Review Sheet
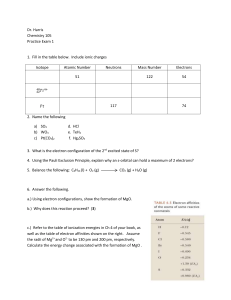
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
summary sheet
... SUMMARY Electrons in Atoms (Section 29.1) The Bohr model fails to fully describe atoms because it combines elements of classical physics with some principles of quantum mechanics. To explain the observed properties of an atom, electrons must be described with a wave function that is determined by so ...
... SUMMARY Electrons in Atoms (Section 29.1) The Bohr model fails to fully describe atoms because it combines elements of classical physics with some principles of quantum mechanics. To explain the observed properties of an atom, electrons must be described with a wave function that is determined by so ...
Notes
... could move only in certain allowed circular orbits without radiating energy (classically, an accelerating charge (such as the electron moving in a circle) would continuously radiate energy and spiral into the nucleus in a very short time). Bohr called these allowed orbits stationary states. A photon ...
... could move only in certain allowed circular orbits without radiating energy (classically, an accelerating charge (such as the electron moving in a circle) would continuously radiate energy and spiral into the nucleus in a very short time). Bohr called these allowed orbits stationary states. A photon ...
Chapter 7
... Light is electromagnetic radiation. A type of energy embodies in oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
... Light is electromagnetic radiation. A type of energy embodies in oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
Part 1 Electron Arrangement
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
honors-chapter6-reading
... 5. Sample problems: Pg. 253: 13, 15, 17, (radiant energy) 6.2 Quantized Energy and Photons 1. What is the relationship between hot objects and quantized energy? 2. Explain the relationship between quantum of energy and Planck’s constant. Be sure to include the equation for energy in your discussion. ...
... 5. Sample problems: Pg. 253: 13, 15, 17, (radiant energy) 6.2 Quantized Energy and Photons 1. What is the relationship between hot objects and quantized energy? 2. Explain the relationship between quantum of energy and Planck’s constant. Be sure to include the equation for energy in your discussion. ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
energy levels
... • An absorption spectrum is obtained by passing a white light from a continuous source ...
... • An absorption spectrum is obtained by passing a white light from a continuous source ...
Chapter 31 Atomic Physics
... corresponding energy. Such integer number is called a quantum number. Quantum mechanics describes the hydrogen atom in terms of four quantum numbers: (1) the principal quantum number n, which can have the integer values n = 1, 2, 3, ...; (2) the orbital quantum number l, which can have values l = 0, ...
... corresponding energy. Such integer number is called a quantum number. Quantum mechanics describes the hydrogen atom in terms of four quantum numbers: (1) the principal quantum number n, which can have the integer values n = 1, 2, 3, ...; (2) the orbital quantum number l, which can have values l = 0, ...
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 6: Quantum mechanics and spectroscopy
... p = mv Prediction: particles (electrons, neutrons, etc.) should diffract like light under appropriate conditions ...
... p = mv Prediction: particles (electrons, neutrons, etc.) should diffract like light under appropriate conditions ...
Section 13.2 - CPO Science
... from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
... from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
stationary state
... jump, from one stationary state to another. During this transition it does emit radiation. When an electron makes a transition from one stationary state to another, the energy difference ∆E is released as a single photon of frequency ν= ∆E /h ( or h ν= Ei-Ef ). • In the limit of large orbits and lar ...
... jump, from one stationary state to another. During this transition it does emit radiation. When an electron makes a transition from one stationary state to another, the energy difference ∆E is released as a single photon of frequency ν= ∆E /h ( or h ν= Ei-Ef ). • In the limit of large orbits and lar ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
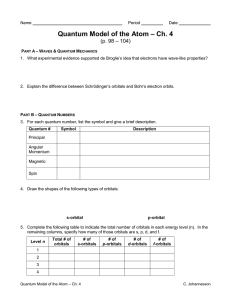
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
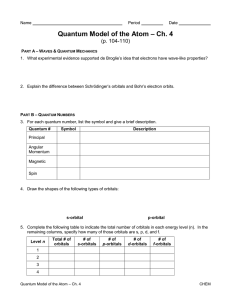
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
... 5. Complete the following table to indicate the total number of orbitals in each energy level (n). In the remaining columns, specify how many of those orbitals are s, p, d, and f. Level n ...
do physics online from quanta to quarks the bohr model of the atom
... electron in “allowed” circular stable orbit such that the electron’s angular momentum was quantised. The electron in a stable orbit did not lose energy by the emission of electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that classical electromagnetic theory was not completely valid for atomic systems. ...
... electron in “allowed” circular stable orbit such that the electron’s angular momentum was quantised. The electron in a stable orbit did not lose energy by the emission of electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that classical electromagnetic theory was not completely valid for atomic systems. ...
Chemistry 2000 Review: quantum mechanics of
... This equation was know to belong to a special class known as an eigenvector equation: an operator acts on a function (ψ) and generates a scalar times the same function Ψ is known as the wavefunction of the electron: there are an infinite number of such wavefunctions, each of which is characterized b ...
... This equation was know to belong to a special class known as an eigenvector equation: an operator acts on a function (ψ) and generates a scalar times the same function Ψ is known as the wavefunction of the electron: there are an infinite number of such wavefunctions, each of which is characterized b ...
The Bohr model depicts atoms as small, positively
... Although it challenged the knowledge of classical physics, the model's success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was intro ...
... Although it challenged the knowledge of classical physics, the model's success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was intro ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.