Document
... 2. Rutherford’s model provided an explanation for the emission of light from atoms. What was this mechanism and why was it unsatisfactory? 3. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Ze ...
... 2. Rutherford’s model provided an explanation for the emission of light from atoms. What was this mechanism and why was it unsatisfactory? 3. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Ze ...
General Chemistry - Valdosta State University
... - Visible light is a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum ...
... - Visible light is a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum ...
1 - shawnschmitt
... g. Mole- the amount of particles in 12g of Carbon-12, also, the amount of substance having 6.022x1023 of any kind of particle h. half-life- the amount of time required for ½ of the mass of an isotope to decay i. metalloid- those elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals j. Ionizatio ...
... g. Mole- the amount of particles in 12g of Carbon-12, also, the amount of substance having 6.022x1023 of any kind of particle h. half-life- the amount of time required for ½ of the mass of an isotope to decay i. metalloid- those elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals j. Ionizatio ...
Lecture 5
... the total angular momentum J=|L-S| has the lowest in energy. If the outermost subshell is more than half-filled, the level with the highest value of J=L+S has the lowest energy. ...
... the total angular momentum J=|L-S| has the lowest in energy. If the outermost subshell is more than half-filled, the level with the highest value of J=L+S has the lowest energy. ...
Modern Atomic Theory (aka the electron chapter!)
... • Run electricity through various gases, creating light • Look at the light using a spectroscope to separate the light into its component colors • Using colored pencils, draw the line spectra (all of the lines) and ...
... • Run electricity through various gases, creating light • Look at the light using a spectroscope to separate the light into its component colors • Using colored pencils, draw the line spectra (all of the lines) and ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... This model is a direct result of the discovery of the nucleus by Rutherford in 1911. In this model, stationary electrons surround a center of positive charge. ...
... This model is a direct result of the discovery of the nucleus by Rutherford in 1911. In this model, stationary electrons surround a center of positive charge. ...
May 2005
... Problem A long, straight coaxial cable of length L has an inner conductor of radius a and an outer conductor of inner radius b. Assume the insulating region between the conductors has free-space values of the electric and magnetic permittivities. One end of the cable is attached to a load resistor R ...
... Problem A long, straight coaxial cable of length L has an inner conductor of radius a and an outer conductor of inner radius b. Assume the insulating region between the conductors has free-space values of the electric and magnetic permittivities. One end of the cable is attached to a load resistor R ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... the energy of the electron is directly related to the energy of the photon. the threshold of energy must be exceeded for electron emission. The total energy of a stream of particles (photons) of that energy will be: ...
... the energy of the electron is directly related to the energy of the photon. the threshold of energy must be exceeded for electron emission. The total energy of a stream of particles (photons) of that energy will be: ...
2 Atomic Structure
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
... Students should be able to draw an energy level diagram, show transitions between different energy levels and recognize that the lines in a line spectrum are directly related to these differences. An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible an ...
Chapter 8 - Bakersfield College
... electron in an atom possesses a specific energy level that is dependent on the orbit it is in. An electron in the innermost orbit has the least energy. B. Electron orbits are identified by a quantum number n, and each orbit corresponds to a specific energy level of the atom. 1. Electrons cannot poss ...
... electron in an atom possesses a specific energy level that is dependent on the orbit it is in. An electron in the innermost orbit has the least energy. B. Electron orbits are identified by a quantum number n, and each orbit corresponds to a specific energy level of the atom. 1. Electrons cannot poss ...
File
... orbital quantum numbers. b. magnetic quantum numbers. c. spin quantum numbers. d. principal quantum numbers. ...
... orbital quantum numbers. b. magnetic quantum numbers. c. spin quantum numbers. d. principal quantum numbers. ...
Periodic Trends/Patterns
... periodic table, but by the isoelectronic series. The more positive an ion is the smaller it is because Zeff increases, while the more negative an ion, the larger it is because Zeff ...
... periodic table, but by the isoelectronic series. The more positive an ion is the smaller it is because Zeff increases, while the more negative an ion, the larger it is because Zeff ...
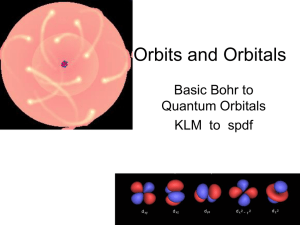
Orbits and Orbitals
... • Look up the Atomic number, and then determine (not look up) the electron orbital ...
... • Look up the Atomic number, and then determine (not look up) the electron orbital ...
Electron-Config
... Energy is always absorbed or emitted in “packets” which he called quanta. Photon= quantum of light 10th grader = High school student ...
... Energy is always absorbed or emitted in “packets” which he called quanta. Photon= quantum of light 10th grader = High school student ...
Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
3.3 Why do atoms radiate light?
... i.e. the dipole moment of the atom will change periodically. Consequently the atom serves as a sender for electromagnetic radiation with the frequency (ω2 − ω1 ). It will loose power in the state with the higher energy. After a short time the atom will be in the ground state which is not a mixed sta ...
... i.e. the dipole moment of the atom will change periodically. Consequently the atom serves as a sender for electromagnetic radiation with the frequency (ω2 − ω1 ). It will loose power in the state with the higher energy. After a short time the atom will be in the ground state which is not a mixed sta ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 Test Multiple Choice (1.5% each) Identify the
... c. the 2s orbital has a slightly different shape. 24. The set of orbitals that are dumbbell-shaped and directed along the x, y, and z axes are called a. f orbitals. c. d orbitals. b. p orbitals. 25. In SI, the frequency of electromagnetic radiation is measured in a. quanta. c. hertz. b. nanometers. ...
... c. the 2s orbital has a slightly different shape. 24. The set of orbitals that are dumbbell-shaped and directed along the x, y, and z axes are called a. f orbitals. c. d orbitals. b. p orbitals. 25. In SI, the frequency of electromagnetic radiation is measured in a. quanta. c. hertz. b. nanometers. ...
Chapter4 Nuclear atom - UCF College of Sciences
... If the atom consisted of a positively charged sphere of radius 10-10 m, containing electrons as in the Thomson model, only a very small scattering deflection angle could be observed. Such model could not possibly account for the large angles scattering. The unexpected large angles α-particles scatt ...
... If the atom consisted of a positively charged sphere of radius 10-10 m, containing electrons as in the Thomson model, only a very small scattering deflection angle could be observed. Such model could not possibly account for the large angles scattering. The unexpected large angles α-particles scatt ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.



![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008517000_1-9aef89c0ca089782f518550164188024-300x300.png)