APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... The smallest unique particle of matter is an atom and atoms can combine physically and chemically. Correlations Unifying Understanding ...
... The smallest unique particle of matter is an atom and atoms can combine physically and chemically. Correlations Unifying Understanding ...
Problem Set 11: Chemistry Graduate Quantum I Physics 6572
... The semi-empirical mass formula treats the nucleus primarily as a drop of liquid, with a ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucleus is a liquid of nucleons of roughly constant density, then its radius R ∼ A1/3 and hen ...
... The semi-empirical mass formula treats the nucleus primarily as a drop of liquid, with a ‘condensation energy’ aV A, where A = N + Z is the number of nucleons, and a surface tension energy aS A2/3 . (If the nucleus is a liquid of nucleons of roughly constant density, then its radius R ∼ A1/3 and hen ...
THE ATOM
... Compare the quantum and wave theories of light and discuss why both are needed. Describe X-rays and interpret their production in terms of the quantum theory of light. Discuss what is meant by the matter wave of a moving particle. State the uncertainty principle and interpret it in terms of matter w ...
... Compare the quantum and wave theories of light and discuss why both are needed. Describe X-rays and interpret their production in terms of the quantum theory of light. Discuss what is meant by the matter wave of a moving particle. State the uncertainty principle and interpret it in terms of matter w ...
The nucleus
... Angular momentum and parity (J+ or J-) a protons and neutrons have spin s=1/2 a protons and neutrons move inside the nucleus and have orbital angular momentum l How do we add the l’s and s’s of the nucleons? J = Σ jnucleon ‘angular momentum’ or ‘spin’ parity of the nucleus: λ = (-1)l where l is the ...
... Angular momentum and parity (J+ or J-) a protons and neutrons have spin s=1/2 a protons and neutrons move inside the nucleus and have orbital angular momentum l How do we add the l’s and s’s of the nucleons? J = Σ jnucleon ‘angular momentum’ or ‘spin’ parity of the nucleus: λ = (-1)l where l is the ...
For these questions, use the simulation “Quantum tunelling” and
... simulation, including the step-by-step exploration (click on the “Step-by-step Exploration” tab). ...
... simulation, including the step-by-step exploration (click on the “Step-by-step Exploration” tab). ...
ap quick review
... Metallic carbonates metal oxides + carbon dioxide Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex Complex format ...
... Metallic carbonates metal oxides + carbon dioxide Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex Complex format ...
atom
... of hydrogen is sometimes called protium. It accounts for 99.9885% of the hydrogen atoms found on Earth. The nucleus of a protium atom consists of one proton only, and it has one electron moving about it. ...
... of hydrogen is sometimes called protium. It accounts for 99.9885% of the hydrogen atoms found on Earth. The nucleus of a protium atom consists of one proton only, and it has one electron moving about it. ...
electron cloud - Wickliffe City School
... Each step from left to right adds a proton and an electron (and 1 or 2 neutrons) and electrons are added to existing energy levels. The effect is that the more positive nucleus has a greater pull on the electron cloud. The nucleus is more positive and the electron cloud is more negative. The increas ...
... Each step from left to right adds a proton and an electron (and 1 or 2 neutrons) and electrons are added to existing energy levels. The effect is that the more positive nucleus has a greater pull on the electron cloud. The nucleus is more positive and the electron cloud is more negative. The increas ...
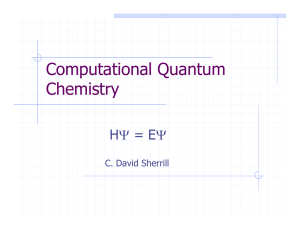
Computational Quantum Chemistry
... part of physics and the whole of chemistry are thus completely known and the difficulty is only that the exact application of these laws leads to equations much too complicated to be soluble.” ---P.A.M. Dirac, Proc. Roy. ...
... part of physics and the whole of chemistry are thus completely known and the difficulty is only that the exact application of these laws leads to equations much too complicated to be soluble.” ---P.A.M. Dirac, Proc. Roy. ...
phet activity key
... 3.Based on his observations, what inference did Rutherford make about the distribution of positive charge in the atom? From this observation he concluded that the positive charge must be concentrated in a small region called a nucleus, rather than distributed throughout the whole atom. Since positiv ...
... 3.Based on his observations, what inference did Rutherford make about the distribution of positive charge in the atom? From this observation he concluded that the positive charge must be concentrated in a small region called a nucleus, rather than distributed throughout the whole atom. Since positiv ...
Nuclear and Radiation Section - University of Toronto Physics
... In 1896, the French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel, noticed that some rocks that he had been studying emitted radiation that could pass through opaque photographic paper. Rutherford – “the father of Nuclear Physics” - identified two of these radiations. He showed that the first, which he called a ...
... In 1896, the French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel, noticed that some rocks that he had been studying emitted radiation that could pass through opaque photographic paper. Rutherford – “the father of Nuclear Physics” - identified two of these radiations. He showed that the first, which he called a ...
Lecture (2) - MIT OpenCourseWare
... backscatter (bounce back). This indicates that most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in a very small volume relative to the volume of the entire atom. We now call this the NUCLEUS. • Rutherford calculated the diameter of the nucleus to be _________ m. His calculation (see below) related the ...
... backscatter (bounce back). This indicates that most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in a very small volume relative to the volume of the entire atom. We now call this the NUCLEUS. • Rutherford calculated the diameter of the nucleus to be _________ m. His calculation (see below) related the ...
ppt Sc10 Review Notes
... ions are particles or groups of particles that have a net charge (either positive or negative) neutral atoms are unstable if their valence level is not full ...
... ions are particles or groups of particles that have a net charge (either positive or negative) neutral atoms are unstable if their valence level is not full ...
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules
... Several decades after the discovery of quantum mechanics. Further research and the availability of computers allow application of Quantum Mechanics to Chemistry From the presentation of the Nobel prize in Chemistry 1998: “Chemistry is not only test tubes and chemicals. In quantum chemistry, quantum ...
... Several decades after the discovery of quantum mechanics. Further research and the availability of computers allow application of Quantum Mechanics to Chemistry From the presentation of the Nobel prize in Chemistry 1998: “Chemistry is not only test tubes and chemicals. In quantum chemistry, quantum ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).