Materials Science 4 - Clarkson University
... • Three mechanisms for heat transfer in solids: 1. Lattice vibrations. Important with strong bonding, as in diamond. 2. Electron motion. Important when there are many free electrons, e.g. metals 3. Radiation. When the material does not absorb the radiation. Depends on the material composition, the p ...
... • Three mechanisms for heat transfer in solids: 1. Lattice vibrations. Important with strong bonding, as in diamond. 2. Electron motion. Important when there are many free electrons, e.g. metals 3. Radiation. When the material does not absorb the radiation. Depends on the material composition, the p ...
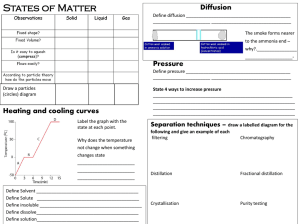
IGCSE Revision document
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
Quantum Molecular Dynamics
... • Use quantum relations to generate effective interactions for electrons and ions Strengths Maps a quantum problem to a classical one Scales well to many more particles than other methods Ability to do electron and ion dynamics near equilibrium Codes are well developed and tuned ...
... • Use quantum relations to generate effective interactions for electrons and ions Strengths Maps a quantum problem to a classical one Scales well to many more particles than other methods Ability to do electron and ion dynamics near equilibrium Codes are well developed and tuned ...
Preview Sample 1
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
Quantum impurity problem in ultracold gases: Dimitri M Gangardt Alex Kamenev,
... Research Centre ...
... Research Centre ...
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Inter-atomic Bonding
... early outgrowth of quantum mechanics. This model represents electrons as particles revolving around the nucleus much like planets around a sun. ...
... early outgrowth of quantum mechanics. This model represents electrons as particles revolving around the nucleus much like planets around a sun. ...
Ch 24: Quantum Mechanics
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
SPC Teachers Problems - University of Oxford
... In the second method of preparation, suggested to me by Prof. Ramsay, everything remained unchanged, except that the first tube of hot copper was replaced by a wash-bottle containing liquid ammonia, through which air was allowed to bubble. The ammonia method is very convenient, but the nitrogen obta ...
... In the second method of preparation, suggested to me by Prof. Ramsay, everything remained unchanged, except that the first tube of hot copper was replaced by a wash-bottle containing liquid ammonia, through which air was allowed to bubble. The ammonia method is very convenient, but the nitrogen obta ...
NMR Spectroscopy
... momentum, p. Furthermore, the maximum observable component of this angular momemtum is quantized and must be an integral or a half-integral multiple of h/2, where h is Planck constant. ...
... momentum, p. Furthermore, the maximum observable component of this angular momemtum is quantized and must be an integral or a half-integral multiple of h/2, where h is Planck constant. ...
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM
... Another example of the complete set is a Fourier series where the functions sin(mu) and cos(nu), m, n = 0.1, …, ∞ form a complete orthogonal set over [0,2π]. Any periodic function with a period of 2π can be expanded in a Fourier series. ...
... Another example of the complete set is a Fourier series where the functions sin(mu) and cos(nu), m, n = 0.1, …, ∞ form a complete orthogonal set over [0,2π]. Any periodic function with a period of 2π can be expanded in a Fourier series. ...
PHY 855 - Quantum Field Theory Course description :
... The energy eigenfunctions Recall the Dirac notation of bra’s and ket’s. A state vector is a ket = |ψ> ; the wavefunction is = ψ(x) .
So, the energy eigenfunctions are
Фn(x) =
...
... The energy eigenfunctions Recall the Dirac notation of bra’s and ket’s. A state vector is a ket = |ψ> ; the wavefunction is
Chapter 10 - Lecture 3
... Structures of many-electron atoms • Because of electron correlation, no simple analytical expression for orbitals is possible • Therefore ψ(r1, r2, ….) can be expressed as ψ(r1)ψ(r2)… • Called the orbital approximation • Individual hydrogenic orbitals modified by presence of other electrons ...
... Structures of many-electron atoms • Because of electron correlation, no simple analytical expression for orbitals is possible • Therefore ψ(r1, r2, ….) can be expressed as ψ(r1)ψ(r2)… • Called the orbital approximation • Individual hydrogenic orbitals modified by presence of other electrons ...
The atom: fragments of a networked history - Latin
... to envision and project worlds which were unsuspected until just a few decades ago. The research on electricity and magnetism carried out by Gauss, called the “Prince of mathematics”, is one of the most representative examples of such alliances, not only due to its relevance in this particular subje ...
... to envision and project worlds which were unsuspected until just a few decades ago. The research on electricity and magnetism carried out by Gauss, called the “Prince of mathematics”, is one of the most representative examples of such alliances, not only due to its relevance in this particular subje ...
quantumwaves
... At t = 0, the wave function is given by the expression above. (a) What is the most likely / least likely places to find the particle? (b) What is the normalization constant N? (c) What is the probability that the particle is at 0 < x < a? •Least likely when function vanishes, at x = 0 •Most likely w ...
... At t = 0, the wave function is given by the expression above. (a) What is the most likely / least likely places to find the particle? (b) What is the normalization constant N? (c) What is the probability that the particle is at 0 < x < a? •Least likely when function vanishes, at x = 0 •Most likely w ...
3D– Modern Physics
... 4. Quantum systems exhibit a radical change in their properties when they interact with a measurement apparatus. This is the least well understood aspect of quantum theory, from a theoretical point of view. We have already suggested that quantum mechanics describes a system in terms of a set of prob ...
... 4. Quantum systems exhibit a radical change in their properties when they interact with a measurement apparatus. This is the least well understood aspect of quantum theory, from a theoretical point of view. We have already suggested that quantum mechanics describes a system in terms of a set of prob ...
Presentation
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
... that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
Lecture 9 Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
... That is, the particle must be found somewhere in the universe. 3. Eigenstates and Eigenvalues: Quantized Energy Levels. In the language of linear algebra, the value of E in the Schrödinger equation is called the eigenvalue, or correct value, of the equation. The wave function that correctly solves ...
... That is, the particle must be found somewhere in the universe. 3. Eigenstates and Eigenvalues: Quantized Energy Levels. In the language of linear algebra, the value of E in the Schrödinger equation is called the eigenvalue, or correct value, of the equation. The wave function that correctly solves ...
Chern-Simons theory and the fractional quantum Hall effect
... the Laughlin function. Each electron jumps from a state with a given angular momentum to another (from a circular orbit to another with bigger radius if you want), leaving an empty state with m = 0 behind, which is the quasi-hole. In order to see that we can consider a very naive but interesting arg ...
... the Laughlin function. Each electron jumps from a state with a given angular momentum to another (from a circular orbit to another with bigger radius if you want), leaving an empty state with m = 0 behind, which is the quasi-hole. In order to see that we can consider a very naive but interesting arg ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).