256 Bit Key — Is It Big Enough?
... This is still a reasonable strategy in some situations, especially where there is a limit on the complexity of the encryption hardware (perhaps for cost or power consumption reasons) and/or insufficient key storage mechanism. Good examples of this situation would be RFID tags which cannot consume ve ...
... This is still a reasonable strategy in some situations, especially where there is a limit on the complexity of the encryption hardware (perhaps for cost or power consumption reasons) and/or insufficient key storage mechanism. Good examples of this situation would be RFID tags which cannot consume ve ...
Secure Email
... privacy (only the intended recipient can read the message) and authentication (the recipient can be assured of the identity of the sender). The technical capabilities for these functions has been known for many years, but they have only been applied to Internet mail recently. – Reality Check: Securi ...
... privacy (only the intended recipient can read the message) and authentication (the recipient can be assured of the identity of the sender). The technical capabilities for these functions has been known for many years, but they have only been applied to Internet mail recently. – Reality Check: Securi ...
Chapter 6
... • Public-key systems provide several advantages over private-key systems: – The combination of keys required to provide private messages between enormous numbers of people is small – Key distribution is not a problem – Public-key systems make implementation of digital signatures possible ...
... • Public-key systems provide several advantages over private-key systems: – The combination of keys required to provide private messages between enormous numbers of people is small – Key distribution is not a problem – Public-key systems make implementation of digital signatures possible ...
Enhancement of Security through a Cryptographic Algorithm
... Using this Decryption NNA (Natural number algorithm) private key technique, we can encrypt any size of file, as well as any kind of file, as NNA protocol can be implemented to any file as each of the characters are represented by natural numbers so any type of message can be sent. There might be lit ...
... Using this Decryption NNA (Natural number algorithm) private key technique, we can encrypt any size of file, as well as any kind of file, as NNA protocol can be implemented to any file as each of the characters are represented by natural numbers so any type of message can be sent. There might be lit ...
FTAA Joint Public-Private Sector Committee of Experts
... activities which can involve vast number of individuals. The current movement from closed network to open network communication systems poses significant challenges to the international trading system. Open networks such as the Internet offer the possibility of interactive communication between part ...
... activities which can involve vast number of individuals. The current movement from closed network to open network communication systems poses significant challenges to the international trading system. Open networks such as the Internet offer the possibility of interactive communication between part ...
Enhancing the Security and Capacity of Collaborative Software for
... Since the RMTP Executes controls over Internet protocols (UDP/IP), RMP makes use of the IP Security Architecture. ...
... Since the RMTP Executes controls over Internet protocols (UDP/IP), RMP makes use of the IP Security Architecture. ...
Getting Security Right in Wireless Sensor Networks
... is given those keys, allowing a secure session between each node and the security manager. The security manager then generates the required keys for all other sessions, and sends them via its secure channels to each of the devices involved. Alternatively, there is another suite of tools using public ...
... is given those keys, allowing a secure session between each node and the security manager. The security manager then generates the required keys for all other sessions, and sends them via its secure channels to each of the devices involved. Alternatively, there is another suite of tools using public ...
Hidden Markov Model Cryptanalysis
... Sequence of hidden, probabilistic states (S) Corresponding observable outputs (O) Each state is independent of every other (memoryless) P (S1 = x1) ...
... Sequence of hidden, probabilistic states (S) Corresponding observable outputs (O) Each state is independent of every other (memoryless) P (S1 = x1) ...
Modular Arithmetic - svmoore
... • If we want to multiply many numbers modulo n, we can first reduce all numbers to their remainders. Then, we can take any pair of them, multiply and reduce again. • For example, suppose we want to find X = 36 * 53 * 91 * 17 * 22 (mod 29) ...
... • If we want to multiply many numbers modulo n, we can first reduce all numbers to their remainders. Then, we can take any pair of them, multiply and reduce again. • For example, suppose we want to find X = 36 * 53 * 91 * 17 * 22 (mod 29) ...
VPNs, PKIs, ISSs, SSLs with narration
... • Browser may authenticate itself but rarely does • Browser selects a symmetric session key, sends to webserver • Adds a digital signature and encrypts all messages with the symmetric key ...
... • Browser may authenticate itself but rarely does • Browser selects a symmetric session key, sends to webserver • Adds a digital signature and encrypts all messages with the symmetric key ...
Hidden Markov Model Cryptanalysis
... attack based on information gained from the physical implementation of a cryptosystem. For example, timing information, power consumption, electromagnetic leaks or even sound can provide an extra source of information which can be exploited to break the system. Timing attack, power monitoring attack ...
... attack based on information gained from the physical implementation of a cryptosystem. For example, timing information, power consumption, electromagnetic leaks or even sound can provide an extra source of information which can be exploited to break the system. Timing attack, power monitoring attack ...
29-sets-dictionaries
... • Write a program that counts the number of unique words in a large text file (say, Moby Dick or the King James Bible). • Store the words in a structure and report the # of unique words. • Once you've created this structure, allow the user to search it to see whether various words appear in the text ...
... • Write a program that counts the number of unique words in a large text file (say, Moby Dick or the King James Bible). • Store the words in a structure and report the # of unique words. • Once you've created this structure, allow the user to search it to see whether various words appear in the text ...
module_70
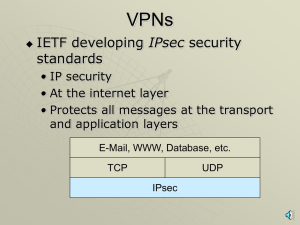
... Transparent network access across multiple proxy servers Easy deployment of authentication and encryption methods Rapid deployment of new network applications Simple network security policy management ...
