Objectives for Third Exam
... b. You should understand how magnets can be formed from ferromagnetic elements. Concept Area III: Atomic Orbital Energy Level Diagrams a. You need to remember what the four quantum numbers tell you (names of orbitals, how many degenerate orbitals). b. You need to know how many orbitals of each type ...
... b. You should understand how magnets can be formed from ferromagnetic elements. Concept Area III: Atomic Orbital Energy Level Diagrams a. You need to remember what the four quantum numbers tell you (names of orbitals, how many degenerate orbitals). b. You need to know how many orbitals of each type ...
Algorithms and Architectures for Quantum Computers—I. Chuang
... rotations. It is useful for many tasks in quantum information theory, but so far its algorithmic applications have been largely unexplored. Recently, we found an efficient (polynomial-time) quantum circuit that, analogous to the quantum Fourier transform, maps the computational basis to the Schur ba ...
... rotations. It is useful for many tasks in quantum information theory, but so far its algorithmic applications have been largely unexplored. Recently, we found an efficient (polynomial-time) quantum circuit that, analogous to the quantum Fourier transform, maps the computational basis to the Schur ba ...
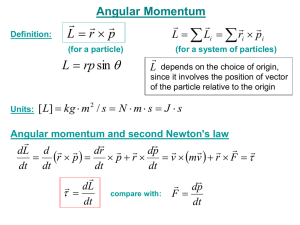
7. SSM REASONING According to Newton`s second
... to the fist is equal to the mass of the fist multiplied by its acceleration. The data in the problem gives the final velocity of the fist and the time it takes to acquire that velocity. The average acceleration can be obtained directly from these data using the definition of average acceleratio ...
... to the fist is equal to the mass of the fist multiplied by its acceleration. The data in the problem gives the final velocity of the fist and the time it takes to acquire that velocity. The average acceleration can be obtained directly from these data using the definition of average acceleratio ...
Thermodynamics: Kinetic Theory
... confused about what its point was. Can you explain that? Writing out 8-2A helped, but I still barely understand anything after 21-2. The amount of equations that are being juggled around and the various equalities and substitutions being made are more than I can follow without a clearer way to wal ...
... confused about what its point was. Can you explain that? Writing out 8-2A helped, but I still barely understand anything after 21-2. The amount of equations that are being juggled around and the various equalities and substitutions being made are more than I can follow without a clearer way to wal ...
Gravitation - Siena College
... Published in Principia, 1687 (needed to develop calculus to prove his assumptions) ...
... Published in Principia, 1687 (needed to develop calculus to prove his assumptions) ...
MECH1 Problem Sheet 6 Solutions Constants of motion, angular
... This function clearly goes to +∞ for r going to zero and infinity, with a single minimum, corresponding to the above circular orbit. Hence, r is finite for every orbit (as for the finite total energy E one must always have E ≥ Uef f . 4. A particle of mass m moves in the central force field with the ...
... This function clearly goes to +∞ for r going to zero and infinity, with a single minimum, corresponding to the above circular orbit. Hence, r is finite for every orbit (as for the finite total energy E one must always have E ≥ Uef f . 4. A particle of mass m moves in the central force field with the ...
Monday, Nov. 12, 2012
... • The spinning electron reacts similarly to the orbiting electron in a magnetic field. (Dirac showed that this is ecessary due to special relativity..) • We should try to find L, Lz, ℓ, and mℓ. • The magnetic spin quantum number ms has only two values, ms = ±½. The electron’s spin will be either “up ...
... • The spinning electron reacts similarly to the orbiting electron in a magnetic field. (Dirac showed that this is ecessary due to special relativity..) • We should try to find L, Lz, ℓ, and mℓ. • The magnetic spin quantum number ms has only two values, ms = ±½. The electron’s spin will be either “up ...