Quantum Mechanical Model
... Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
... Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
chapter 7 – cyu
... Geissler develop the gas discharge tube. This tube, when it has all the air pumped out of it, initially glowed blue then green at one end when under very low pressure. The green glow at the anode end was the result of the electrons being released from the cathode at the opposite end of the tube. The ...
... Geissler develop the gas discharge tube. This tube, when it has all the air pumped out of it, initially glowed blue then green at one end when under very low pressure. The green glow at the anode end was the result of the electrons being released from the cathode at the opposite end of the tube. The ...
Chemistry Name______________________________________
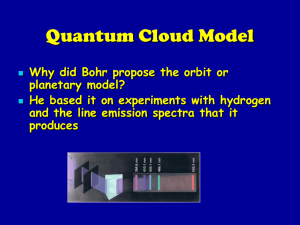
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
o Lecturer: Dr. Peter Gallagher Email:
... 1. Fails describe why certain spectral lines are brighter than others => no mechanism for calculating transition probabilities. 2. Violates the uncertainty principal which dictates that position and momentum cannot be simultaneously determined. o Bohr model gives a basic conceptual model of elect ...
... 1. Fails describe why certain spectral lines are brighter than others => no mechanism for calculating transition probabilities. 2. Violates the uncertainty principal which dictates that position and momentum cannot be simultaneously determined. o Bohr model gives a basic conceptual model of elect ...
Basic Chemistry Notes II
... 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most important electrons because they determine bonding/reactivity of atom. ...
... 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most important electrons because they determine bonding/reactivity of atom. ...
Physics 228, Lecture 11 Monday, February 28, 2005 Bohr Model
... More complicated atoms also have a discrete set of states, although it is not possible to calculate the energies exactly for complex atoms the way it is for hydrogen. But the states play the same role, in particular for the emission and absorption of photons. As we saw, the atom can emit light if it ...
... More complicated atoms also have a discrete set of states, although it is not possible to calculate the energies exactly for complex atoms the way it is for hydrogen. But the states play the same role, in particular for the emission and absorption of photons. As we saw, the atom can emit light if it ...
The Particulate Nature of Light
... The Bohr model was developed in the early 20th century and has since been superseded by more advanced theories. In modern theory the wave-particle duality model has been replaced by describing all matter in terms of wave functions. These wave functions are useful in computational terms and they all ...
... The Bohr model was developed in the early 20th century and has since been superseded by more advanced theories. In modern theory the wave-particle duality model has been replaced by describing all matter in terms of wave functions. These wave functions are useful in computational terms and they all ...
Slide 1
... 4. Some of these photons run in a direction parallel to the ruby's axis, so they bounce back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
... 4. Some of these photons run in a direction parallel to the ruby's axis, so they bounce back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
Homework 3
... 1. Explain the terms wavelength and amplitude. If a photon has a frequency of 9 1010 Hz what is its wavelength? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does this correspond to? ...
... 1. Explain the terms wavelength and amplitude. If a photon has a frequency of 9 1010 Hz what is its wavelength? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does this correspond to? ...
from last time:
... Start by writing down the S.E. with the appropriate potential energy, e.g. for the S.H. Oscillator U = ½ kx2. If U is not cts you may need to write down the S.E. for each distinct region where there is a different U. Find a wave function which is a solution to the S.E. – this is often done by educat ...
... Start by writing down the S.E. with the appropriate potential energy, e.g. for the S.H. Oscillator U = ½ kx2. If U is not cts you may need to write down the S.E. for each distinct region where there is a different U. Find a wave function which is a solution to the S.E. – this is often done by educat ...
quantum mechanical model
... energy of atoms changes when the atom absorbs or emits light. • Stated that the electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun. ...
... energy of atoms changes when the atom absorbs or emits light. • Stated that the electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun. ...
Quantum numbers
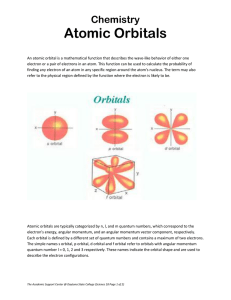
... When solving Schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen model we find wave functions / orbitals. Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called Quantum ...
... When solving Schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen model we find wave functions / orbitals. Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called Quantum ...
Example solution to the exercise 1
... The lifespan of the classical atom can be calculated when the above differential is integrated from t = 0 to tend when the electron collapses into the nucleus. During this time the radius changes from r = a0 , when t = 0 to r = 0 when t = tend . For the final calculation one requires the natural con ...
... The lifespan of the classical atom can be calculated when the above differential is integrated from t = 0 to tend when the electron collapses into the nucleus. During this time the radius changes from r = a0 , when t = 0 to r = 0 when t = tend . For the final calculation one requires the natural con ...
Modern Physics Important Concepts for AP Test
... o J.J. Thomson “plum pudding” model o Rutherford’s experiment found most matter concentrated in nucleus proposed planetary type atomic model o Bohr Model of Hydrogen Electrons exist only in certain allowed orbits determined by integer, n. (quantized energy levels) Bohr radius = 0.0529 nm (Use fo ...
... o J.J. Thomson “plum pudding” model o Rutherford’s experiment found most matter concentrated in nucleus proposed planetary type atomic model o Bohr Model of Hydrogen Electrons exist only in certain allowed orbits determined by integer, n. (quantized energy levels) Bohr radius = 0.0529 nm (Use fo ...
08_lecture_ppt
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.