Atomic Structure, the Periodic Table, and Nuclear Radiation
... – The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the more strongly it is attracted. – The more protons in a nucleus, the more strongly an electron is attracted. 2. Electrons are repelled by other electrons in an atom. So, if other electrons are between a valence electron and the nucleus, the valence elec ...
... – The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the more strongly it is attracted. – The more protons in a nucleus, the more strongly an electron is attracted. 2. Electrons are repelled by other electrons in an atom. So, if other electrons are between a valence electron and the nucleus, the valence elec ...
Course Syllabus
... for a successful research career in just about any area of physics of current interest. Thus, in doing physics, you will find that you will use Quantum Mechanics “all the time.” ...
... for a successful research career in just about any area of physics of current interest. Thus, in doing physics, you will find that you will use Quantum Mechanics “all the time.” ...
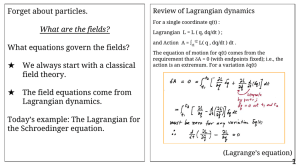
Forget about particles. What equations govern the fields? What are the fields?
... would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
... would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions and Equations Study Guide
... 6. What is the criss-cross method? Give an example to explain it. We cross the charges to make a neutral compound. Ca+2 ...
... 6. What is the criss-cross method? Give an example to explain it. We cross the charges to make a neutral compound. Ca+2 ...
Chapter 4 Bohr`s model of the atom
... Chapter 4 Bohr’s model of the atom 4.5 Bohr’s postulate Bohr’s postulate (1913): (1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb attraction between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. (2) An electron move i ...
... Chapter 4 Bohr’s model of the atom 4.5 Bohr’s postulate Bohr’s postulate (1913): (1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb attraction between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. (2) An electron move i ...
Deep-sea clams feel the heat
... we can always represent a complex number by its amplitude and phase, this implies that only the amplitude can be measured directly. The phase is also needed to uniquely describe the quantum state, but how does one find this phase experimentally? The question of ‘phase retrieval’ has a long experimen ...
... we can always represent a complex number by its amplitude and phase, this implies that only the amplitude can be measured directly. The phase is also needed to uniquely describe the quantum state, but how does one find this phase experimentally? The question of ‘phase retrieval’ has a long experimen ...
Answers
... Exam Review - Chapter 2: Stoichiometry 1) The formula for fructose is C6H12O6. Which of the following is true for fructose? ____ a) the empirical formula is C2H4O2 ____ b) there is a total of six atoms in each molecule ____ c) a molecule contains six carbon atoms ____ d) the ratio of carbon to oxyge ...
... Exam Review - Chapter 2: Stoichiometry 1) The formula for fructose is C6H12O6. Which of the following is true for fructose? ____ a) the empirical formula is C2H4O2 ____ b) there is a total of six atoms in each molecule ____ c) a molecule contains six carbon atoms ____ d) the ratio of carbon to oxyge ...
Scanning gate microscopy of electron flow from a spin-orbit
... Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Kraków, Poland Scanning gate microscopy (SGM) is a technique that allows for spatial mapping of current flow and charge densities in semiconductor nanostructures. This technique has been used to map electron flow from a const ...
... Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Kraków, Poland Scanning gate microscopy (SGM) is a technique that allows for spatial mapping of current flow and charge densities in semiconductor nanostructures. This technique has been used to map electron flow from a const ...
Quantum Computing at the Speed of Light
... Harnessing quantum states for information storage and manipulation (in so called “qubits”) is the objective of quantum computing, with the potential to revolutionize technology in areas of great importance to society (e.g. cryptography, data base searching, quantum simulation of advance materials, s ...
... Harnessing quantum states for information storage and manipulation (in so called “qubits”) is the objective of quantum computing, with the potential to revolutionize technology in areas of great importance to society (e.g. cryptography, data base searching, quantum simulation of advance materials, s ...
Quantum/Nuclear - Issaquah Connect
... Calculate wavelengths of spectral lines from energy level differences and vice versa ...
... Calculate wavelengths of spectral lines from energy level differences and vice versa ...
Deuterium – Tritium pulse propulsion with hydrogen as propellant
... general high efficiency is needed if one wants to avoid a large radiator to remove the waste heat from the space craft. More serious is the heating of the space craft by the absorption of neutrons, in particular for the DT reaction where 80% of the energy goes into neutrons. But even the DHe3 reacti ...
... general high efficiency is needed if one wants to avoid a large radiator to remove the waste heat from the space craft. More serious is the heating of the space craft by the absorption of neutrons, in particular for the DT reaction where 80% of the energy goes into neutrons. But even the DHe3 reacti ...
Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Calulating Land`e g factor
... σ and g to get the last form. This last equation is used to determine g in this experiment by measuring the field and the frequency at which resonance occurs. If g does not equal ge , the implication is that the ratio of the unpaired electron’s spin magnetic moment to its angular momentum differs fr ...
... σ and g to get the last form. This last equation is used to determine g in this experiment by measuring the field and the frequency at which resonance occurs. If g does not equal ge , the implication is that the ratio of the unpaired electron’s spin magnetic moment to its angular momentum differs fr ...
Notes 7
... OVERALL IDEA of Hartree technique is that any one electron moves in a potential which is a spherical average of the potential due to all the other electrons and the nucleus, wand this is expressed as a single charge centered on the nucleus. (This is the central field approximation; but it is not ass ...
... OVERALL IDEA of Hartree technique is that any one electron moves in a potential which is a spherical average of the potential due to all the other electrons and the nucleus, wand this is expressed as a single charge centered on the nucleus. (This is the central field approximation; but it is not ass ...
Molecular Statistics
... sign for electrons and positive for protons; neutrons are electrically neutral. The masses for proton and neutrons have approximately the same value, 1 . 67 10 kg . ...
... sign for electrons and positive for protons; neutrons are electrically neutral. The masses for proton and neutrons have approximately the same value, 1 . 67 10 kg . ...
Lesson 9 Core notation File
... Lesson 9: Spin and Core notation Orally: Several experimental observations can be explained by treating the electron as though it were spinning. The spin can be clockwise or counterclockwise, and so there are two possible values of the spin quantum number that describe the electron. Quantum theory w ...
... Lesson 9: Spin and Core notation Orally: Several experimental observations can be explained by treating the electron as though it were spinning. The spin can be clockwise or counterclockwise, and so there are two possible values of the spin quantum number that describe the electron. Quantum theory w ...
Part VIII - TTU Physics
... Citation: “For their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations.” Störmer & Tsui made the discovery in 1982 in an experiment using extremely high magnetic fields very low temperatures. Within a year Laughlin had succeeded in explaining their result. His theory sho ...
... Citation: “For their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations.” Störmer & Tsui made the discovery in 1982 in an experiment using extremely high magnetic fields very low temperatures. Within a year Laughlin had succeeded in explaining their result. His theory sho ...
The Structure of Matter
... The chance of finding an electron is given by the square of the wave function at a certain location Mathematical predictions from the Schrödinger equation ...
... The chance of finding an electron is given by the square of the wave function at a certain location Mathematical predictions from the Schrödinger equation ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).