* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 111
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
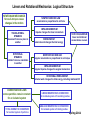
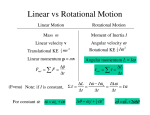
Topic Outline for Physics 1 Spring 2011 Spring 2011 1 Linear and Rotational Mechanics: Logical Structure NEWTONIAN MECHANICS forces & torques cause changes in the motion TRANSLATIONAL DYNAMICS movement from one place to another ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS rotation from one orientation to another NEWTON’S SECOND LAW acceleration is proportional to net force IMPULSE-MOMENTUM impulse changes the linear momentum STATIC EQUILIBRIUM linear and rotational accelerations are zero WORK-ENERGY external work changes the total energy NEWTON’S SECOND LAW angular acceleration is proportional to net torque IMPULSE-MOMENTUM angular impulse changes the angular momentum ROTATIONAL WORK-ENERGY external work changes the total energy, including rotational KE CONSERVATION LAWS some quantities remain constant for an isolated system TOTAL ENERGY IS CONSERVED for isolated system of particles LINEAR MOMENTUM IS CONSERVED for isolated system of translating bodies ANGULAR MOMENTUM IS CONSERVED for isolated system of rotating bodies Spring 2011 Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Introduction to the course Measurement • Measurements • Systems of units • Conversion of units Vectors • Vectors and scalars • Vector addition and subtraction • Components of vectors and unit vectors • Adding vectors by components (analytic method) • Vectors and the laws of physics • Multiplying vectors: – Scalar multiplication – Dot product – Cross product (vector product One dimensional motion • Introduction to motion & kinematics, definitions • Position and displacement • Average velocity, average speed • Instantaneous velocity and speed • Acceleration • Constant accleration - a special case • Kinematics equations • Free fall acceleration • Constant acceleration (using integrals). Two and three dimensional motion • Position and displacement • Average and instantaneous velocity • Average and instantaneous acceleration • Kinematic equations in 2 & 3 D • Projectile motion defined (free fall) • Projectile motion analyzed, range • Uniform circular motion • Relative motion in one and two Spring 2011 dimensions Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Linear dynamics • Dynamics, some history • What causes an acceleration • Force • Newton’s first law • Where we can use the second and third laws • Mass • Newton’s second law • • • • Free body diagrams Some particular forces Newton’s third law Application to sample problems • • • • Linear dynamics with friction • Dynamics summary • Friction basics • • • • Static friction Kinetic friction Properties of friction and sample problems Drag forces and terminal speed Uniform circular motion - centripetal force • • Free body diagrams Sample problems with friction Pulley problems Block sliding problems Simple block on plane with friction Simple equilibrium Spring 2011 Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Work and Energy • Energy overview • Work – – – – – • Work and kinetic energy – – • • • • A simple constant force 1D 3D, constant force - dot product Units Variable force 1D General vector 3D definition with variable force Kinetic energy Simple derivation of work-ke theorem General form of work-KE theorem Gravitational force and examples Variable (spring) force and examples. Power Potential energy and energy conservation • Overview and summary • Potential energy • Conservative forces • Determining potential energy values – – • • Conservation of mechanical energy Reading potential energy curves – – – – • • • • • Gravitational potential energy Elastic potential energy Energy levels Finding the force (gradient) Turning points Equilibrium points Work done by external (nonconservative) forces Work-energy theorem Conservation of energy (general) Isolated systems Power Spring 2011 Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Systems of particles, momentum • Center of mass – – • • • • • Systems of particles Solid bodies Newtons second law for a system of particles Linear momentum Linear momentum for a system of particles Conservation of linear momentum Systems with varying mass (A rocket) - read only Impulse and collisions • What is a collision? • Impulse and linear momentum – – • • • • • Single collisions Series of collisions Momentum and kinetic energy in collisions Inelastic collisions in one dimension Elastic collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimensions Projectile collisions and explosions Spring 2011 Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Rotational variables, kinetic energy • Translation and rotation • Rotational variables - kinematics of rotation • • • – – Angular position and displacement Angular velocity and acceleration Relating linear and angular variables rotation with constant angular acceleration Kinetic energy of rotation Angular quantities as vectors Rotational inertia/moment of inertia — – – – Particles and rigid bodies Parallel axis theorem definition Proof of parallel axis theorem Standard moments of inertia Angular momentum • Rolling • Kinetic energy and forces of rolling • Rotational quantities as vectors • Cross product revisited • Torque as a vector • Angular momentum – conceptual • Newton’s second law in angular form • Angular momentum as a vector • Angular momentum of a system of particles • Angular momentum of a rigid body about a fixed axis • Conservation of angular momentum for particles, rigid bodies, and systems Torque – rotational analog of force — Moment arm for 2 dimensions — Cross product, cross product review Newton’s second law for rotation Work and rotational kinetic energy Spring 2011 Physics 1 Topics - Checklist Equilibrium • Overview - equilibrium defined • Conditions for equilibrium • Center of gravity – – – • • Definition Finding it When do mass center and CG not coincide? Methods for equilibrium problems Examples of static equilibrium problems Gravitation • Newton’s law of gravitation (force) • Gravitational field (acceleration) • Superposition • Shell theorem • Gravitational potential energy and escape speed • Kepler’s 3 laws: orbits, period, radius • Satellites and planets • Orbits and energy Oscillations • Simple harmonic motion • X(t), v(t), a(t) as trig functions • The spring oscillator and the force law for simple harmonic motion • Kinetic and potential energy • SHM: torsion pendulum, simple and physical pendula • Damped and forced oscillations, Spring 2011 resonance