Lecture Exam 1
... help them better adapt to the warmer waters because natural selection leads to more complex and well adapted organisms. C. The mutation rate will increase in this group of worms in order to promote evolution. D. Worms possessing genetic variations that help them to survive and thrive in the new envi ...
... help them better adapt to the warmer waters because natural selection leads to more complex and well adapted organisms. C. The mutation rate will increase in this group of worms in order to promote evolution. D. Worms possessing genetic variations that help them to survive and thrive in the new envi ...
Evolution Study Guide
... 1. Describe how Darwin arrived at his idea about species variation. What accounts for the variation Darwin observed? 2. Recognize variation and adaptations within a species (such as finches or tortoises). Be able to give and/or explain examples for both variation and adaptation. Theory of Natural ...
... 1. Describe how Darwin arrived at his idea about species variation. What accounts for the variation Darwin observed? 2. Recognize variation and adaptations within a species (such as finches or tortoises). Be able to give and/or explain examples for both variation and adaptation. Theory of Natural ...
Document
... ◦ Reasoned that if the human population grew continuously, there would not be enough resources for everyone ◦ His reasoning explained why plants and animals produced more a high amount of offspring since a portion will not survive due to environmental factors ◦ Ex: Maple tree produces thousands of s ...
... ◦ Reasoned that if the human population grew continuously, there would not be enough resources for everyone ◦ His reasoning explained why plants and animals produced more a high amount of offspring since a portion will not survive due to environmental factors ◦ Ex: Maple tree produces thousands of s ...
File
... 3. Scientists have collected many fossils of horse ancestors. The use of fossils to trace the evolution of the horse is known ...
... 3. Scientists have collected many fossils of horse ancestors. The use of fossils to trace the evolution of the horse is known ...
Nov19
... These finches, better known as 'Darwin's Finches' illustrated adaptive radiation. This is where species all deriving from a common ancestor have over time successfully adapted to their environment via natural selection. Previously, the finches occupied the South American mainland, but somehow manage ...
... These finches, better known as 'Darwin's Finches' illustrated adaptive radiation. This is where species all deriving from a common ancestor have over time successfully adapted to their environment via natural selection. Previously, the finches occupied the South American mainland, but somehow manage ...
Evolution PPT - Liberty Union High School District
... There is variation within populations Some variations are favorable Not all young produced in each generation can survive Individuals that survive and reproduce are those with favorable variations Favorable traits will increase in future generations. ...
... There is variation within populations Some variations are favorable Not all young produced in each generation can survive Individuals that survive and reproduce are those with favorable variations Favorable traits will increase in future generations. ...
Evolution Review Questions 1. What is evolution? Why is evolution
... 16. What is meant by the term vestigial structure? How do they provide evidence of evolution? 17. a) How is the general understanding of survival of the fittest misleading? b) What do we mean when we describe an organism as “more fit” than some other organism? 18. How might natural selection have pr ...
... 16. What is meant by the term vestigial structure? How do they provide evidence of evolution? 17. a) How is the general understanding of survival of the fittest misleading? b) What do we mean when we describe an organism as “more fit” than some other organism? 18. How might natural selection have pr ...
Figure 22.0 Title page from The Origin of Species
... Gradualism - Hutton: geologist: profound change in the Earth’s features, ...
... Gradualism - Hutton: geologist: profound change in the Earth’s features, ...
Selection and Evolution
... I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection. - Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species ...
... I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection. - Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species ...
Name: Gr.12 Biology Unit 3: Evolution (Ch.27) Section A: Multiple
... 12. Human birth weight is an example of the result of: a. Stabilizing selection b. Directional selection c. Disruptive selection d. Typical selection ...
... 12. Human birth weight is an example of the result of: a. Stabilizing selection b. Directional selection c. Disruptive selection d. Typical selection ...
Evolutionary Theory 2
... • He did not report his ideas for many years. • He took time to gather more data and to form a strong explanation for how evolution happens. ...
... • He did not report his ideas for many years. • He took time to gather more data and to form a strong explanation for how evolution happens. ...
Population Genetics 2
... • Two species evolve in two separate environments • When brought back together species are now separated by reproductive isolation • No gene flow is occurring 2 new species have evolved ...
... • Two species evolve in two separate environments • When brought back together species are now separated by reproductive isolation • No gene flow is occurring 2 new species have evolved ...
