* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
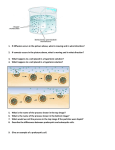
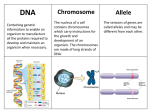
Honors Biology Semester 1 Final Exam Review Guide 2016 Directions: Answer the questions below on separate pieces of paper or notecards: paraphrase the objective, underline or highlight, then provide your answers on the lines below. This will act as a study guide for the final exam. This will be turned in the day of your final exam. You will have a set number of questions that need to complete at the beginning of the hour each day of the week as listed below to receive credit: Friday 12/16: Monday 12/19: Tuesday 12/20: Questions 1 – 10 Questions 11 – 20 Questions 21 – 28 You will receive a stamp each day if the questions are complete the day they are due. The stamp earns you your points for completing the review: NO STAMP = NO POINTS. Tuesday 12/20 in-class you will be writing the short answer part of the exam. You will be writing 2 paragraphs. You may prepare for this ahead of time, but you may not use any materials on the day you are writing. The first paragraph must explain the importance of scientists running ‘controlled’ experiments. In the second paragraph you will be designing an experiment by writing detailed directions of how to complete an experiment, stating the independent, dependent, and controlled variables of the experiment. Unit 1: Organic Chemistry – Chapter 1 & 2 1. Define biology. 2. Define the scientific method. a. List and describe the steps to the scientific method. Smithers notices many of his workers slacking on the job. The productivity of his workers has decreased. He thinks that a special juice will increase the productivity of workers. He creates two groups of 50 workers each and assigns each group the same task (in this case, they're supposed to staple a set of papers). Group A is given the special juice to drink while they work. Group B is not given the special juice. After an hour, Smithers counts how many stacks of papers each group has made. Group A made 1,587 stacks, Group B made 2,113 stacks. Use the above passage to answer the following: a. Isolate steps of the scientific method in an experiment. b. Identify independent and dependent variables in an experiment. 3. Explain what it means for an experiment to be “controlled”. 1 4. State the monomer to each macromolecule of life. (i.e. carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, proteins) Unit 2: Cytology – Chapters 7, 8, 9, 10 5. Summarize the ideas of the cell theory. 6. Differentiate between prokaryote and eukaryote cells. 7. Differentiate between plant and animal cells. 8. Explain why the cell membrane is arranged into a bi-layer. Figure 7-6 9. Name and state each function of the structures F, I N in Figure 7-6. 10. Describe the direction that water moves (in or out the cell) in each osmotic solution: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. a. State which solution above will cause a cell to shrink and to burst. 11. Describe the differences between passive and active transport. a. List and describe the types of passive and active transport. 12. Identify the process of photosynthesis within a chloroplast. a. Name the 2 reactions that make-up photosynthesis. b. State the products of light-dependent reactions. c. State the products of the Calvin cycle. d. Name the cell structure that photosynthesis takes place. e. Write the equation to photosynthesis. 13. Describe what is occurring in cellular respiration. a. State reactants and products of aerobic respiration. b. Name the cell structure that cellular respiration takes place. 14. Draw and label the parts of a replicated chromosome. a. Name the phases of mitosis in which replicated chromosomes are visible. 15. List and briefly summarize the phases of the cell cycle (in order). 2 a. Name the 2 main stages of cell division. b. Sequence the phases of mitosis. c. Describe what occurs in each phase of mitosis. d. Draw centrioles and spindle fibers in a cell and state their functions. 16. Define cancer. a. List the causes of cancer. Figure 8-8 b. Describe the effects to cells because of cancer. Use Figure 8-8 to answer letters a – b. c. Which of the cells depicted in the line graph in Figure 8-8 are least likely cancerous? d. If cancer is present, what is the likely explanation for what happened to cells B and D? Unit 3: Genetics – Chapter 11, 12 & 13 17. Define crossing over, describe the result of crossing over, identify a picture showing crossing over taking place, and provide allele combinations of crossing over given: 18. Draw the phases of meiosis a. Name the phase in which crossing over occurs in meiosis 19. Give genotypes for a homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, and heterozygous individual 20. Define the terms ‘diploid’ and ‘haploid’ 21. Conduct Mendelian crosses (monohybrid and dihybrid), incomplete and codominance crosses providing genotypes/phenotypes of parents and genotypes/phenotypes/probabilities offspring: a. Pea plants come in two sizes. Tall plants are dominant. Short plants are recessive. Cross a homozygous recessive male with a heterozygous female. 3 b. Puffer fish come in three colors. Blue fish are homozygous for the allele. Yellow fish are homozygous for the allele. Green fish are heterozygous. Cross a yellow male with a green female puffer fish. c. Chickens have 3 different feather-color combinations. Chickens with all black feathers are homozygous for the black allele. Chickens with all white feathers are homozygous for the white allele. Chickens that have both black and white feathers are heterozygous. Cross a black male with a white female. d. In mice the gene for coat color has two forms. The allele for colored coat is dominant to the allele for albino. There are two forms for the gene controlling whiskers as well; straight is dominant to bent. Consider a cross between two mice heterozygous for both these genes. 22. Provide the chromosome numbers that result from mitosis and meiosis and the name of the cells where the chromosomes come from in each process 23. Define an ‘allele’ 24. State the composition and structure of DNA and RNA. a. State the components of the backbone of DNA. b. Explain the base-pairing rules of DNA. c. Name the 4 nitrogenous bases in DNA. d. Differentiate between the bases of DNA and RNA. 25. State and differentiate a between the 3 types of RNA. 26. State the molecule that is formed as a result of transcription. a. Given a strand of DNA, write the mRNA codons that are formed. 27. Identify the process of translation. a. Draw and label the molecules that are involved in the process of translation. b. State the molecule that is formed as a result of translation. c. Determine the number of codons that will specify a certain number of amino acids. d. Given a sequence of DNA, determine the amino acids from that sequence. 28. Provide an example of the 3 types of point mutations. 4