quiz
... 15._P__The charge on an “gamma” particle. R) Henry Moseley 16._M__The empty space around the nucleus containing S) Dimitri Mendeleev electrons. T) atomic mass 17._Z__The name that describes protons, neutrons, U) chemical formula and electrons. V) proton 18._O__The short form way of representing an e ...
... 15._P__The charge on an “gamma” particle. R) Henry Moseley 16._M__The empty space around the nucleus containing S) Dimitri Mendeleev electrons. T) atomic mass 17._Z__The name that describes protons, neutrons, U) chemical formula and electrons. V) proton 18._O__The short form way of representing an e ...
history of particle physics (PowerPoint 13.93MB)
... Particle and Nuclear Physics are the studies to answer this question ...
... Particle and Nuclear Physics are the studies to answer this question ...
Hydrogen Atom Energy Levels
... Note: The energy, frequency, and wavelength of emitted or absorbed light should always be a positive number! The words absorption and emission indicate whether ...
... Note: The energy, frequency, and wavelength of emitted or absorbed light should always be a positive number! The words absorption and emission indicate whether ...
Electrons and Photons
... • A specific quantity of light • Bohr said that when energy is added to atoms, the electrons gain a “quantum” of energy to move to a higher level. • When electrons relax back to their normal state, they emit a quantum of energy to go back to the lowest level. ...
... • A specific quantity of light • Bohr said that when energy is added to atoms, the electrons gain a “quantum” of energy to move to a higher level. • When electrons relax back to their normal state, they emit a quantum of energy to go back to the lowest level. ...
Lab-on-a-chip Microfluidic System.
... • Separation and characterization of specific particle and cell is important for a wide range of applications in pharmaceutical companies or cancer cell research. • We have applied AC-based DEP to capture and separate vast number of particles and cells in single particle level. • The electrical prop ...
... • Separation and characterization of specific particle and cell is important for a wide range of applications in pharmaceutical companies or cancer cell research. • We have applied AC-based DEP to capture and separate vast number of particles and cells in single particle level. • The electrical prop ...
EP-307 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... if you do an experiment it should tell you whether it will behave as a wave or particle. Second Question brings us to the domain of the theory ...
... if you do an experiment it should tell you whether it will behave as a wave or particle. Second Question brings us to the domain of the theory ...
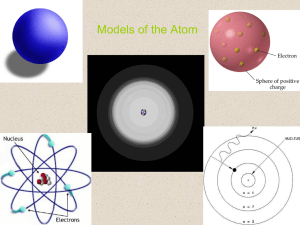
Models of the Atom
... • The modern description of electrons in an atom • Determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus. • Based on probability ...
... • The modern description of electrons in an atom • Determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus. • Based on probability ...
Testing Lorentz Invariance in High-Energy
... For example, the discovery that in string theory the tachyon potential often contains a minimum where Lorentz symmetry would be spontaneously broken spurred a great deal of interest in this subject. [Kostelecký and Samuel, PRD 39, 683 (1989)] ...
... For example, the discovery that in string theory the tachyon potential often contains a minimum where Lorentz symmetry would be spontaneously broken spurred a great deal of interest in this subject. [Kostelecký and Samuel, PRD 39, 683 (1989)] ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.