* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The DNA Song
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
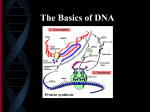
The DNA Song Deoxyribose and phosphate gro-ups, Make up the back-bone of DNA And the ba-ses make up the ru-ungs Ooh learn about DNA In replication, heli-ca-ase Splits up the helix , into two strands Then an enzyme builds new pieces, It’s DNA po-ly- merase Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), is composed of monomers, called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to the original strand. Remember the base pairing rule: C-G, and A-T. In transcription, we make R-N-A, A mes-sen-ger, into the cell, It carries info to make proteins, It’s messenger RNA In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. In translation, we build proteins, To carry out the body’s needs, We use amino’s linked together, By transfer RNA. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the proteins in your body. Amino acids hook on one end, Of transfer RNA, Anticodons, put them in order, Ba-ased on mRNA. In order to make the proteins, tRNA must use mRNA as a template (remember, mRNA has the “directions” from DNA). The anti-codons on tRNA match up to complimentary codons on mRNA. Translation starts with a start codon on mRNA and ends with a stop codon on mRNA. Ribosomes, pair up the codons, With the matching, tRNA When they’re done, we have a protein, A chain of monomers The whole process of assembling proteins is accomplished by ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The ribosomes match the tRNA anti-codons to the mRNA codons, then link all of the amino acids together. These long links of amino acids are called polypeptides, or proteins. These polypeptides, they determine, The very function of every cell, Without this process, we’d only wonder Could we sing this song very well?