* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Physics
Survey
Document related concepts
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
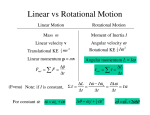
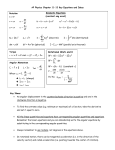
Introduction to Physics Measurement: Standards and units, dimensional analysis Motion in one dimension: Descriptions of motion, average and instantaneous velocities, motion with constant acceleration Vectors: Vector components, adding vectors, multiplication of vectors Motion in two dimensions: motion with constant acceleration, uniform circular motion, relative motion Forces and laws of motion: Newton’s first, second and third laws and their applications Motion with friction: Static and kinetic friction Work and energy: Work done by constant forces, kinetic energy, work-energy theorem, power Potential energy: Gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy Linear momentum: Single particle and a system of particles, center of mass, conservation of linear momentum Collisions: Impulse and momentum, elastic and plastic collisions Rotational motion: Rotation with constant angular acceleration, moment of inertia, kinetic energy of rotation, torque, combined rotational and translational motion Angular momentum: Single particle and a system of particles, angular momentum and angular velocity, conservation of angular momentum Equilibrium of rigid bodies: Conditions for equilibrium, center of gravity, examples Sources: 1. F.W. Sears, M.W. Zemansky, H.D. Young, Mechanics, 7th Edition (QC 125.2 s412)