* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide on Ch 5 and 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
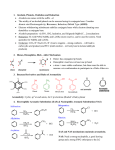
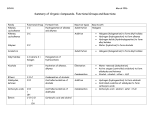
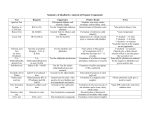
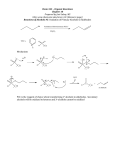
Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions A. Exergonic vs Endergonic Reactions B. 3 Types of chemical reactions: Synthesis, Decomposition, and Exchange Reactions C. How to calculate Calories D. Factors influencing the rate of reactions E. Chemical Reactions a. Hydrogenation b. Hydration i. How to apply the Markovnikov’s Rule ii. How to recognize the right product F. Organic Oxidation and Reduction a. OIL RIG b. Loss/Gain of Oxygen c. Loss/Gain of Hydrogen G. Condensation and Hydrolysis a. Condensation I i. RCOOH + A carboxylic acid R’OH → an alcohol b. Condensation II i. RCOOH + A carboxylic acid R’NH2 → RCOKHR’ an amine an amide RCOOR’ an ester + H. Hydrolysis is a reverse reaction of G.a. and G.b. I. Functional Groups a. Review the handout on the functional groups b. Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols c. Primary, secondary, tertiary amines and ammonium ion J. Balance the combustion (oxidation) of alkanes CnH2n+2 H2O + H2O Chapter 6: Carbohydrates A. Classification a. Mono-, Di-, Oligo- and Poly-saccharides b. Triose, tetrose, pentose, and hexose c. Aldose and Ketose B. Fischer Projection vs Wedge-and-dash (p. 219) C. Identify chiral centers D. D- and L-isomers (or configurations) E. Drawing of Mirror Image F. What is a hemiacetal group (p. 228) G. What is an anomeric carbon (pp. 228 – 229) a. What are alpha- () and beta- () anomers? (p. 229 bottom) H. Primary alcohols Oxidize to corresponding aldehydes (see the equation below) I. Aldehydes are further oxidized to carboxylic acids. J. Secondary alcohols to corresponding ketones. No more oxidation! K. Benedict’s Test: a. Positive for aldehydes only b. Sugars which are Benedict’s positive are Reducing Sugars! c. Negative for the rest of functional groups including ketones L. Glycocidic Bonds (p. 236) a. Used to link another sugar molecule. b. (1→4) glycocidic bond c. (1→4) glycocidic bond M. We’ll skip this section! << BEST LUCK TO ALL!!! >>