File
... Gradualism which states that landforms resulted from slow changes over a long period of time. • Gradualism is a major component of evolutionary theory ...
... Gradualism which states that landforms resulted from slow changes over a long period of time. • Gradualism is a major component of evolutionary theory ...
Chapter 5 - life.illinois.edu
... Has there been enough time for evolution to have produced all of the biological diversity that we see today? ...
... Has there been enough time for evolution to have produced all of the biological diversity that we see today? ...
Browsing Genomes Module – For Teachers
... consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to ...
... consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to ...
Discovering the Genome: Browsing Genomes Module – For Teachers
... consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to ...
... consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to ...
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 3/25
... 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) • Characteristics of ...
... 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) • Characteristics of ...
Theory of Evolution and Natural Selection
... arise as a modification of old features and in combination with new mutations -adaptations Natural selection is non-random, but not progressive ...
... arise as a modification of old features and in combination with new mutations -adaptations Natural selection is non-random, but not progressive ...
Evolution PPT - Pearland ISD
... • C. Vestigial structures are structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. • Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. ...
... • C. Vestigial structures are structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. • Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. ...
Biodiversity PPT Notes
... • C. Vestigial structures are structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. • Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. ...
... • C. Vestigial structures are structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. • Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. ...
Lesson 6-2 Lecture PDF
... explain how different species on the Galapagos evolved. Variations are slight differences within members of a species. Populations are groups of individuals from the same species living in the same area. ...
... explain how different species on the Galapagos evolved. Variations are slight differences within members of a species. Populations are groups of individuals from the same species living in the same area. ...
Chapter Six Section one and two Study Guide Outline Teacher Copy
... The finches developed different shaped beaks depending on what type of food they ate. The tortoises developed longer necks in order or eat from different types of plants. ...
... The finches developed different shaped beaks depending on what type of food they ate. The tortoises developed longer necks in order or eat from different types of plants. ...
Fitness and Life Histories
... acclimate to the food and nutrients • LOG PHASE: metabolic machinery is running, exponentially multiplication of population density, doubling in number every few minutes. • STATIONARY PHASE: competition for food and nutrients causes number of bacteria to ...
... acclimate to the food and nutrients • LOG PHASE: metabolic machinery is running, exponentially multiplication of population density, doubling in number every few minutes. • STATIONARY PHASE: competition for food and nutrients causes number of bacteria to ...
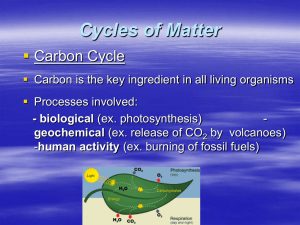
Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium
... Evolution is the change in a population’s genetic material over generations Change in a population’s allele frequencies Any exception to the HardyWeinberg equilibrium can result in evolution ...
... Evolution is the change in a population’s genetic material over generations Change in a population’s allele frequencies Any exception to the HardyWeinberg equilibrium can result in evolution ...
Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
... _________________________ is the way in which nature favours the reproductive success of some individuals within a population over others ...
... _________________________ is the way in which nature favours the reproductive success of some individuals within a population over others ...
howard overhead notes evolutionary biology
... A. mutation rates are small to negligible. B. population size will still give a good fit to Hardy-Weinberg even if the population is fairly small, say 100 individuals. C. Also, since the equilibrium is established after one generation, the population will come back to equilibrium within one generati ...
... A. mutation rates are small to negligible. B. population size will still give a good fit to Hardy-Weinberg even if the population is fairly small, say 100 individuals. C. Also, since the equilibrium is established after one generation, the population will come back to equilibrium within one generati ...
Supporting Evidence for Evolution
... Convergent evolution Convergent evolution: unrelated pathways to different species develop similar traits. Similar traits develop due to ...
... Convergent evolution Convergent evolution: unrelated pathways to different species develop similar traits. Similar traits develop due to ...
Biology: Unit 14 Directed Reading Guide
... A. Human birth rate was higher than the death rate. B. War caused the death of thousands of people. C. Famines were common in England in the 1800s. D. The offspring of most species survived into adulthood. _______ 10. Which of the following is an idea attributed to Malthus? A. As a population decrea ...
... A. Human birth rate was higher than the death rate. B. War caused the death of thousands of people. C. Famines were common in England in the 1800s. D. The offspring of most species survived into adulthood. _______ 10. Which of the following is an idea attributed to Malthus? A. As a population decrea ...
NATURAL SELECTION AND THE EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
... • In nature, more offspring than can survive are produced • In any population, individuals have variations • Over time, those with favorable variations survive and pass those traits on to their offspring • Over time, individuals with variations look entirely different from their ancestors and make u ...
... • In nature, more offspring than can survive are produced • In any population, individuals have variations • Over time, those with favorable variations survive and pass those traits on to their offspring • Over time, individuals with variations look entirely different from their ancestors and make u ...
Adaptation and Natural Selection
... no soil exists. Ex. bare rock, areas covered by volcanic ash – Secondary succession occurs in an area where a disturbances changes an existing community without destroying the soil. Ex. plowed land, area burned by wildfire ...
... no soil exists. Ex. bare rock, areas covered by volcanic ash – Secondary succession occurs in an area where a disturbances changes an existing community without destroying the soil. Ex. plowed land, area burned by wildfire ...
b2revisioncards
... Natural selection describes how the organisms with random mutations that help them to survive are more likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not e ...
... Natural selection describes how the organisms with random mutations that help them to survive are more likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not e ...
Evidence of Evolution - Sonoma Valley High School
... Vestigial Structures • Structure is coded for in the DNA. • Function has apparently been lost. – Ex: Human appendix? ...
... Vestigial Structures • Structure is coded for in the DNA. • Function has apparently been lost. – Ex: Human appendix? ...
preview images for j..
... •Allopatric speciation thought to occur relatively rapidly; natural selection and genetic drift can cause significant change in a few hundred to a few thousand generations •If a species survives (leaves fossils!) for five million years, first 50,000 years of its existance would be only 1% of its exi ...
... •Allopatric speciation thought to occur relatively rapidly; natural selection and genetic drift can cause significant change in a few hundred to a few thousand generations •If a species survives (leaves fossils!) for five million years, first 50,000 years of its existance would be only 1% of its exi ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.