* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Review
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
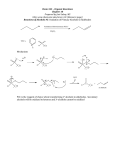
Chemistry 242 Exam #3 Summer 2009 The third exam will be on Wed, July 29, covering material in Chapter 17 – 19 of the text. The test will focus on chemistry of alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, and organic synthesis. The following textbook sections will be covered on the exam: 17.1 to 17.9 17.12 (NMR of alcohols only) (skip sections 17.10, 17.11) 18.1, 18.2, 18.3 19.1 to 19.11 and 19.16 skip enamines in 19.9 It is particularly important to study and do the problems for the following sections: 17.4 17.5 17.6 17.7 18.3 19.4 19.8 19.11 Questions that may appear on the exam: What is the name for this alcohol / ether / aldehyde / ketone? Is an alcohol 1°, 2°, or 3°? Describe hydrogen bonding in alcohols, and compare alcohol polarity to ether polarity. What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more reactive than ketones? Classify the following compounds as either alcohols, diols, ethers, hemi-acetals, or acetals. What is the mechanism of acid catalyzed acetal formation? (section 19.11) Given NMR and molecular formula, what is the structure of this alcohol, aldehyde, or ketone? Preparation of alcohols: Hydration of alkenes: acid-catalyzed addition of water (Markov.) or BH3/ox (Anti-Markov.) Reduction of carbonyl compounds: NaBH4 (ald/ketones), LiAlH4 (ald/ketones/esters) SN2 reaction of an unhindered alkyl halide R-X with OH- to form the alcohol R-OH **Addition of Grignards (RMgX) or R-Li to aldehydes and ketones: mechanism, limitations Reactions of alcohols: Deprotonation with strong base (NH2-, K metal) to form the alkoxide: RO– Oxidation to carbonyl compounds: PCC or CrO3 (know when to use each reagent) Conversion to R-X: dry HBr/HCl, PBr3, SOCl2 (know when to use each reagent) Elimination to alkenes - POCl3 (for all alcohols) or H2SO4 (for 3° alcohols) Protecting –OH groups: Me3Si-Cl/Et3N (TMS chloride/weak base) puts on TMS ether; aqueous acid removes protecting group Carbonyl Reactions: Prep of aldehydes/ketones: alcohol oxidation (PCC/CrO3) (also ozonolysis) Rxn of aldehydes / ketones: reduction, Grignard reaction, acetal formation, hydration imine formation, Wolff-Kishner reaction, cyanohydrin formation Other Reactions: Williamson ether synthesis Synthesis Problems: starting with an alkane (or other specified material), make the compound shown. alkane + X2 / hv → haloalkane RCH2Br + OH- → RCH2OH Useful R-Br + Mg → R-Mg-Br RCH2OH + PBr3 → RCH2Br Synthesis RCH2OH + PCC → aldehyde R2C=CR2 + H2 / cat. → alkane Reactions Wolff-Kishner: Remember: O H2N-NH2 H H “The nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon!” Exam 3 Review Problems 1. Show how each starting materials could be transformed into the product shown. Give reagents and draw the product for each step. O OH OH OH OH OH and 2. Show how ethanol can be made from methane: CH4 → → CH3CH2OH CH3CH3 → → CH3CH2CH2CH3 3. Show how butane can be made from ethane: 4. Show how ethylamine can be made from methane: → CH4 → CH3CH2NH2 5. Give two different ways to prepare each alcohol from a carbonyl compound and a Grignard reagent. OH OH Br 6. Starting with ethane, propose a synthesis of 1-butanol. 7. Starting with ethane, prepare: H2N OH O 8. Using the Williamson ether synthesis, prepare the ether shown from any starting materials. 9. Give products (after aqueous workup) for the four reactions below. OH OH Ph + PBr3 Ph + CrO3 acetone O O CH3CH2-Li + acetone Et2O H + 2 CH3OH THF


![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-150x150.png)