Natural Selection vs. Selective Breeding
... became covered with soot and turned dark. Over a period of 45 years, the dark variety of the peppered moth became more common. ...
... became covered with soot and turned dark. Over a period of 45 years, the dark variety of the peppered moth became more common. ...
Mutation, Evolution, and Natural Selection
... is especially important for an organism's survival. For example, the adaptation of horses' teeth to the grinding of grass, or their ability to run fast and escape predators. Such adaptations are produced in a variable population by the better suited forms reproducing more successfully, which is na ...
... is especially important for an organism's survival. For example, the adaptation of horses' teeth to the grinding of grass, or their ability to run fast and escape predators. Such adaptations are produced in a variable population by the better suited forms reproducing more successfully, which is na ...
1 Chapter 16: Evolutionary Theory Section 1: Developing a Theory
... b) i.e. Person’s muscles may decrease or increase in size due to use or disuse - Lamark thought offspring could inherit this change D. Population Growth ...
... b) i.e. Person’s muscles may decrease or increase in size due to use or disuse - Lamark thought offspring could inherit this change D. Population Growth ...
Observation Or Inference - Liberty Union High School District
... There is variation within populations Some variations are favorable Not all young produced in each generation can survive Individuals that survive and reproduce are those with favorable variations Favorable traits will increase in future generations. ...
... There is variation within populations Some variations are favorable Not all young produced in each generation can survive Individuals that survive and reproduce are those with favorable variations Favorable traits will increase in future generations. ...
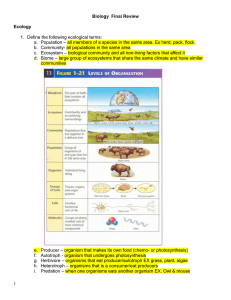
Biology 5 Final Review
... 28. What was Darwin’s theory of evolution? Natural selection is based on excess reproduction, variation, inheritance and the advantages of certain traits in certain environments. The “fittest” survive and reproduce. This can result in the appearance of new species. 29. What did Malthus predict would ...
... 28. What was Darwin’s theory of evolution? Natural selection is based on excess reproduction, variation, inheritance and the advantages of certain traits in certain environments. The “fittest” survive and reproduce. This can result in the appearance of new species. 29. What did Malthus predict would ...
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life AP
... 3. Explain the process of natural selection. 4. For each observation that follows, give an example: (A) variations in traits exist, (B) these variations (traits) are heritable, (C) species overproduce, and (D) there is competition for resources; not all offspring survive. 5. From these four observat ...
... 3. Explain the process of natural selection. 4. For each observation that follows, give an example: (A) variations in traits exist, (B) these variations (traits) are heritable, (C) species overproduce, and (D) there is competition for resources; not all offspring survive. 5. From these four observat ...
Slide 1
... The faster turtles would be more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, more turtles in the species would have the “fast-swimmer” trait. ...
... The faster turtles would be more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, more turtles in the species would have the “fast-swimmer” trait. ...
How to Review for Biology - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 6) Describe how disruptive, stabilizing, and directional natural selection act on variation. 7) Distinguish between natural selection and artificial (human-driven) selection. 8) Outline how scientists determine whether a gene pool has changed, according to the criteria for genetic equilibrium. (Incl ...
... 6) Describe how disruptive, stabilizing, and directional natural selection act on variation. 7) Distinguish between natural selection and artificial (human-driven) selection. 8) Outline how scientists determine whether a gene pool has changed, according to the criteria for genetic equilibrium. (Incl ...
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life
... i. Learned that most species there occur nowhere else in the world, but many resemble species in South America ii. Species on the islands are related but, like finches, were adapted to different lifestyles iv. Darwin’s Focus on Adaptation 1. Darwin reassessed all observations made during the voyage ...
... i. Learned that most species there occur nowhere else in the world, but many resemble species in South America ii. Species on the islands are related but, like finches, were adapted to different lifestyles iv. Darwin’s Focus on Adaptation 1. Darwin reassessed all observations made during the voyage ...
History of Evolution History of Evolution
... • Darwin made two points in The Origin of Species: – (1) Today’s organisms descended from ancestral species. – (2)Natural selection provided a mechanism for evolutionary change in populations. ...
... • Darwin made two points in The Origin of Species: – (1) Today’s organisms descended from ancestral species. – (2)Natural selection provided a mechanism for evolutionary change in populations. ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.