* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chem 130 Fall 2004 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 8.1
Survey
Document related concepts
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
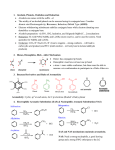
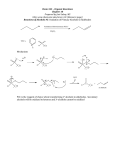
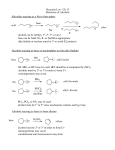
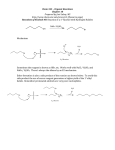
Chem 130 Fall 2004 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 8.1-8.4 – Alcohols 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols 2. Properties Hydrogen Bonding: boiling point 3. Reactions of Alcohols Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcohol: no reaction Conversion into ethers, ROR (with Na metal, then RCl) Chapter 9.1-9.4, 9.6-9.8 – Benzene and its Derivatives 1. Structure of the benzene ring 2. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Benzene (nucleophile) + electrophile (E+) Bromination (Br+): Br2/FeBr3 Chlorination (Cl+): Cl2/FeCl3 Nitration (NO2+): HNO3/H2SO4 Sulfonation (+SO3H): SO3/ H2SO4 Alkylation (R+): RCl/AlCl3 Acylation (RC+=O): RCOCl/AlCl3 3. Substituent Effects (orientation effects for monosubstituted products) Ortho/Para activating substituents: -NH2, -OH, -OCH3, -R Ortho/Para deactivating substituents: -Cl, -Br Meta deactivating substituents: -NO2, -CN, -SO3H, -COCH3, -COOH, -CO2CH3, -CH=O (aldehyde) 4. Mechanisms of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Chapter 13.1-13.8, 13.10-13.11 – Aldehydes and Ketones 1. Nomenclature 2. Reactions Oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7 or AgNO3 in NH4OH) Reduction of aldehydes to primary alcohol (with NaBH4) Reduction of ketones to secondary alcohol (with NaBH4) Grignard reaction and mechanism: synthesis of alcohols (formation of new carbon-carbon bond)