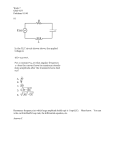
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A moving object has a tendency to keep moving, this is momentum
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (mechanics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Continuously variable transmission wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
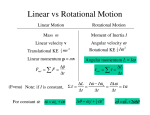
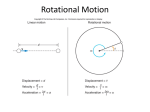
A moving object has a tendency to keep moving, this is momentum. A rotating object has a tendency to keep rotating; this is angular momentum. If the net external torque on an object is zero, the angular momentum does not change. This is the law of conservation of angular momentum. When an ice skater pulls his arms in closer to his body, he decreases the length of the torque arm, which decreases the moment of inertia. Angular momentum is equal to moment of inertia X angular speed. If the moment of inertia is decreased (by pulling the arms in) the angular speed must increase. If you walk to the middle of a spinning merry-go-round, it will speed up. Neutron stars are formed by the collapse of a star's matter following a supernova. Angular momentum must be conserved in this situation, so the star's rotation speed must increase. Some neutron stars rotate in seconds. A rotating object also has kinetic energy due to its rotation. This is the nature of the need for the infamous frictionless, massless pulley used in physics problems. A machine is a device used to multiply forces or to change the direction of forces. The six simple machines are the lever, the pulley, the wheel and axle, the inclined plane, the wedge, and the screw. The ratio of input force to output force for a machine is the mechanical advantage. Efficiency of a machine is the ratio of useful work output to total work input. Efficiency is also the ratio of actual mechanical advantage to theoretical mechanical advantage. These two values in the ratio would be the same and efficiency would be 100% if it were not for friction.