... Transparent network access across multiple proxy servers Easy deployment of authentication and encryption methods Rapid deployment of new network applications Simple network security policy management ...
Java Security
... order of the providers in which providers are searched for requested services when no specific provider is requested. Implementation interoperability means that various implementations can work with each other, use each other's keys, or verify each other's signatures. ...
... order of the providers in which providers are searched for requested services when no specific provider is requested. Implementation interoperability means that various implementations can work with each other, use each other's keys, or verify each other's signatures. ...
Detailed Overview of Security and Privacy lecture slides
... receiver with a key can decipher the content A single (symmetric) secret key is used to encrypt and decrypt Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
... receiver with a key can decipher the content A single (symmetric) secret key is used to encrypt and decrypt Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
Security & Privacy on the WWW
... receiver with a key can decipher the content A single (symmetric) secret key is used to encrypt and decrypt Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
... receiver with a key can decipher the content A single (symmetric) secret key is used to encrypt and decrypt Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
pdf
... 3. Identity-based signatures. In class we showed how to obtain an identity-based signature scheme: the master public key is a modulus N and an exponent e; the master secret key is d such that ed = 1 mod ϕ(N ). A user with identity ID is given secret key SKID = H(ID)d mod N (where H is modeled as a ...
... 3. Identity-based signatures. In class we showed how to obtain an identity-based signature scheme: the master public key is a modulus N and an exponent e; the master secret key is d such that ed = 1 mod ϕ(N ). A user with identity ID is given secret key SKID = H(ID)d mod N (where H is modeled as a ...
DCN-7-Network_Security
... •IDs and Passwords: –Tips to Select & Protect IDs and Passwords: •Select a password which is, –At least 8 characters long and, »Including all types of symbols such as lowercase, uppercase, numbers and special characters. ...
... •IDs and Passwords: –Tips to Select & Protect IDs and Passwords: •Select a password which is, –At least 8 characters long and, »Including all types of symbols such as lowercase, uppercase, numbers and special characters. ...
Rivest-Shamir
... P, NP, NP-hard, NP-complete • A problem belongs to the class P if the problem can be solved by a polynomial-time algorithm • A problem belongs to the class NP if the correctness of the problem’s solution can be verified by a polynomialtime algorithm • A problem is NP-hard if it is as hard as any pr ...
... P, NP, NP-hard, NP-complete • A problem belongs to the class P if the problem can be solved by a polynomial-time algorithm • A problem belongs to the class NP if the correctness of the problem’s solution can be verified by a polynomialtime algorithm • A problem is NP-hard if it is as hard as any pr ...
Database Security
... • Stored profiles should be kept secure, possibly in encrypted form • Profile normally includes a password, allegedly known only to the user • Passwords should be kept secret and changed frequently • System should never display passwords at signin time ...
... • Stored profiles should be kept secure, possibly in encrypted form • Profile normally includes a password, allegedly known only to the user • Passwords should be kept secret and changed frequently • System should never display passwords at signin time ...
here
... i=1 (1 − pi ). (Notice the interesting fact that this fraction only depends on which primes divide n.) ...
... i=1 (1 − pi ). (Notice the interesting fact that this fraction only depends on which primes divide n.) ...
CIS 5357 - FSU Computer Science
... If b’ = b, the attacker wins. If every attacker has only a negligible probability of success, we say that the scheme is secure under chosen-plaintext attacks. ...
... If b’ = b, the attacker wins. If every attacker has only a negligible probability of success, we say that the scheme is secure under chosen-plaintext attacks. ...
UNIT ONE: KEY TERMS Learn(ing)
... The process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs. 2. Circle each important word in the definition for CRITICAL THINKING and list the words from the definition that are also listed in the KEY TERMS above. a. b. c. 4. Re-word the defin ...
... The process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs. 2. Circle each important word in the definition for CRITICAL THINKING and list the words from the definition that are also listed in the KEY TERMS above. a. b. c. 4. Re-word the defin ...
Ecommerce: Security and Control
... – because it use Mathematics to calculate the key. Public key cryptography uses two keys, rather than one – hence, sometimes referred to asymmetric. Symmetric encryption is still in use, and will continue to be This is because of the computational overhead associated with public key encryption ...
... – because it use Mathematics to calculate the key. Public key cryptography uses two keys, rather than one – hence, sometimes referred to asymmetric. Symmetric encryption is still in use, and will continue to be This is because of the computational overhead associated with public key encryption ...
Diffie–Hellman key exchange
Diffie–Hellman key exchange (D–H) is a specific method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a public channel and was one of the first public-key protocols as originally conceptualized by Ralph Merkle. D–H is one of the earliest practical examples of public key exchange implemented within the field of cryptography. The Diffie–Hellman key exchange method allows two parties that have no prior knowledge of each other to jointly establish a shared secret key over an insecure channel. This key can then be used to encrypt subsequent communications using a symmetric key cipher.The scheme was first published by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976. By 1975, James H. Ellis, Clifford Cocks and Malcolm J. Williamson within GCHQ, the British signals intelligence agency, had also shown how public-key cryptography could be achieved; however, their work was kept secret until 1997.Although Diffie–Hellman key agreement itself is a non-authenticated key-agreement protocol, it provides the basis for a variety of authenticated protocols, and is used to provide perfect forward secrecy in Transport Layer Security's ephemeral modes (referred to as EDH or DHE depending on the cipher suite).The method was followed shortly afterwards by RSA, an implementation of public-key cryptography using asymmetric algorithms.U.S. Patent 4,200,770, from 1977, is now expired and describes the now public domain algorithm. It credits Hellman, Diffie, and Merkle as inventors.