* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Transport Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
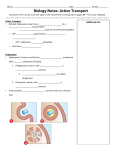
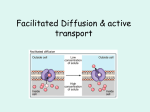
Concept: Key Point Active Transport Is energy needed? Why? Details Energy in the form of ATP is needed because substances are being moved AGAINST their concentration gradient (from low to high) This pump has specially shaped “holders” for ions of Na+ and K+. Using ENERGY, it moves Na+ and K+ AGAINST the concentration gradient. 3 Na+ ions are pumped out of the cell, and 2 K+ ions are pumped into the cell. Na+ and K+ are important ions in our body that help keep our cells healthy. Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to ENTER the cell. Endocytosis is used for transporting molecules INTO the cell that are too large for facilitated diffusion. Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to EXIT the cell. Exocytosis is used for transporting molecules OUT OF the cell that are too large for facilitated diffusion. The receptor can cause membrane channels to open. The receptor may cause the formation of a second messenger that will have an effect in another part of the cytoplasm. (sends a message like a walkie-talkie) The receptor can act as an enzyme (causes a reaction to occur or effects the permeability of the membrane). YES! It does require energy Several types of active transport 1. Sodium – Potassium Pump 3 Na+ 2 K+ 2. Endocytosis 3. Exocytosis 4. Receptor Proteins